对imori_gamma.jpg进行伽马校正(c=1,g=2.2)吧!
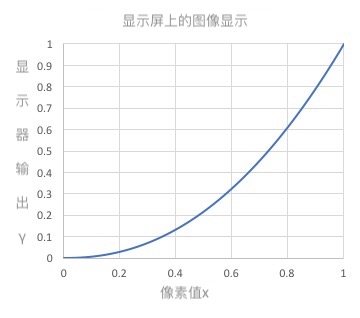
伽马校正用来对照相机等电子设备传感器的非线性光电转换特性进行校正。如果图像原样显示在显示器等上,画面就会显得很暗。伽马校正通过预先增大 RGB 的值来排除显示器的影响,达到对图像修正的目的。
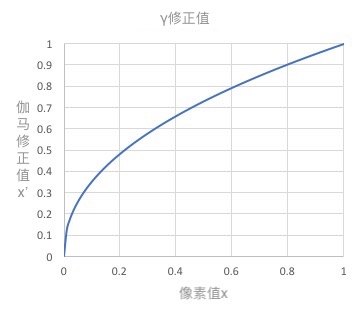
由于下式引起非线性变换,在该式中,x被归一化,限定在[0,1]范围内。c是常数,g为伽马变量(通常取2.2):
x’ = c\ {I_{in}}^ g
因此,使用下面的式子进行伽马校正:
I_{out} ={\frac{1}{c}\ I_{in}} ^ {\frac{1}{g}}
python实现:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# gamma correction
def gamma_correction(img, c=1, g=2.2):
out = img.copy()
out /= 255.
out = (1/c * out) ** (1/g)
out *= 255
out = out.astype(np.uint8)
return out
# Read image
img = cv2.imread("imori_gamma.jpg").astype(np.float)
# Gammma correction
out = gamma_correction(img)
# Save result
cv2.imshow("result", out)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.imwrite("out.jpg", out)
c++实现:
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
// gamma correction
cv::Mat gamma_correction(cv::Mat img, double gamma_c, double gamma_g){
// get height and width
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
int channel = img.channels();
// output image
cv::Mat out = cv::Mat::zeros(height, width, CV_8UC3);
double val;
// gamma correction
for (int y = 0; y< height; y++){
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++){
for (int c = 0; c < channel; c++){
val = (double)img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[c] / 255;
out.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[c] = (uchar)(pow(val / gamma_c, 1 / gamma_g) * 255);
}
}
}
return out;
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]){
// read image
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("imori_gamma.jpg", cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
// gamma correction
cv::Mat out = gamma_correction(img, 1, 2.2);
//cv::imwrite("out.jpg", out);
cv::imshow("answer", out);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
| 显示屏上的图像显示 | $$\gamma$$修正值 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
输入:

输出:

 极客教程
极客教程