matplotlib.axes.axes.angle_spectrum()
matplotlib.axes.axes.angle_spectrum()函数,利用matplotlib库的axis模块中的Axes.angle_spectrum()函数绘制角度谱。
语法:
Axes.angle_spectrum(self, x, Fs=None, Fc=None, window=None, pad_to=None, sides=None, *, data=None, **kwargs)
参数:该方法接受如下参数说明:
- x:数据序列。
- Fs:标量。默认值为2。
- window:该参数接受一个数据段作为参数,并返回该段的窗口版本。其默认值是window_hanning()
- sides:该参数指定返回频谱的哪一边。它可以有以下值:’ default ‘, ‘ onesided ‘和’ twosided ‘。
- pad_to:该参数包含填充数据段的整数值。
- Fc:该参数还包含整数值,用于偏移图形的x个区段,以反映频率范围。默认值为0
返回如下内容:
- spectrum:以弧度为单位返回角度谱。
- freqs:返回与频谱中元素对应的频率。
- line:返回由该函数创建的行。
结果是(spectrum, freqs, line)
下面的例子演示了matplotlib.axes中的matplotlib.axes.xcorr()函数:
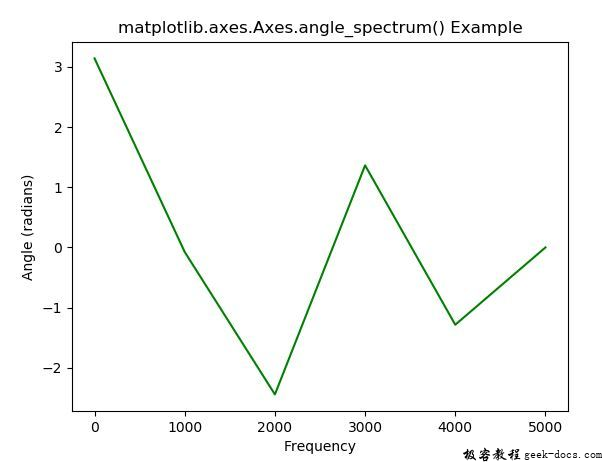
示例1
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(10**5)
dt = 0.0001
Fs = 1 / dt
geeks = np.array([22.00, 61.90,
7.80, 24.40,
110.25, 20.05,
15.00, 22.80,
34.90, 57.30])
nse = np.random.randn(len(geeks))
r = np.exp(-geeks / 0.05)
s = 0.5 * np.sin(1.5 * np.pi * geeks) + nse
# plot angle_spectrum
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.angle_spectrum(s, Fs = Fs, color ="green")
ax.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.angle_spectrum() Example')
plt.show()
输出:
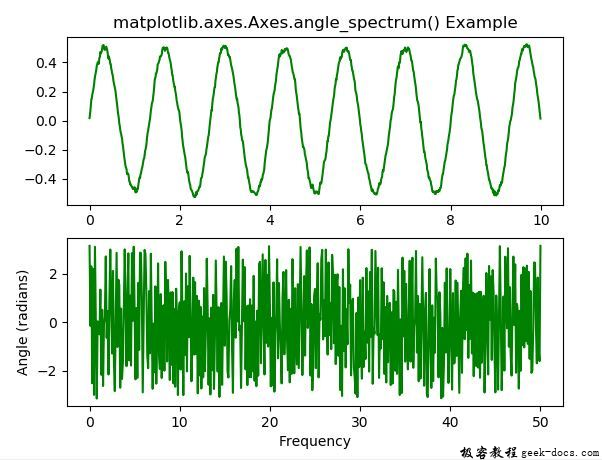
示例2
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
dt = 0.01
Fs = 1 / dt
t = np.arange(0, 10, dt)
res = np.random.randn(len(t))
r = np.exp(-t / 0.05)
cres = np.convolve(res, r)*dt
cres = cres[:len(t)]
s = 0.5 * np.sin(1.5 * np.pi * t) + cres
# plot simple spectrum
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1)
ax1.plot(t, s, color ="green")
# plot angle_spectrum
ax2.angle_spectrum(s, Fs = Fs, color ="green")
ax1.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.angle_spectrum() Example')
plt.show()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程