Pygame 移动矩形物体
Pygame.Rect类具有存储和操作矩形区域的功能。一个Rect对象可以由左、上、宽和高的值构成。Rect类中的函数可以复制、移动和调整Rect对象的大小。
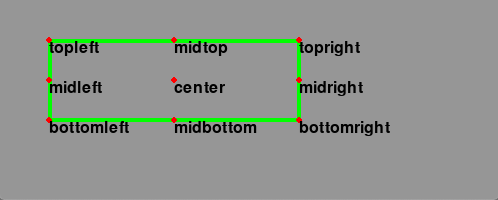
一个Rect对象有以下虚拟属性 –
除了移动之外,Rect类还有测试矩形之间碰撞的方法。
| copy() | 返回一个新的矩形,其位置和大小与原矩形相同。 |
|---|---|
| move() | 返回一个按给定偏移量移动的新矩形。x和y参数可以是任何整数,正数或负数。 |
| move_ip() | 与Rect.move()方法相同,但在原地操作。 |
| inflate(x,y) | 返回一个新的矩形,其大小由给定的偏移量改变。负值会缩小矩形。 |
| inflate_ip(x, y) | 和Rect.inflate()方法一样,但在原地操作。 |
| clamp(Rect) | 返回一个新的矩形,该矩形被移动到完全在参数Rect的内部。 |
| clip(Rect) | 返回一个新的矩形,该矩形被裁剪成完全在参数 Rect 内。 |
| union(Rect) | 返回一个新的矩形,该矩形完全覆盖两个提供的矩形的面积。 |
| union_ip(Rect) | 与 Rect.union() 方法相同,但在原地操作。 |
| contains(Rect) | 当参数完全在Rect里面时返回true。 |
| collidepoint((x,y)) | 如果给定的点在矩形内,返回真。 |
| colliderect(Rect) | 如果两个矩形的任何部分重叠,返回真。 |
例子
在下面的程序中,一个Rect对象被画上了红色的轮廓。使用copy()方法,它的克隆被创建用于移动。移动是通过move_ip()方法实现的。箭头键通过增加/减少X/Y坐标的+或-5像素来移动复制的矩形的位置。
import pygame
from pygame.locals import *
from sys import exit
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((400,300))
rect1 = Rect(50, 60, 200, 80)
rect2=rect1.copy()
running = True
x=0
y=0
while running:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == QUIT:
running = False
if event.type == KEYDOWN:
if event.key==K_LEFT:
x= -5
y=0
if event.key == K_RIGHT:
x=5
y=0
if event.key == K_UP:
x = 0
y = -5
if event.key == K_DOWN:
x = 0
y = 5
rect2.move_ip(x,y)
screen.fill((127,127,127))
pygame.draw.rect(screen, (255,0,0), rect1, 1)
pygame.draw.rect(screen, (0,0,255), rect2, 5)
pygame.display.update()
pygame.quit()
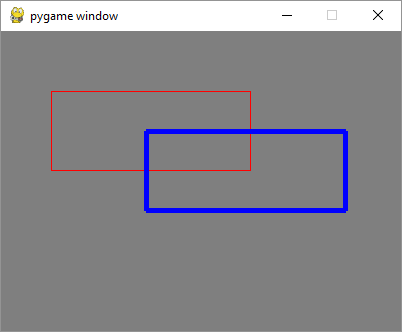
输出
下面的输出显示红色轮廓的矩形是原始矩形。它的副本不断地响应方向键而移动,并有蓝色的轮廓。
例子
将move_ip()方法改为inflate_ip()方法,以根据所按下的箭头来增长/缩小矩形。
while running:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == QUIT:
running = False
if event.type == KEYDOWN:
if event.key==K_LEFT:
x= -5
y=0
if event.key == K_RIGHT:
x=5
y=0
if event.key == K_UP:
x = 0
y = -5
if event.key == K_DOWN:
x = 0
y = 5
rect2.inflate_ip(x,y)
screen.fill((127,127,127))
pygame.draw.rect(screen, (255,0,0), rect1, 1)
pygame.draw.rect(screen, (0,0,255), rect2, 5)
pygame.display.update()
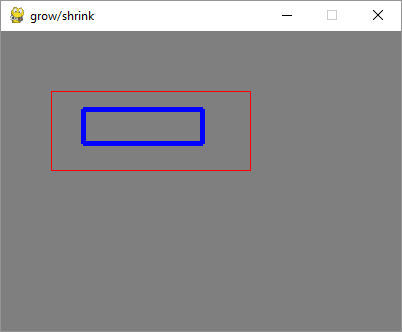
输出
以下是箭头按压活动的截图
例子
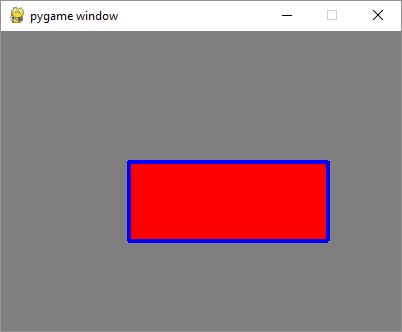
为了通过检测MOUSEMOTION事件使矩形移动,我们需要首先在原矩形内按下鼠标。为了验证鼠标位置是否在矩形内,我们使用Rect对象的collidepoint()方法。当鼠标在运动时,矩形对象通过move_ip()方法在原地移动。当鼠标被释放时,运动将停止。
import pygame
from pygame.locals import *
from sys import exit
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((400,300))
rect = Rect(50, 60, 200, 80)
moving = False
running = True
while running:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == QUIT:
running = False
elif event.type == MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
if rect.collidepoint(event.pos):
moving = True
elif event.type == MOUSEBUTTONUP:
moving = False
elif event.type == MOUSEMOTION and moving:
rect.move_ip(event.rel)
screen.fill((127,127,127))
pygame.draw.rect(screen, (255,0,0), rect)
if moving:
pygame.draw.rect(screen, (0,0,255), rect, 4)
pygame.display.flip()
pygame.quit()
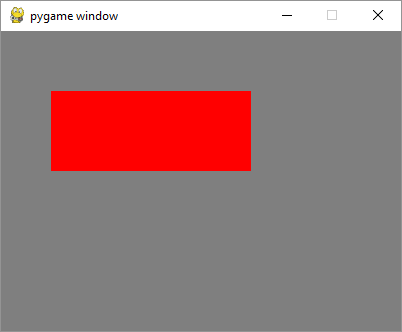
输出
例子
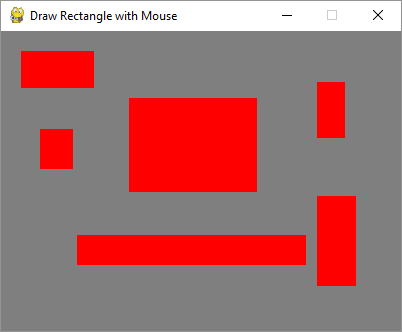
用鼠标绘制矩形,在MOUSEBUTTONDOWN和MOUSEBUTTONUP事件中捕获鼠标指针坐标,计算左上角坐标、宽度和高度,并调用rect()函数。
import pygame
from pygame.locals import *
from sys import exit
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((400,300))
pygame.display.set_caption("Draw Rectangle with Mouse")
screen.fill((127,127,127))
x=0
y=0
w=0
h=0
drawmode=True
running = True
while running:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == QUIT:
running = False
if event.type == MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
x,y = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
drawmode = True
if event.type == MOUSEBUTTONUP:
x1,y1 = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
w=x1-x
h=y1-y
drawmode= False
rect = pygame.Rect(x,y,w,h)
if drawmode == False:
pygame.draw.rect(screen, (255,0,0), rect)
pygame.display.flip()
pygame.quit()
输出
 极客教程
极客教程