matplotlib.pyplot.winter()函数
matplotlib.pyplot.winter()函数:
使用matplotlib库pyplot模块中的winter()函数将colormap设置为“winter”。
语法:
matplotlib.pyplot.winter()
参数:此方法不接受任何参数。
返回:此方法不返回任何值。
下面的例子演示了matplotlib.pyplot.winter()函数在matplotlib.pyplot中的作用:
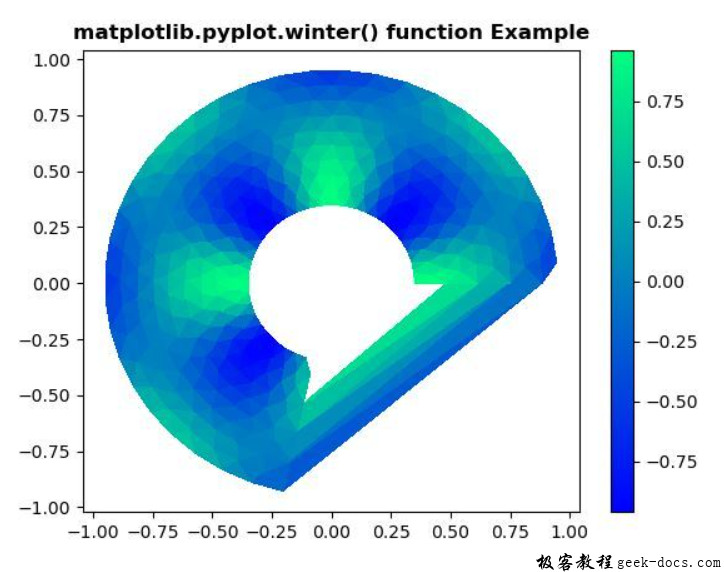
示例1
#Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.tri as tri
import numpy as np
ang = 32
rad = 10
radm = 0.35
radii = np.linspace(radm, 0.95, rad)
angles = np.linspace(0, 1.4*np.pi, ang)
angles = np.repeat(angles[..., np.newaxis], rad, axis=1)
angles[:, 1::2] += np.pi / ang
x = (radii * np.cos(angles)).flatten()
y = (radii * np.sin(angles)).flatten()
z = (np.sin(4*radii) * np.cos(4 * angles)).flatten()
triang = tri.Triangulation(x, y)
triang.set_mask(np.hypot(x[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1),
y[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1))
< radm)
tpc = plt.tripcolor(triang, z, shading='flat')
plt.colorbar(tpc)
plt.winter()
plt.title('matplotlib.pyplot.winter() function Example'
,fontweight="bold")
plt.show()
输出:
示例2
#Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import LogNorm
dx, dy = 0.015, 0.05
x = np.arange(-2.0,2.0, dx)
y = np.arange(-2.0, 2.0, dy)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
extent = np.min(x), np.max(x), np.min(y), np.max(y)
Z1 = np.add.outer(range(4), range(4)) % 2
plt.imshow(Z1, cmap="binary_r", interpolation='nearest',
extent=extent, alpha=1)
def geeks(x, y):
return (1 - x / 2 + x**5 + y**6) * np.exp(-(x**2 + y**2))
Z2 = geeks(X, Y)
plt.imshow(Z2, alpha=0.7, interpolation='bilinear',
extent=extent)
plt.winter()
plt.title('matplotlib.pyplot.winter() function Example'
,fontweight="bold")
plt.show()
输出:

 极客教程
极客教程