matplotlib.pyplot.xticks()函数
matplotlib.pyplot.xticks()函数
matplotlib库的pyplot模块中的annotate()函数用于获取和设置x轴的当前标记位置和标签。
语法:
matplotlib.pyplot.xticks(ticks=None, labels=None, **kwargs)
参数:该方法接受如下参数说明:
- ticks:该参数是xtick位置列表。和一个可选参数。如果一个空列表作为参数传递,那么它将删除所有xticks
- labels:该参数包含要放置在给定刻度位置的标签。它是一个可选参数。
- **kwargs:这个参数是Text属性,用于控制标签的外观。
返回如下内容:
- locs:返回ytick位置列表。
- 返回ylabel Text对象的列表。
结果是(locs, labels)
下面的例子演示了matplotlib.pyplot.xticks()函数在matplotlib.pyplot中的作用:
示例1
# Implementation of matplotlib.pyplot.xticks()
# function
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
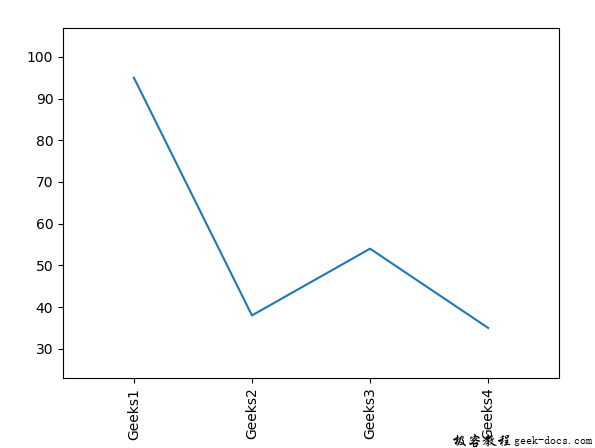
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
y = [95, 38, 54, 35]
labels = ['Geeks1', 'Geeks2', 'Geeks3', 'Geeks4']
plt.plot(x, y)
# You can specify a rotation for the tick
# labels in degrees or with keywords.
plt.xticks(x, labels, rotation ='vertical')
# Pad margins so that markers don't get
# clipped by the axes
plt.margins(0.2)
# Tweak spacing to prevent clipping of tick-labels
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom = 0.15)
plt.show()
输出:
示例2
# Implementation of matplotlib.pyplot.xticks()
# function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator import inset_axes, zoomed_inset_axes
def get_demo_image():
from matplotlib.cbook import get_sample_data
import numpy as np
f = get_sample_data("axes_grid / bivariate_normal.npy",
asfileobj = False)
z = np.load(f)
# z is a numpy array of 15x15
return z, (3, 19, 4, 13)
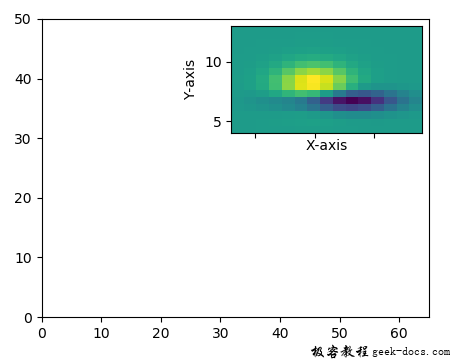
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize =[5, 4])
Z, extent = get_demo_image()
ax.set(aspect = 1,
xlim =(0, 65),
ylim =(0, 50))
axins = zoomed_inset_axes(ax, zoom = 2,
loc ='upper right')
im = axins.imshow(Z, extent = extent,
interpolation ="nearest",
origin ="upper")
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.xticks(visible = False)
plt.show()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程