Python Pandas Series.tshift()
Pandas系列是一个带有轴标签的一维ndarray。标签不需要是唯一的,但必须是一个可散列的类型。该对象支持基于整数和标签的索引,并提供了大量的方法来执行涉及索引的操作。
Pandas Series.tshift()函数用于转移时间索引,如果有的话,使用该索引的频率。如果没有指定freq,它会尝试使用索引的freq或inferred_freq属性。如果这些属性都不存在,就会抛出一个ValueError。
语法: Series.tshift(periods=1, freq=None, axis=0)
参数:
periods:移动的周期数,可以是正数或负数
freq : 使用tseries模块或时间规则的增量(例如,’EOM’)。
axis:对应于包含索引的轴。
返回 : shifted : NDFrame
示例#1:使用Series.tshift()函数将给定系列对象的基于Datetime的索引按一定周期进行移动。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio', 'Moscow'])
# Create the Datetime Index
didx = pd.DatetimeIndex(start ='2014-08-01 10:00', freq ='W',
periods = 6, tz = 'Europe/Berlin')
# set the index
sr.index = didx
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
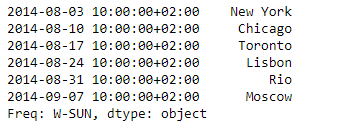
现在我们将使用Series.tshift()函数,在已经应用的系列对象的频率上,将指数移动2个周期。
# shift by 2 periods
sr.tshift(periods = 2)
输出 :
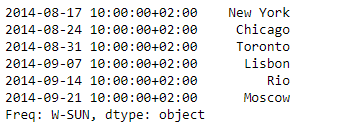
正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.tshift()函数已经成功地将给定系列的基于DateTime的索引转移了2个周期。
例子2:使用Series.tshift()函数将给定系列对象的基于DateTime的索引按一定周期递增,同时对其应用 “每日 “频率。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio', 'Moscow'])
# Create the Datetime Index
didx = pd.DatetimeIndex(start ='2014-08-01 10:00', freq ='W',
periods = 6, tz = 'Europe/Berlin')
# set the index
sr.index = didx
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
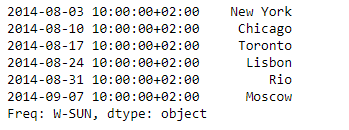
现在我们将使用Series.tshift()函数,在已经应用的系列对象的频率上,将指数增加4个周期。
# increment by 4 periods
sr.tshift(periods = 4, freq = 'D')
输出 :
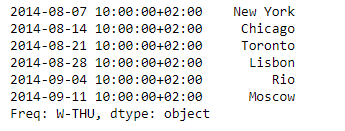
正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.tshift()函数已经成功地将给定系列的基于DateTime的索引增加了4个周期。
 极客教程
极客教程