Python Pandas Series.to_latex()
Pandas系列是一个带有轴标签的一维ndarray。标签不需要是唯一的,但必须是一个可散列的类型。该对象支持基于整数和标签的索引,并提供了大量的方法来执行涉及索引的操作。
Pandas Series.to_latex()函数将一个对象渲染成LaTeX的表格环境表。
语法: Series.to_latex(buf=None, columns=None, col_space=None, header=True, index=True, na_rep=’NaN’, formatters=None, float_format=None, sparsify=None, index_names=True, bold_rows=False, column_format=None, longtable=None, escape=None, encoding=None, decimal=’.’, multicolumn=None, multicolumn_format=None, multirow=None)
参数:
buf : 要写入的缓冲区。如果没有,输出将作为一个字符串返回。
columns :要写入的列的子集。默认情况下是写所有的列。
col_space :每列的最小宽度。
header:写出列名。如果给了一个字符串的列表,则假定它是列名的别名。
index :写行名(索引)。
na_rep :缺失的数据表示。
formatters:格式化函数,按位置或名称应用于列的元素。
float_format :浮点数的格式字符串。
sparsify :对于具有分层索引的DataFrame,设置为False,以打印每一行的每个多索引键。
返回 : 如果buf是None,返回结果LateX格式的字符串,否则,返回None。
示例#1:使用Series.to_latex()函数将给定的系列对象渲染成LaTeX表格环境表。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio', 'Moscow'])
# Create the Datetime Index
didx = pd.DatetimeIndex(start ='2014-08-01 10:00', freq ='W',
periods = 6, tz = 'Europe/Berlin')
# set the index
sr.index = didx
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
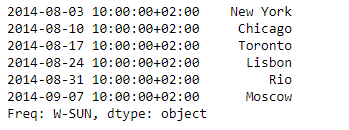
现在我们将使用Series.to_latex()函数将给定的系列对象渲染成LaTeX表格环境表。
# render to LaTeX tabular environment table.
sr.to_latex()
输出 :

正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.to_latex()函数已经成功地将给定的系列对象渲染成LaTeX表格环境表。
示例#2:使用Series.to_latex()函数将给定的系列对象渲染成LaTeX表格环境表。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series([19.5, 16.8, 22.78, 20.124, 18.1002])
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
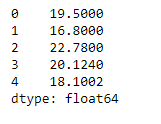
现在我们将使用Series.to_latex()函数将给定的系列对象渲染成LaTeX表格环境表。
# render to LaTeX tabular environment table.
sr.to_latex()
输出 :

正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.to_latex()函数已经成功地将给定的系列对象渲染成LaTeX表格环境表。
 极客教程
极客教程