使用双线性插值将图像放大1.5倍吧!
双线性插值考察4邻域的像素点,并根据距离设置权值。虽然计算量增大使得处理时间变长,但是可以有效抑制画质劣化。
- 放大后图像的座标(x’,y’)除以放大率a,可以得到对应原图像的座标(\lfloor \frac{x’}{a}\rfloor , \lfloor \frac{y’}{a}\rfloor)。
-
求原图像的座标(\lfloor \frac{x’}{a}\rfloor , \lfloor \frac{y’}{a}\rfloor)周围4邻域的座标I(x,y),I(x+1,y),I(x,y+1),I(x+1, y+1):
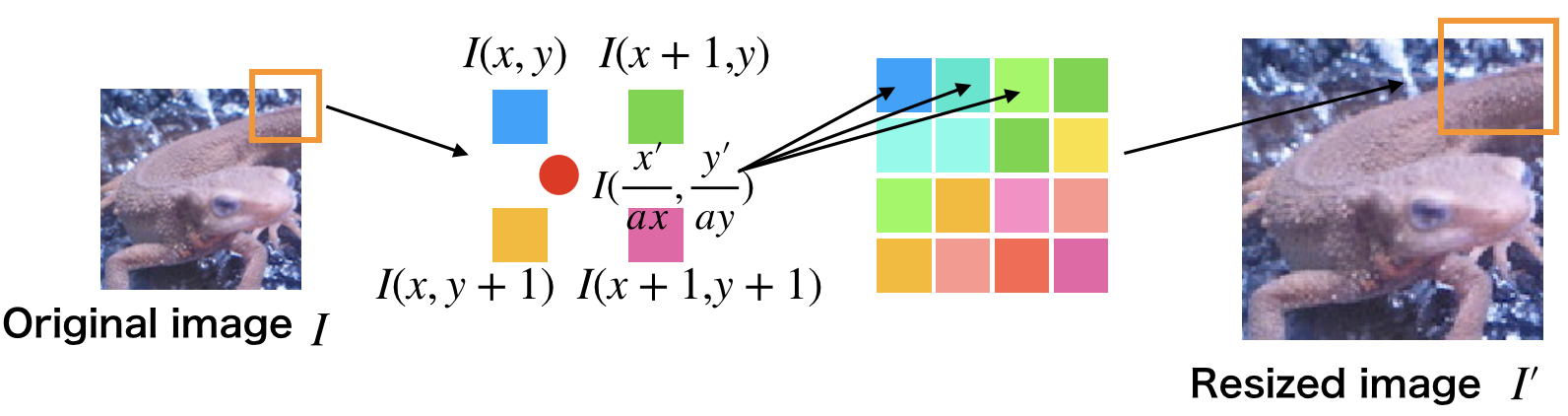
-
分别求这4个点与(\frac{x’}{a}, \frac{y’}{a})的距离,根据距离设置权重:w = \frac{d}{\sum\ d}
-
根据下式求得放大后图像(x’,y’)处的像素值:
d_x = \frac{x’}{a} – x\\
d_y = \frac{y’}{a} – y\\
I'(x’,y’) = (1-d_x)\ (1-d_y)\ I(x,y) + d_x\ (1-d_y)\ I(x+1,y) + (1-d_x)\ d_y\ I(x,y+1) + d_x\ d_y\ I(x+1,y+1)
python实现:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Bi-Linear interpolation
def bl_interpolate(img, ax=1., ay=1.):
H, W, C = img.shape
aH = int(ay * H)
aW = int(ax * W)
# get position of resized image
y = np.arange(aH).repeat(aW).reshape(aW, -1)
x = np.tile(np.arange(aW), (aH, 1))
# get position of original position
y = (y / ay)
x = (x / ax)
ix = np.floor(x).astype(np.int)
iy = np.floor(y).astype(np.int)
ix = np.minimum(ix, W-2)
iy = np.minimum(iy, H-2)
# get distance
dx = x - ix
dy = y - iy
dx = np.repeat(np.expand_dims(dx, axis=-1), 3, axis=-1)
dy = np.repeat(np.expand_dims(dy, axis=-1), 3, axis=-1)
# interpolation
out = (1-dx) * (1-dy) * img[iy, ix] + dx * (1 - dy) * img[iy, ix+1] + (1 - dx) * dy * img[iy+1, ix] + dx * dy * img[iy+1, ix+1]
out = np.clip(out, 0, 255)
out = out.astype(np.uint8)
return out
# Read image
img = cv2.imread("imori.jpg").astype(np.float)
# Bilinear interpolation
out = bl_interpolate(img, ax=1.5, ay=1.5)
# Save result
cv2.imshow("result", out)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.imwrite("out.jpg", out)
c++实现:
#include <opencv2/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
// bilinear
cv::Mat bilinear(cv::Mat img, double rx, double ry){
// get height and width
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
int channel = img.channels();
// get resized shape
int resized_width = (int)(width * rx);
int resized_height = (int)(height * ry);
int x_before, y_before;
double dx, dy;
double val;
// output image
cv::Mat out = cv::Mat::zeros(resized_height, resized_width, CV_8UC3);
// bi-linear interpolation
for (int y = 0; y < resized_height; y++){
y_before = (int)floor(y / ry);
y_before = fmin(y_before, height - 1);
dy = y / ry - y_before;
for (int x = 0; x < resized_width; x++){
x_before = (int)floor(x / rx);
x_before = fmin(x_before, width - 1);
dx = x / rx - x_before;
// compute bi-linear
for (int c = 0; c < channel; c++){
val = (1. - dx) * (1. - dy) * img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y_before, x_before)[c] +
dx * (1. - dy) * img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y_before, x_before + 1)[c] +
(1. - dx) * dy * img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y_before + 1, x_before)[c] +
dx * dy * img.at<cv::Vec3b>(y_before + 1, x_before)[c];
// assign pixel to new position
out.at<cv::Vec3b>(y, x)[c] = (uchar)val;
}
}
}
return out;
}
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]){
// read image
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("imori.jpg", cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
// bilinear
cv::Mat out = bilinear(img, 1.5, 1.5);
//cv::imwrite("out.jpg", out);
cv::imshow("answer", out);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
输入:

输出:

 极客教程
极客教程