matplotlib.axes.axes.stackplot()
matplotlib.axes.axes.stackplot() 函数,matplotlib库的axes模块中的Axes.stackplot()函数被用来创建一个堆积的面积图。
语法:
Axes.stackplot(axes, x, *args, labels=(), colors=None, baseline=’zero’, data=None, **kwargs)
参数:该方法接受如下参数说明:
- x:该参数为x坐标序列。
- y:这个参数是y坐标序列。
- baseline:该参数是基线{‘ zero ‘, ‘ sym ‘, ‘ wiggle ‘, ‘ weighted_wiggle ‘}。
- colors:该参数是颜色的列表或元组。
- label:该参数是分配给每个数据系列的标签。
返回如下内容:
- list:返回PolyCollection实例的列表,堆叠区域图中的每个元素对应一个实例。
下面的例子演示了matplotlib.axes中的matplotlib.axes.axes.stackplot()函数:
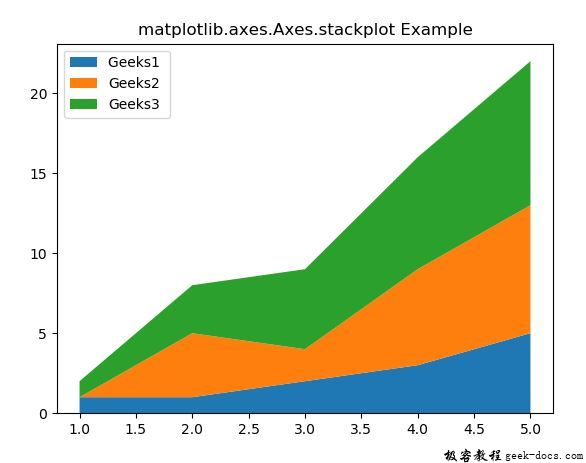
示例1
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y1 = [1, 1, 2, 3, 5]
y2 = [0, 4, 2, 6, 8]
y3 = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
y = np.vstack([y1, y2, y3])
labels = ["Geeks1 ", "Geeks2", "Geeks3"]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.stackplot(x, y1, y2, y3,
labels = labels)
ax.legend(loc ='upper left')
ax.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.stackplot Example')
plt.show()
输出:
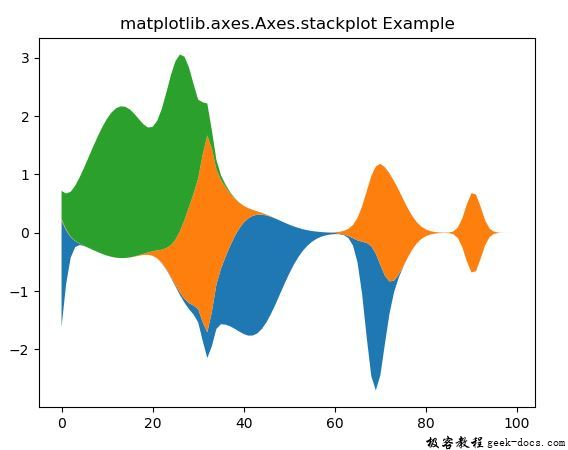
示例2
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def GFG(n, m):
def geeks(a):
x = 1 / (.1 + np.random.random())
y = 2 * np.random.random() - .5
z = 10 / (.1 + np.random.random())
for i in range(m):
w = (i / m - y) * z
a[i] += x * np.exp(-w * w)
a = np.zeros((m, n))
for i in range(n):
for j in range(5):
geeks(a[:, i])
return a
test = GFG(3, 100)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.stackplot(range(100), test.T,
baseline ='wiggle')
ax.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.stackplot Example')
plt.show()
 极客教程
极客教程