Matplotlib.axes.axes.annotate()
Matplotlib是Python中的一个库,它是NumPy库的数值-数学扩展。Axes包含了大多数图形元素:Axis、Tick、Line2D、Text、Polygon等,并设置坐标系。Axes的实例通过callbacks属性支持回调。
函数:matplotlib.axes.axes.annotate()
matplotlib库的Axes模块中的Axes.annotate()函数也用于用文本文本.注释xy点,换句话说,我曾经将文本放置在xy。
语法:
Axes.annotate(self, s, xy, *args, **kwargs)
参数:该方法接受如下参数说明:
- s:标注文本。
- xy:该参数是要注释的点(x, y)。
- xytext:可选参数。它是放置文本的位置(x, y)。
- xycoords:该参数也是一个可选参数,包含字符串值。
- textcoords:该参数包含字符串值. xytext所给定的坐标系统,可能与xy所使用的坐标系统不同
- arrowprops:此参数也是可选参数,包含dict类型.,默认值为None。
- annotation_clip:该参数也是一个可选参数,包含布尔值.其默认值为None,表现为True。
返回:该方法返回注释。
下面的例子演示了matplotlib.axes.axes.annotate()函数在matplotlib.axes中的作用:
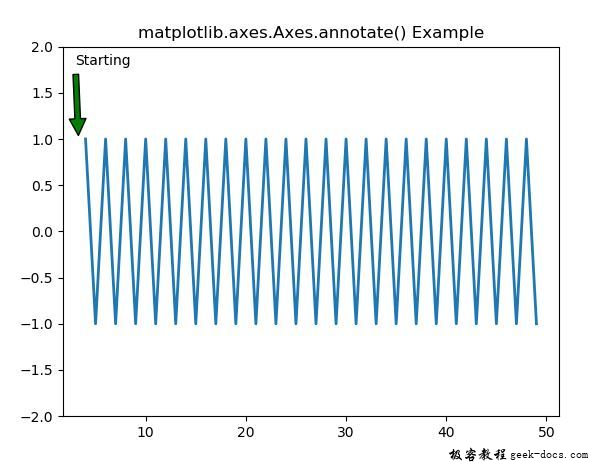
示例1
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
t = np.arange(4, 50., 1)
s = np.cos(np.pi * t)**3- np.sin(3 * np.pi * t)**2
ax1.plot(t, s, lw = 2)
ax1.annotate('Starting', xy =(3.3, 1),
xytext =(3, 1.8),
arrowprops = dict(facecolor ='green',
shrink = 0.05), )
ax1.set_ylim(-2, 2)
ax1.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.annotate() Example')
plt.show()
输出:
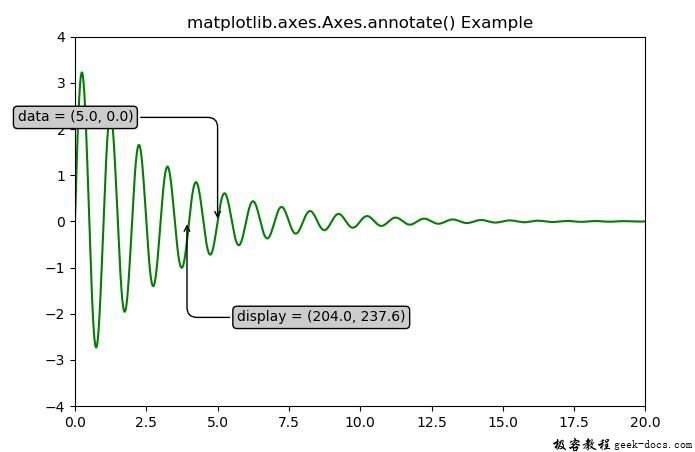
示例2
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.arange(0, 20, 0.005)
y = 3.5 * np.exp(-x / 3.) * np.sin(2 * np.pi * x)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y, color ="green")
ax.set_xlim(0, 20)
ax.set_ylim(-4, 4)
xdata, ydata = 5, 0
xdisplay, ydisplay = ax.transData.transform((xdata,
ydata))
bbox = dict(boxstyle ="round", fc ="0.8")
arrowprops = dict(
arrowstyle = "->",
connectionstyle = "angle, angleA = 0, \
angleB = 90, rad = 10")
offset = 72
# Annotation
ax.annotate('data = (%.1f, %.1f)'%(xdata, ydata),
(xdata, ydata), xytext =(-2 * offset,
offset),
textcoords ='offset points',
bbox = bbox, arrowprops = arrowprops)
ax.annotate('display = (%.1f, %.1f)'%(xdisplay, ydisplay),
(xdisplay, ydisplay), xytext =(0.5 * offset,
-offset),
xycoords ='figure pixels',
textcoords ='offset points',
bbox = bbox, arrowprops = arrowprops)
ax.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.annotate() Example')
plt.show()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程