Python Pandas Series.take()
Pandas系列是一个带有轴标签的一维ndarray。标签不需要是唯一的,但必须是一个可散列的类型。该对象支持基于整数和标签的索引,并提供了大量的方法来执行涉及索引的操作。
Pandas Series.take()函数沿轴线返回给定位置索引中的元素。这里我们不是根据对象的索引属性中的实际值来进行索引。我们是根据元素在对象中的实际位置进行索引的。
语法: Series.take(indices, axis=0, convert=None, is_copy=True, **kwargs)
参数:
indices :一个表示要采取哪些位置的ints数组。
axis:选择元素的轴。
– > ** 0表示我们正在选择行。
**- > ** 1表示我们正在选择列。
**convert : 是否将负数指数转换成正数指数
is_copy :是否返回原始对象的副本。
**kwargs : 为了与numpy.take()兼容。对输出没有影响。
返回: 采取:与调用者的类型相同
例子#1:使用Series.take()函数,根据对象中元素的实际位置,从给定的系列对象中提取一些元素。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio', 'Moscow'])
# Create the Datetime Index
didx = pd.DatetimeIndex(start ='2014-08-01 10:00', freq ='W',
periods = 6, tz = 'Europe/Berlin')
# set the index
sr.index = didx
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
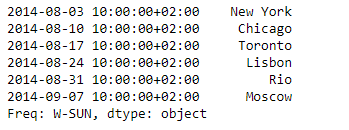
现在我们将使用Series.take()函数来提取对应于所传递位置的值。
# return elements corresponding to
# the passed index position
sr.take(indices = [0, 2])
输出 :
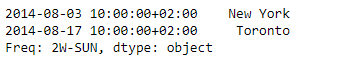
正如我们在输出中所看到的,Series.take()函数已经成功地返回了与所给系列对象中传递的索引位置相对应的元素。
例子#2:使用Series.take()函数,根据对象中元素的实际位置,从给定的系列对象中提取一些元素。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series([19.5, 16.8, None, 22.78, None, 20.124, None, 18.1002, None])
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
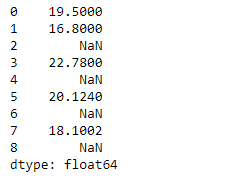
现在我们将使用Series.take()函数来提取对应于所传递位置的值。
# return elements corresponding to
# the passed index position
sr.take(indices = [1, 2, 5, 8])
输出 :

正如我们在输出中所看到的,Series.take()函数已经成功地返回了与所给系列对象中传递的索引位置相对应的元素。
 极客教程
极客教程