matplotlib.pyplot.table()函数
Matplotlib.pyplot.table()是Matplotlib库的一个子部分,在该子部分中,使用绘制的图生成表进行分析。这种方法使分析更容易,更有效,因为表格提供了比图表更精确的细节。matplotlib.pyplot.table创建的表通常挂在堆叠的条形图下面,以便读者了解上面图表生成的数据。
语法:
matplotlib.pyplot.table(cellText=None, cellColours=None, cellLoc=’right’, colWidths=None,rowLabels=None, rowColours=None, rowLoc=’left’, colLabels=None, colColours=None, colLoc=’center’, loc=’bottom’, bbox=None, edges=’closed’, **kwargs)
示例1
考虑一个分析农作物价格在几个月内增长的图表。下面的代码是一个非线性图。
# importing necessary packagess
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# input data values
data = [[322862, 876296, 45261, 782372, 32451],
[58230, 113139, 78045, 99308, 516044],
[89135, 8552, 15258, 497981, 603535],
[24415, 73858, 150656, 19323, 69638],
[139361, 831509, 43164, 7380, 52269]]
# preparing values for graph
columns = ('Soya', 'Rice', 'Wheat', 'Bakri', 'Ragi')
rows = ['%d months' % x for x in (50, 35, 20, 10, 5)]
values = np.arange(0, 2500, 500)
value_increment = 1000
# Adding pastel shades to graph
colors = plt.cm.Oranges(np.linspace(22, 3, 12))
n_rows = len(data)
index = np.arange(len(columns)) + 0.3
bar_width = 0.4
# Initialing vertical-offset for the graph.
y_offset = np.zeros(len(columns))
# Plot bars and create text labels for the table
cell_text = []
for row in range(n_rows):
plt.plot(index, data[row], bar_width, color=colors[row])
y_offset = y_offset + data[row]
cell_text.append(['%1.1f' % (x / 1000.0) for x in y_offset])
# Reverse colors and text labels to display table contents with
# color.
colors = colors[::-1]
cell_text.reverse()
# Add a table at the bottom
the_table = plt.table(cellText=cell_text,
rowLabels=rows,
rowColours=colors,
colLabels=columns,
loc='bottom')
# make space for the table:
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.2, bottom=0.2)
plt.ylabel("Price in Rs.{0}'s".format(value_increment))
plt.yticks(values * value_increment, ['%d' % val for val in values])
plt.xticks([])
plt.title('Cost price increase')
# plt.show()-display graph
# Create image. plt.savefig ignores figure edge and face color.
fig = plt.gcf()
plt.savefig('pyplot-table-original.png',
bbox_inches='tight',
dpi=150)
输出:
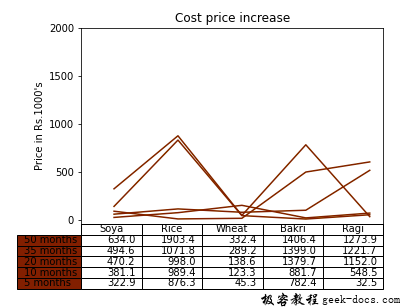
示例2
让我们考虑过去几年不同品牌牛奶价格的上涨
# importing necessary packagess
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# input data values
data = [[322862, 876296, 45261, 782372, 32451],
[58230, 113139, 78045, 99308, 516044],
[89135, 8552, 15258, 497981, 603535],
[24415, 73858, 150656, 19323, 69638],
[139361, 831509, 43164, 7380, 52269]]
# preparing values for graph
columns = ('Gokul', 'Kwality', 'Bakhri', 'Arun', 'Amul')
rows = ['%d months' % x for x in (50, 35, 20, 10, 5)]
values = np.arange(0, 2500, 500)
value_increment = 1000
# Adding pastel shades to graph
colors = plt.cm.Oranges(np.linspace(22, 3, 12))
n_rows = len(data)
index = np.arange(len(columns)) + 0.3
bar_width = 0.4
# Initialing vertical-offset for the graph.
y_offset = np.zeros(len(columns))
# Plot bars and create text labels for the table
cell_text = []
for row in range(n_rows):
plt.bar(index, data[row], bar_width, bottom=y_offset, color=colors[row])
y_offset = y_offset + data[row]
cell_text.append(['%1.1f' % (x / 1000.0) for x in y_offset])
# Reverse colors and text labels to display table contents with
# color.
colors = colors[::-1]
cell_text.reverse()
# Add a table at the bottom
the_table = plt.table(cellText=cell_text,
rowLabels=rows,
rowColours=colors,
colLabels=columns,
loc='bottom')
# make space for the table:
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.2, bottom=0.2)
plt.ylabel("Rise in Rs's".format(value_increment))
plt.yticks(values * value_increment, ['%d' % val for val in values])
plt.xticks([])
plt.title('Cost of Milk od diff. brands')
# plt.show()-display graph
# Create image. plt.savefig ignores figure edge and face color.
fig = plt.gcf()
plt.savefig('pyplot-table-original.png',
bbox_inches='tight',
dpi=150)
输出:
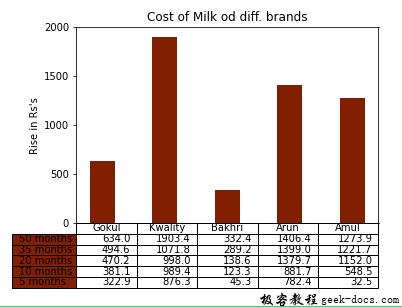
 极客教程
极客教程