将imori.jpg大津二值化之后,进行两次形态学膨胀处理。
在形态学处理的过程中,二值化图像中白色(255)的部分向4-近邻(上下左右)膨胀或收缩一格 。
反复进行膨胀和收缩操作,可以消除独立存在的白色像素点(见问题四十九:开操作);或者连接白色像素点(见问题五十:闭操作)。
形态学处理中的膨胀算法如下。对于待操作的像素I(x,y)=0,I(x, y-1),I(x-1, y),I(x+1, y),I(x, y+1)中不论哪一个为255,令I(x,y)=255。
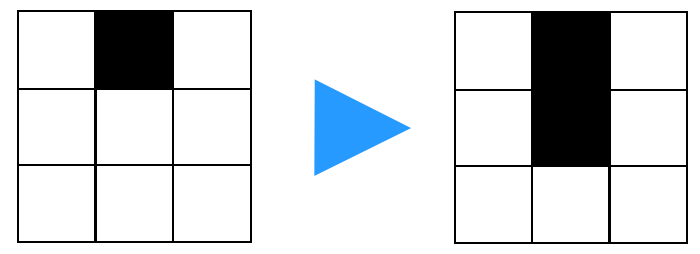
换句话说,如果将上面的操作执行两次,则可以扩大两格。
在实际进行形态学处理的时候,待操作的像素4-近邻与矩阵\left[\begin{matrix}0&1&0\\1&0&1\\0&1&0\end{matrix}\right]相乘,结果大于255的话,将中心像素设为255
python实现:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Gray scale
def BGR2GRAY(img):
b = img[:, :, 0].copy()
g = img[:, :, 1].copy()
r = img[:, :, 2].copy()
# Gray scale
out = 0.2126 * r + 0.7152 * g + 0.0722 * b
out = out.astype(np.uint8)
return out
# Otsu Binalization
def otsu_binarization(img, th=128):
H, W = img.shape
out = img.copy()
max_sigma = 0
max_t = 0
# determine threshold
for _t in range(1, 255):
v0 = out[np.where(out < _t)]
m0 = np.mean(v0) if len(v0) > 0 else 0.
w0 = len(v0) / (H * W)
v1 = out[np.where(out >= _t)]
m1 = np.mean(v1) if len(v1) > 0 else 0.
w1 = len(v1) / (H * W)
sigma = w0 * w1 * ((m0 - m1) ** 2)
if sigma > max_sigma:
max_sigma = sigma
max_t = _t
# Binarization
print("threshold >>", max_t)
th = max_t
out[out < th] = 0
out[out >= th] = 255
return out
# Morphology Erode
def Morphology_Erode(img, Dil_time=1):
H, W = img.shape
# kernel
MF = np.array(((0, 1, 0),
(1, 0, 1),
(0, 1, 0)), dtype=np.int)
# each dilate time
out = img.copy()
for i in range(Dil_time):
tmp = np.pad(out, (1, 1), 'edge')
for y in range(1, H+1):
for x in range(1, W+1):
if np.sum(MF * tmp[y-1:y+2, x-1:x+2]) >= 255:
out[y-1, x-1] = 255
return out
# Read image
img = cv2.imread("imori.jpg").astype(np.float32)
# Grayscale
gray = BGR2GRAY(img)
# Otsu's binarization
otsu = otsu_binarization(gray)
# Morphology - dilate
out = Morphology_Erode(otsu, Dil_time=2)
# Save result
cv2.imwrite("out.jpg", out)
cv2.imshow("result", out)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
c++实现:
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
// BGR -> Gray
cv::Mat BGR2GRAY(cv::Mat img){
// get height and width
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
// prepare output
cv::Mat out = cv::Mat::zeros(height, width, CV_8UC1);
// each y, x
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++){
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++){
// BGR -> Gray
out.at<uchar>(y, x) = 0.2126 * (float)img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[2] \
+ 0.7152 * (float)img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[1] \
+ 0.0722 * (float)img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[0];
}
}
return out;
}
// Gray -> Binary
cv::Mat Binarize_Otsu(cv::Mat gray){
int width = gray.cols;
int height = gray.rows;
// determine threshold
double w0 = 0, w1 = 0;
double m0 = 0, m1 = 0;
double max_sb = 0, sb = 0;
int th = 0;
int val;
// Get threshold
for (int t = 0; t < 255; t++){
w0 = 0;
w1 = 0;
m0 = 0;
m1 = 0;
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++){
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++){
val = (int)(gray.at<uchar>(y, x));
if (val < t){
w0++;
m0 += val;
} else {
w1++;
m1 += val;
}
}
}
m0 /= w0;
m1 /= w1;
w0 /= (height * width);
w1 /= (height * width);
sb = w0 * w1 * pow((m0 - m1), 2);
if(sb > max_sb){
max_sb = sb;
th = t;
}
}
std::cout << "threshold:" << th << std::endl;
// prepare output
cv::Mat out = cv::Mat::zeros(height, width, CV_8UC1);
// each y, x
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++){
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++){
// Binarize
if (gray.at<uchar>(y, x) > th){
out.at<uchar>(y, x) = 255;
} else {
out.at<uchar>(y, x) = 0;
}
}
}
return out;
}
// Morphology Erode
cv::Mat Morphology_Erode(cv::Mat img, int Erode_time){
int height = img.cols;
int width = img.rows;
// output image
cv::Mat tmp_img;
cv::Mat out = img.clone();
// for erode time
for (int i = 0; i < Erode_time; i++){
tmp_img = out.clone();
// each pixel
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++){
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++){
// check left pixel
if ((x > 0) && (tmp_img.at<uchar>(y, x - 1) == 255)){
out.at<uchar>(y, x) = 255;
continue;
}
// check up pixel
if ((y > 0) && (tmp_img.at<uchar>(y - 1, x) == 255)){
out.at<uchar>(y, x) = 255;
continue;
}
// check right pixel
if ((x < width - 1) && (tmp_img.at<uchar>(y, x + 1) == 255)){
out.at<uchar>(y, x) = 255;
continue;
}
// check left pixel
if ((y < height - 1) && (tmp_img.at<uchar>(y + 1, x) == 255)){
out.at<uchar>(y, x) = 255;
continue;
}
}
}
}
return out;
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]){
// read image
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("imori.jpg", cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
// BGR -> Gray
cv::Mat gray = BGR2GRAY(img);
// Gray -> Binary
cv::Mat bin = Binarize_Otsu(gray);
// Morphology Erode
cv::Mat out = Morphology_Erode(bin, 2);
//cv::imwrite("out.jpg", out);
cv::imshow("sample", out);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
输入:

大津二值化:

输出:

 极客教程
极客教程