低通滤波(Low-pass filter) 是一种过滤方式,规则为低频信号能正常通过,而超过设定临界值的高频信号则被阻隔、减弱。但是阻隔、减弱的幅度则会依据不同的频率以及不同的滤波程序(目的)而改变。它有的时候也被叫做高频去除过滤(high-cut filter)或者最高去除过滤(treble-cut filter)。低通过滤是高通过滤的对立。
将imori.jpg灰度化之后进行傅立叶变换并进行低通滤波,之后再用傅立叶逆变换复原吧!
通过离散傅立叶变换得到的频率在左上、右上、左下、右下等地方频率较低,在中心位置频率较高.
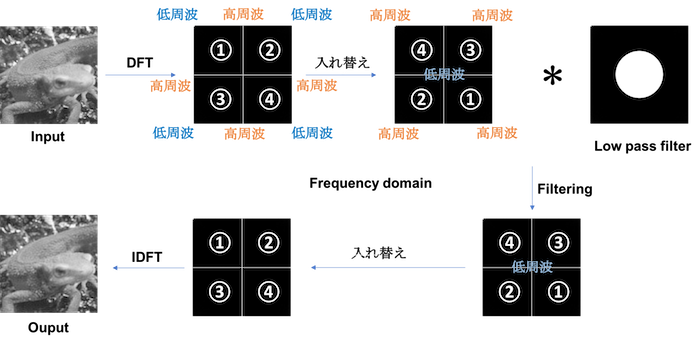
在图像中,高频成分指的是颜色改变的地方(噪声或者轮廓等),低频成分指的是颜色不怎么改变的部分(比如落日的渐变)。在这里,使用去除高频成分,保留低频成分的低通滤波器吧!
在这里,假设从低频的中心到高频的距离为r,我们保留0.5\ r的低频分量。
python实现:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# DFT hyper-parameters
K, L = 128, 128
channel = 3
# bgr -> gray
def bgr2gray(img):
gray = 0.2126 * img[..., 2] + 0.7152 * img[..., 1] + 0.0722 * img[..., 0]
return gray
# DFT
def dft(img):
# Prepare DFT coefficient
G = np.zeros((L, K, channel), dtype=np.complex)
# prepare processed index corresponding to original image positions
x = np.tile(np.arange(W), (H, 1))
y = np.arange(H).repeat(W).reshape(H, -1)
# dft
for c in range(channel):
for l in range(L):
for k in range(K):
G[l, k, c] = np.sum(img[..., c] * np.exp(-2j * np.pi * (x * k / K + y * l / L))) / np.sqrt(K * L)
#for n in range(N):
# for m in range(M):
# v += gray[n, m] * np.exp(-2j * np.pi * (m * k / M + n * l / N))
#G[l, k] = v / np.sqrt(M * N)
return G
# IDFT
def idft(G):
# prepare out image
H, W, _ = G.shape
out = np.zeros((H, W, channel), dtype=np.float32)
# prepare processed index corresponding to original image positions
x = np.tile(np.arange(W), (H, 1))
y = np.arange(H).repeat(W).reshape(H, -1)
# idft
for c in range(channel):
for l in range(H):
for k in range(W):
out[l, k, c] = np.abs(np.sum(G[..., c] * np.exp(2j * np.pi * (x * k / W + y * l / H)))) / np.sqrt(W * H)
# clipping
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
out = out.astype(np.uint8)
return out
# LPF
def lpf(G, ratio=0.5):
H, W, _ = G.shape
# transfer positions
_G = np.zeros_like(G)
_G[:H//2, :W//2] = G[H//2:, W//2:]
_G[:H//2, W//2:] = G[H//2:, :W//2]
_G[H//2:, :W//2] = G[:H//2, W//2:]
_G[H//2:, W//2:] = G[:H//2, :W//2]
# get distance from center (H / 2, W / 2)
x = np.tile(np.arange(W), (H, 1))
y = np.arange(H).repeat(W).reshape(H, -1)
# make filter
_x = x - W // 2
_y = y - H // 2
r = np.sqrt(_x ** 2 + _y ** 2)
mask = np.ones((H, W), dtype=np.float32)
mask[r > (W // 2 * ratio)] = 0
mask = np.repeat(mask, channel).reshape(H, W, channel)
# filtering
_G *= mask
# reverse original positions
G[:H//2, :W//2] = _G[H//2:, W//2:]
G[:H//2, W//2:] = _G[H//2:, :W//2]
G[H//2:, :W//2] = _G[:H//2, W//2:]
G[H//2:, W//2:] = _G[:H//2, :W//2]
return G
# Read image
img = cv2.imread("imori.jpg").astype(np.float32)
H, W, C = img.shape
# Gray scale
gray = bgr2gray(img)
# DFT
G = dft(img)
# LPF
G = lpf(G)
# IDFT
out = idft(G)
# Save result
cv2.imshow("result", out)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.imwrite("out.jpg", out)
c++实现:
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <complex>
const int height = 128, width = 128;
struct fourier_str {
std::complex<double> coef[height][width];
};
// RGB to Gray scale
cv::Mat BGR2GRAY(cv::Mat img){
// prepare output
cv::Mat out = cv::Mat::zeros(height, width, CV_8UC1);
// BGR -> Gray
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++){
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++){
out.at<uchar>(y, x) = (int)((float)img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[0] * 0.0722 + \
(float)img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[1] * 0.7152 + \
(float)img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[2] * 0.2126);
}
}
return out;
}
// Discrete Fourier transformation
fourier_str dft(cv::Mat img, fourier_str fourier_s){
double I;
double theta;
std::complex<double> val;
for ( int l = 0; l < height; l ++){
for ( int k = 0; k < width; k ++){
val.real(0);
val.imag(0);
for ( int y = 0; y < height; y ++){
for ( int x = 0; x < width; x ++){
I = (double)img.at<uchar>(y, x);
theta = -2 * M_PI * ((double)k * (double)x / (double)width + (double)l * (double)y / (double)height);
val += std::complex<double>(cos(theta), sin(theta)) * I;
}
}
val /= sqrt(height * width);
fourier_s.coef[l][k] = val;
}
}
return fourier_s;
}
// Inverse Discrete Fourier transformation
cv::Mat idft(cv::Mat out, fourier_str fourier_s){
double theta;
double g;
std::complex<double> G;
std::complex<double> val;
for ( int y = 0; y < height; y ++){
for ( int x = 0; x < width; x ++){
val.real(0);
val.imag(0);
for ( int l = 0; l < height; l ++){
for ( int k = 0; k < width; k ++){
G = fourier_s.coef[l][k];
theta = 2 * M_PI * ((double)k * (double)x / (double)width + (double)l * (double)y / (double)height);
val += std::complex<double>(cos(theta), sin(theta)) * G;
}
}
g = std::abs(val) / sqrt(height * width);
g = fmin(fmax(g, 0), 255);
out.at<uchar>(y, x) = (uchar)g;
}
}
return out;
}
// Low pass Filter
fourier_str lpf(fourier_str fourier_s, double pass_r){
// filtering
int r = height / 2;
int filter_d = (int)((double)r * pass_r);
for ( int j = 0; j < height / 2; j++){
for ( int i = 0; i < width / 2; i++){
if (sqrt(i * i + j * j) >= filter_d){
fourier_s.coef[j][i] = 0;
fourier_s.coef[j][width - i] = 0;
fourier_s.coef[height - i][i] = 0;
fourier_s.coef[height - i][width - i] = 0;
}
}
}
/*
fourier_str tmp_s;
// region change
for ( int j = 0; j < height / 2; j++){
for ( int i = 0; i < width / 2; i++){
// left top > right bottom
tmp_s.coef[height / 2 + j][width / 2 + i] = fourier_s.coef[j][i];
// right top > left bottom
tmp_s.coef[height / 2 + j][i] = fourier_s.coef[j][width / 2 + i];
// left bottom > right top
tmp_s.coef[j][width / 2 + i] = fourier_s.coef[height / 2 + j][i];
// right bottom > left top
tmp_s.coef[j][i] = fourier_s.coef[height / 2 + j][width / 2 + i];
}
}
// filtering
int r = height / 2;
int filter_d = (int)((double)r / 2);
for ( int j = 0; j < height / 2; j++){
for ( int i = 0; i < width / 2; i++){
if (sqrt(i * i + j + j) >= filter_d){
tmp_s.coef[height / 2 - j][width / 2 + i] = 0;
tmp_s.coef[height / 2 - j][width / 2 - i] = 0;
tmp_s.coef[height / 2 + i][width / 2 + i] = 0;
tmp_s.coef[height / 2 + i][width / 2 - i] = 0;
}
}
}
// return region
for ( int j = 0; j < height / 2; j++){
for ( int i = 0; i < width / 2; i++){
// left top > right bottom
fourier_s.coef[height / 2 + j][width / 2 + i] = tmp_s.coef[j][i];
// right top > left bottom
fourier_s.coef[height / 2 + j][i] = tmp_s.coef[j][width / 2 + i];
// left bottom > right top
fourier_s.coef[j][width / 2 + i] = tmp_s.coef[height / 2 + j][i];
// right bottom > left top
fourier_s.coef[j][i] = tmp_s.coef[height / 2 + j][width / 2 + i];
}
}
*/
return fourier_s;
}
// Main
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]){
// read original image
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("imori.jpg", cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
// Fourier coefficient
fourier_str fourier_s;
// output image
cv::Mat out = cv::Mat::zeros(height, width, CV_8UC1);
// BGR -> Gray
cv::Mat gray = BGR2GRAY(img);
// DFT
fourier_s = dft(gray, fourier_s);
// LPF
fourier_s = lpf(fourier_s, 0.5);
// IDFT
out = idft(out, fourier_s);
//cv::imwrite("out.jpg", out);
cv::imshow("answer", out);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
输入:

输出:

 极客教程
极客教程