Python Pandas Series.where
Python是一种进行数据分析的伟大语言,主要是因为以数据为中心的Python包的奇妙生态系统。Pandas就是这些包中的一个,它使导入和分析数据变得更加容易。
Pandas系列是一个带有轴标签的一维ndarray。标签不需要是唯一的,但必须是一个可散列的类型。该对象支持基于整数和标签的索引,并提供了大量的方法来执行涉及索引的操作。
Pandas Series.where()函数在输入条件为False时,替换给定系列对象的值。它接受另一个对象作为输入,将用于替换原始对象的值。
语法: Series.where(cond, other=nan, inplace=False, axis=None, level=None, errors=’raise’, try_cast=False, raise_on_error=None)
参数 :
cond : boolean NDFrame, array-like, or callable
other:标量,NDFrame,或可调用。
inplace : boolean, default False
axis: int, 默认为 None
level: int, 默认无
errors: str, {‘提高’, ‘忽略’}, 默认提高
try_cast : boolean, default False
返回: wh:与调用者类型相同
例子#1:使用Series.where()函数,当传递的条件不满足时,用一些其他的值替换给定的Series对象中的值。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
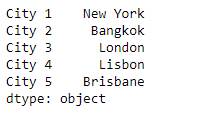
# Creating the First Series
sr1 = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio'])
# Creating the row axis labels
sr1.index = ['City 1', 'City 2', 'City 3', 'City 4', 'City 5']
# Print the series
print(sr1)
# Creating the second Series
sr2 = pd.Series(['New York', 'Bangkok', 'London', 'Lisbon', 'Brisbane'])
# Creating the row axis labels
sr2.index = ['City 1', 'City 2', 'City 3', 'City 4', 'City 5']
# Print the series
print(sr2)
输出 :

现在我们将使用Series.where()函数来替换那些不满足传递条件的值。
# replace the values
sr1.where(sr1 == 'Rio', sr2)
输出 :
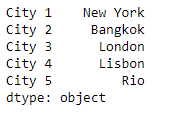
正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.where()函数已经替换了所有城市的名字,除了’里约’城市。
示例#2 :使用Series.where()函数,当传递的条件不满足时,用一些其他的值替换给定的Series对象中的值。
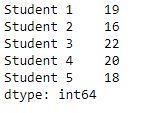
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the First Series
sr1 = pd.Series([22, 18, 19, 20, 21])
# Creating the row axis labels
sr1.index = ['Student 1', 'Student 2', 'Student 3', 'Student 4', 'Student 5']
# Print the series
print(sr1)
# Creating the second Series
sr2 = pd.Series([19, 16, 22, 20, 18])
# Creating the row axis labels
sr2.index = ['Student 1', 'Student 2', 'Student 3', 'Student 4', 'Student 5']
# Print the series
print(sr2)
输出 :

现在我们将使用Series.where()函数来替换那些不满足传递条件的值。
# replace the values
sr1.where(sr1 >20, sr2)
输出 :

正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.where()函数已经替换了所有不满足所传递条件的值。
 极客教程
极客教程