matplotlib.pyplot.semilogy()函数
Matplotlib是最流行的python就绪包,用于可视化数据。我们使用matplotlib来绘制高质量的图表、图形和图形。
matplotlib.pyplot.semilogy()函数
使用matplotlib库pyplot模块中的matplotlib.pyplot.semilogy()函数来绘制y轴上具有对数缩放的绘图。
语法:matplotlib.pyplot.semilogy (* args, * * kwargs)
参数:该方法接受如下参数说明:
- base:可选参数,默认值为10,为y对数的底数。
- subsy:该参数是小y的位置顺序,可选。
- nonposy:该参数是y中的一个非正数,可以被屏蔽为无效,或剪切为一个非常小的正数。
返回如下内容:
- lines:返回表示绘制数据的Line2D对象列表。
下面的例子演示了matplotlib.pyplot.semilogy()函数在matplotlib.pyplot中的作用:
示例1
# importing necessary libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plot
import numpy as np
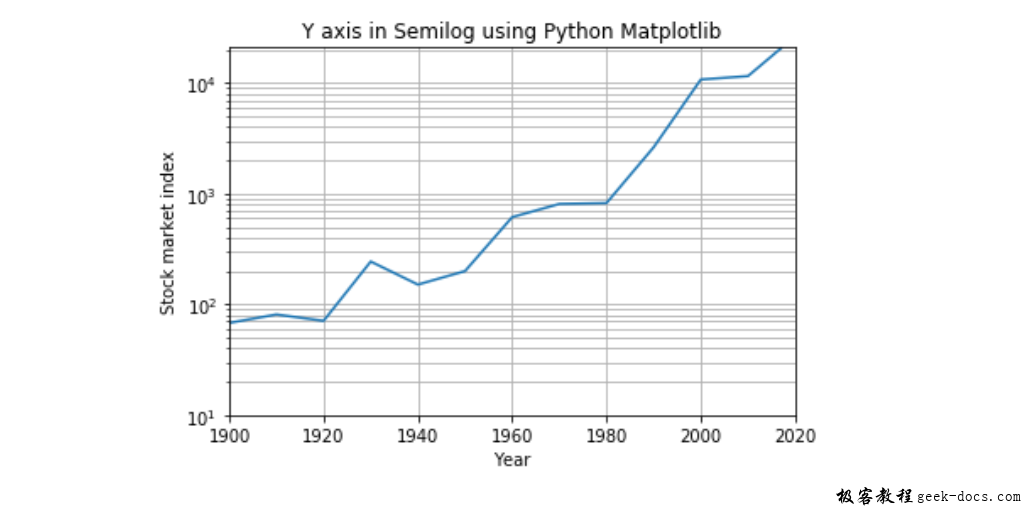
# Year data for the semilogy plot
years = [1900, 1910, 1920, 1930, 1940, 1950,
1960, 1970, 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010,
2017]
# index data - taken at end of every
# decade - for the semilogy plot
indexValues = [68, 81, 71, 244, 151, 200, 615,
809, 824, 2633, 10787, 11577,
20656]
# Display grid
plot.grid(True, which ="both")
# Linear X axis, Logarithmic Y axis
plot.semilogy(years, indexValues )
plot.ylim([10, 21000])
plot.xlim([1900, 2020])
# Provide the title for the semilogy plot
plot.title('Y axis in Semilogy using Python Matplotlib')
# Give x axis label for the semilogy plot
plot.xlabel('Year')
# Give y axis label for the semilogy plot
plot.ylabel('Stock market index')
# Display the semilogy plot
plot.show()
输出:
示例2
# importing necessary libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
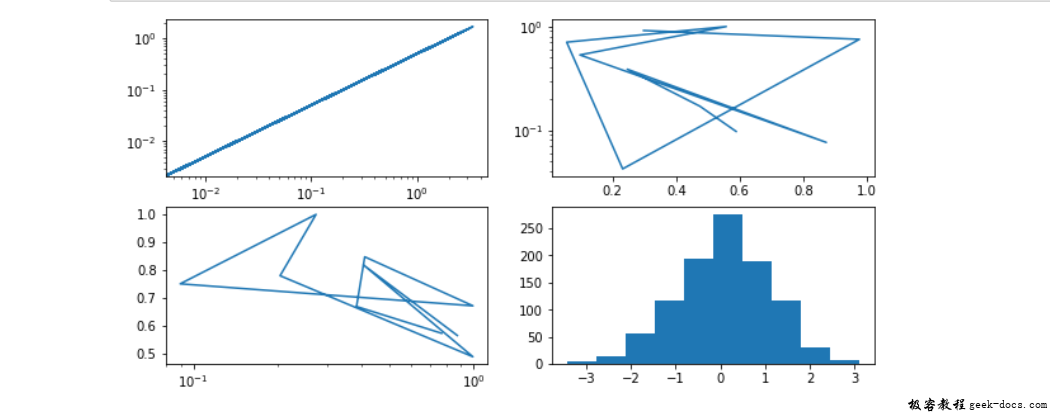
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows = 2,
ncols = 2,
figsize =(10, 5))
x = np.random.randn(1000)
# Plot to each different index
ax[0, 0].loglog(x, x / 2);
ax[0, 1].semilogy(np.random.random(10), np.random.random(10));
ax[1, 0].semilogx(np.random.random(10), np.random.random(10));
ax[1, 1].hist(np.random.randn(1000));
输出:
示例3
# importing necessary libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
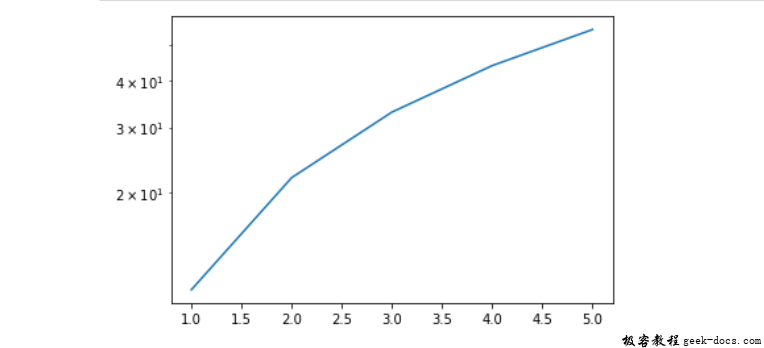
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y = [11, 22, 33, 44, 55]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.semilogy(x, y);
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程