Python Pandas tseries.offsets.BusinessDay.freqstr
Dateoffsets是一种标准的日期增量,用于Pandas中的日期范围。就我们传入的关键字args而言,它的工作方式与relativedelta完全一样。DateOffets的工作原理如下,每个偏移量指定一组符合DateOffset的日期。例如,Bday定义这个集合为工作日(M-F)的日期集合。
DateOffsets可以被创建,以将日期向前移动一个给定的有效日期的数量。例如,Bday(2)可以被添加到日期中,使其向前移动两个工作日。如果日期不是从一个有效的日期开始,首先它被移动到一个有效的日期,然后创建偏移。
Pandas tseries.offsets.BusinessDay.freqstr属性以字符串形式返回应用于给定偏移对象的频率。
语法: pandas.tseries.offsets.BusinessDay.freqstr
参数:无
返回:偏移频率为字符串
例子#1:使用pandas.tseries.offsets.BusinessDay.freqstr属性来返回应用于给定的商业日偏移对象的频率,作为一个字符串。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating Timestamp
ts = pd.Timestamp('2019-10-10 07:15:11')
# Create an offset of 5 Business days
bd = pd.tseries.offsets.BusinessDay(n = 5)
# Print the Timestamp
print(ts)
# Print the DateOffset
print(bd)
输出 :
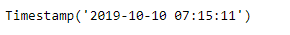
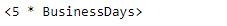
现在,我们将在给定的时间戳对象上添加商业日偏移量,以增加数据时间值。我们还将打印应用于给定偏移量对象的频率。
# Adding the Business day offset to the given timestamp
new_timestamp = ts + bd
# Print the updated timestamp
print(new_timestamp)
# Print the frequency applied on
# the given offset object
print(bd.freqstr)
输出 :
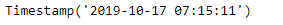

正如我们在输出中看到的,我们已经成功地创建了一个5个工作日的偏移量,并将其添加到给定的时间戳中。我们还将应用于给定偏移量对象的频率打印成一个字符串。
示例#2 : 使用pandas.tseries.offsets.BusinessDay.freqstr属性来返回应用于给定的商业日偏移对象的频率为一个字符串。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# importing the to_offset function
from pandas.tseries.frequencies import to_offset
# Creating Timestamp
ts = pd.Timestamp('2019-10-10 07:15:11')
# Create an offset of 10 Business days and 10 hours
bd = pd.tseries.offsets.BusinessDay(offset = datetime.timedelta(days = 10, hours = 10))
# Print the Timestamp
print(ts)
# Print the DateOffset
print(bd)
输出 :
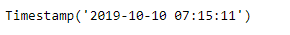
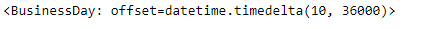
现在,我们将在给定的时间戳对象上添加商业日偏移量,以增加数据时间值。我们还将打印应用于给定偏移量对象的频率。
# Adding the Business day offset to the given timestamp
new_timestamp = ts + bd
# Print the updated timestamp
print(new_timestamp)
# Print the frequency applied on
# the given offset object
print(bd.freqstr)
输出 :
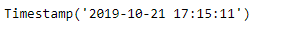
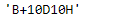
正如我们在输出中看到的,我们已经成功地创建了一个10个工作日和10个小时的偏移量,并将其添加到给定的时间戳中。我们还将应用于给定偏移量对象的频率打印成一个字符串。
 极客教程
极客教程