Pygame 在窗口中显示文本
要在Pygame窗口中显示文本,我们首先需要获取一个字体对象,可以使用pygame.font模块中定义的SysFont()函数来帮助实现。
Fnt= SysFont(name, size, bold=False, italic=False)
可以通过get_fonts()函数获取当前计算机安装的字体列表。
fonts = pygame.font.get_fonts()
for f in fonts:
print(f)
让我们定义一个表示Arial字体,大小为36点的字体对象。
font = pygame.font.SysFont("Arial", 36)
接下来,我们使用Font对象的render()方法,在新创建的字体中渲染“Hello World”文本,获得一个新的Surface对象。
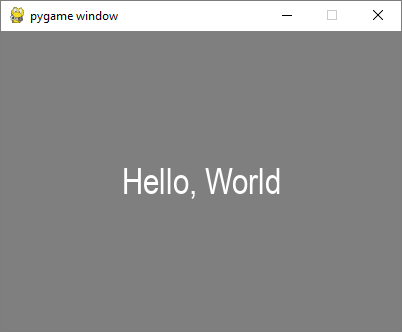
txtsurf = font.render("Hello, World", True, white)
第一个参数是一行字符串,第二个参数表示是否开启抗锯齿。如果设置为False,则渲染的图像是8位图像,如果设置为True,则为24位。还可以使用可选的背景颜色参数。
现在我们需要在屏幕窗口中心绘制文字表面。
screen.blit(txtsurf,(200 - txtsurf.get_width() // 2, 150 - txtsurf.get_height() // 2))
示例
以下是完整的代码−
import pygame
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((400, 300))
done = False
white=(255,255,255)
red = (255,0,0)
green = (0,255,0)
blue = (0,0,255)
bg = (127,127,127)
while not done:
for event in pygame.event.get():
screen.fill(bg)
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
done = True
font = pygame.font.SysFont("Arial", 36)
txtsurf = font.render("Hello, World", True, white)
screen.blit(txtsurf,(200 - txtsurf.get_width() // 2, 150 - txtsurf.get_height() // 2))
pygame.display.update()
输出
除了SysFont()方法之外,还可以从字体文件(扩展名为.ttf)或指向ttf文件的Python文件对象中获得Font对象。也可以使用.ttc文件构建字体对象。字体类定义了以下方法 –
| bold() | 获取或设置是否以粗体显示字体。 |
|---|---|
| italic() | 获取或设置是否以斜体显示字体。 |
| underline() | 获取或设置是否以下划线显示字体。 |
| render() | 在新Surface上绘制文本。 |
| size() | 计算绘制文本所需的大小。 |
| set_underline() | 控制是否以下划线显示文本。 |
| get_underline() | 检查文本是否以下划线显示。 |
| set_bold() | 启用伪粗体文本的渲染。 |
| get_bold() | 检查文本是否以粗体显示。 |
| set_italic() | 启用伪斜体文本的渲染。 |
| metrics() | 获取每个字符的度量。 |
| get_italic() | 检查文本是否以斜体显示。 |
| get_linesize() | 获取字体文本的行间距。 |
| get_height() | 获取字体的高度。 |
| get_ascent() | 获取字体的上升高度。 |
| get_descent() | 获取字体的下降高度。 |
给出以下使用ttf和ttc文件来渲染文本的示例。
font1 = pygame.font.SysFont('chalkduster.ttf', 72)
img1 = font1.render('Hello World', True, BLUE)
font2 = pygame.font.SysFont('didot.ttc', 72)
img2 = font2.render('Hello Pygame', True, GREEN)
screen.blit(img1, (20, 50))
screen.blit(img2, (20, 120))
pygame.display.update()
在上面的示例中,一个预定义的字符串被渲染为一个表面对象。然而,通过读取KEYDOWN事件的键值,可以与用户交互地输入字符串并显示出来。
首先,我们渲染一个空字符串。接下来,我们定义一个边界矩形,然后定义一个光标矩形,该矩形与文本边界矩形重叠。在每个被识别为KEYDOWN事件的按键中,被添加到原始空字符串中并重复渲染。
示例
以下代码最初显示一个空白窗口。每个按下的字母都会一个接一个地显示出来。
import pygame
pygame.init()
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((400, 300))
done = False
white=(255,255,255)
red = (255,0,0)
green = (0,255,0)
blue = (0,0,255)
bg = (127,127,127)
text=""
while not done:
for event in pygame.event.get():
screen.fill(bg)
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
done = True
if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:
text=text+event.unicode
font = pygame.font.SysFont("Arial", 36)
img = font.render(text, True, white)
rect = img.get_rect()
cursor = pygame.Rect(rect.topright, (3, rect.height))
img = font.render(text, True, white)
rect.size=img.get_size()
cursor.topleft = rect.topright
screen.blit(img,(200 - img.get_width() // 2, 150 - img.get_height() // 2))
pygame.display.update()
输出
运行以上代码并输入一些文本。示例输出如下:
 极客教程
极客教程