matplotlib.axes.axes.xcorr()
matplotlib.axes.axes.xcorr()函数,使用matplotlib库的Axes模块中的Axes.xcorr()函数绘制x与y的互相关系。
语法:
Axes.xcorr(self, x, y, normed=True, detrend=, usevlines=True, maxlags=10, *, data=None, **kwargs)
参数:该方法接受如下参数说明:
- x, y:这些参数是标量的序列。
- dettrend:可选参数。默认值为mlab.detrend_none
- 这个参数也是一个可选参数,它包含bool值。默认值为True
- usevlines:该参数也是一个可选参数,包含bool值。默认值为True
- maxlag:可选参数,取值为整型。默认值为10
- linestyle:该参数也是可选参数,仅当usevlines为False时,用于绘制数据点。
- marker:该参数也是可选参数,包含字符串。它的默认值是’ o ‘
该方法返回如下内容:
- lag:这个方法返回滞后向量
- c:这个方法返回自相关向量。
- line: usevlines为True时增加LineCollection,否则增加Line2D。
- 如果usevlines为真,则此方法返回水平线为0,否则为None。
结果是(lag, c, line, b)。
下面的例子演示了matplotlib.axes中的matplotlib.axes.xcorr()函数:
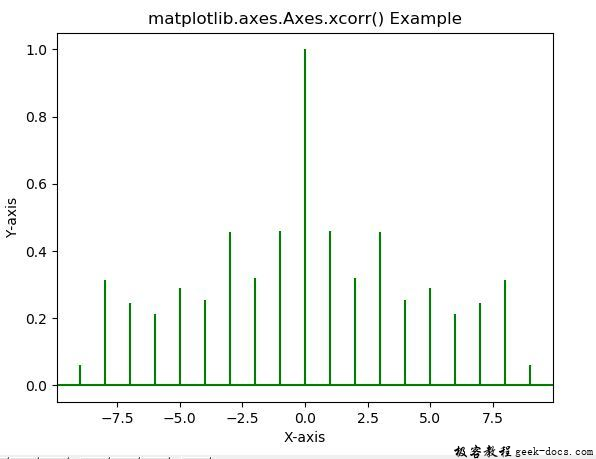
示例1
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Time series data
geeksx = np.array([24.40, 110.25, 20.05,
22.00, 61.90, 7.80,
15.00, 22.80, 34.90,
57.30])
geeksy = np.array([24.40, 110.25, 20.05,
22.00, 61.90, 7.80,
15.00, 22.80, 34.90,
57.30])
# Plot autocorrelation
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.xcorr(geeksx, geeksy, maxlags = 9,
color ="green")
# Add labels to autocorrelation
# plotax.xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y-axis')
ax.set_xlabel('X-axis')
ax.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.xcorr() Example')
plt.show()
输出:
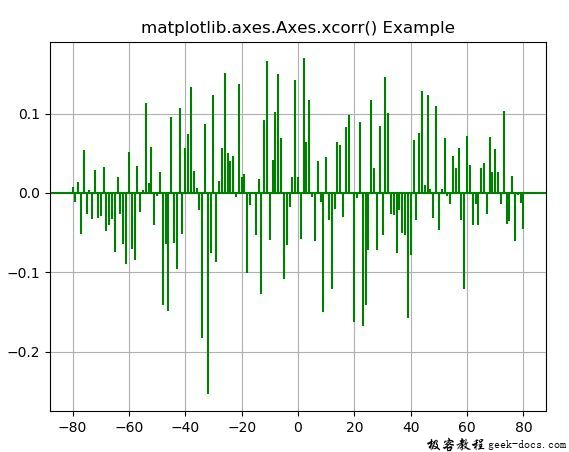
示例2
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Fixing random state for
# reproducibility
np.random.seed(10**7)
geeksx = np.random.randn(100)
geeksy = np.random.randn(100)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.xcorr(geeksx, geeksy, usevlines = True,
normed = True, maxlags = 80,
color ="green")
ax.grid(True)
ax.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.xcorr() Example')
plt.show()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程