matplotlib.pyplot.xcorr()函数
Matplotlib构建在NumPy和并行框架上,这就是它快速高效的原因。它是开源的,有巨大的社区支持。它具有与许多操作系统和图形后端良好工作的能力。要获得matplotlib.pyplot.xcorr(),我们需要理解交叉相关。
互相关
相关系数是两个变量相对运动关系强度的统计度量。
举个例子:我们取两个实值函数f和g g在x处是x轴上的差值。现在计算xne使用交叉相关。
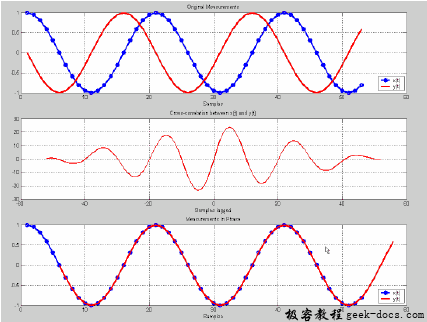
matplotlib.pyplot.xcorr()
matplotlib.pyplot.xcorr()函数绘制两个数组列表之间的相互关系。
参数:
| Parameter | Input type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | 实数或复数浮点数的向量。 | 相互关系的第一个变量。 |
| y | 实数或复数浮点数的向量。默认值为“x”。 | 相互关系的第二个变量。 |
| detrend | callable | x和y被detrendcallable消除趋势。这必须是一个接受并返回numpy.array的函数x = detrend(x)。它是可选的参数default是不规格化。 |
| normed | bool | 如果为真,输入向量将被规范化为单位长度。 |
| usevlines | bool | 如果为True,则使用axis从0到xcorr值绘制垂直线。可选参数 |
| maxlags | int | 延迟的数量显示。如果None,将返回所有2 * len(x) – 1的滞后值。可选参数,默认值为10。 |
返回值:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| lags | 数组(2 * maxlags长度+ 1) | 滞后向量。 |
| c | 数组(2 * maxlags长度+ 1) | 自相关向量。 |
| line | 线路收集或Line2D | 美术人员添加了相关轴: 1. 如果use lines为True,则行集合。 2. 如果use lines为False则为Line2D。 |
| b | Line2D 或 None | 水平线在0如果使用线是真None使用线是假。 |
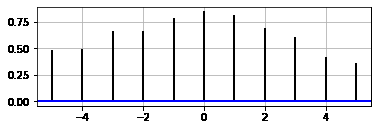
示例1
# import matplotlib library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# float lists for cross
# correlation
x=[11.37, 14.23, 16.3, 12.36,
6.54, 4.23, 19.11, 12.13,
19.91, 11.00]
y=[15.21, 12.23, 4.76, 9.89,
8.96, 19.26, 12.24, 11.54,
13.39, 18.96]
# Plot graph
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(211)
# cross correlation using
# xcorr() function
ax1.xcorr(x, y, usevlines=True,
maxlags=5, normed=True,
lw=2)
# adding grid to the graph
ax1.grid(True)
ax1.axhline(0, color='blue', lw=2)
# show final plotted graph
plt.show()
输出:
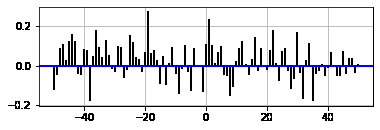
示例2
# import matplotlib library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# float lists for cross
# correlation
x, y = np.random.randn(2, 100)
# Plot graph
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(211)
# cross correlation using xcorr()
# function
ax1.xcorr(x, y, usevlines=True,
maxlags=50, normed=True,
lw=2)
# adding grid to the graph
ax1.grid(True)
ax1.axhline(0, color='blue', lw=2)
# show final plotted graph
plt.show()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程