Python Pandas Series.transform()
Pandas系列是一个带有轴标签的一维ndarray。标签不需要是唯一的,但必须是一个可散列的类型。该对象支持基于整数和标签的索引,并提供了大量的方法来执行涉及索引的操作。
Pandas Series.transform() 函数 在自己身上调用func(传递的函数),产生一个具有转换值的系列,其轴长与自己相同。
语法: Series.transform(func, axis=0, *args, **kwargs)
参数:
func : 如果是一个函数,必须在传递给系列时起作用,或者在传递给系列.apply时起作用。
axis:参数需要与DataFrame兼容。
*args :传递给func的位置参数。
**kwargs :关键字参数,传递给func。
返回:返回的系列必须与自己有相同的长度。
示例#1:使用Series.transform()函数来转换给定系列对象的元素。在每个城市名称的后面加上”_City”。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio', 'Moscow'])
# Create the Datetime Index
didx = pd.DatetimeIndex(start ='2014-08-01 10:00', freq ='W',
periods = 6, tz = 'Europe/Berlin')
# set the index
sr.index = didx
# Print the series
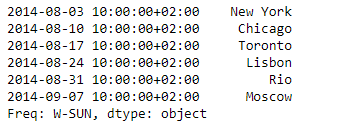
print(sr)
输出 :
现在我们将使用Series.transform()函数在每个城市名称的末尾添加”_City”。
# append '_City'
sr.transform(lambda x : x + '_City')
输出 :
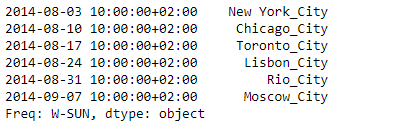
正如我们在输出中所看到的,Series.transform()函数已经成功地将所需的关键词附加在哪个城市名称的后面。
例子#2:使用Dataframe.transform()函数来转换给定Dataframe的数据。将每个人的门票费用增加1000。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Dataframe
df = pd.DataFrame({'Date':['10/2/2011', '11/2/2011', '12/2/2011', '13/2/2011'],
'Event':['Music', 'Poetry', 'Theatre', 'Comedy'],
'Cost':[10000, 5000, 15000, 2000]})
# Print the dataframe
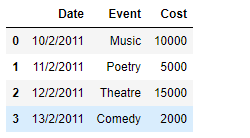
print(df)
输出 :
现在我们将使用Dataframe.transform()函数将票价提高1000
# transform the 'Cost' column
df['Cost'] = df['Cost'].transform(lambda x : x + 1000)
# Print the dataframe after modification
print(df)
输出 :
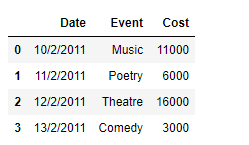
正如我们在输出中看到的,Dataframe.transform()函数成功地将每个事件的门票成本增加了1000。
 极客教程
极客教程