Python Pandas Series.select()
Pandas系列是一个带有轴标签的一维ndarray。标签不需要是唯一的,但必须是一个可散列的类型。该对象支持基于整数和标签的索引,并提供了大量的方法来执行涉及索引的操作。
Pandas Series.select()函数返回与标准匹配的轴标签对应的数据。我们把函数的名称作为参数传给这个函数,这个函数会应用于所有的索引标签。满足条件的索引标签被选中。
语法: Series.select(crit, axis=0)
参数:
crit :在每个索引(标签)上调用。应该返回True或False
axis: int值
返回:选择:与调用者的类型相同
例子#1:使用Series.select()函数从给定的Series对象中选择所有那些城市的名字,因为它的索引标签有偶数结尾。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['New York', 'Chicago', 'Toronto', 'Lisbon', 'Rio', 'Moscow'])
# Create the Datetime Index
index_ = ['City 1', 'City 2', 'City 3', 'City 4', 'City 5', 'City 6']
# set the index
sr.index = index_
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
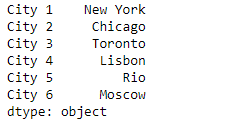
现在我们将使用Series.select()函数来选择所有那些索引标签以偶数整数值结尾的城市名称。
# Define a function to Select those cities whose index
# label's last character is an even integer
def city_even(city):
# if last character is even
if int(city[-1]) % 2 == 0:
return True
else:
return False
# Call the function and select the values
selected_cities = sr.select(city_even, axis = 0)
# Print the returned Series object
print(selected_cities)
输出 :

正如我们在输出中所看到的,Series.select()函数已经成功地返回了所有符合给定条件的城市。
例子2:使用Series.select()函数从给定的Series对象中选择 “可口可乐 “和 “雪碧 “的销售额。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series([100, 25, 32, 118, 24, 65])
# Create the Index
index_ = ['Coca Cola', 'Sprite', 'Coke', 'Fanta', 'Dew', 'ThumbsUp']
# set the index
sr.index = index_
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
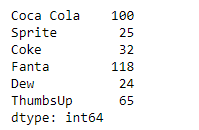
现在,我们将使用Series.select()函数,从给定的系列对象中选择列出的饮料的销售额。
# Function to select the sales of
# Coca Cola and Sprite
def show_sales(x):
if x == 'Sprite' or x == 'Coca Cola':
return True
else:
return False
# Call the function and select the values
selected_cities = sr.select(show_sales, axis = 0)
# Print the returned Series object
print(selected_cities)
输出 :
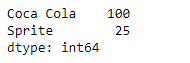
正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.select()函数已经成功地从给定的Series对象中返回了所需饮料的销售数据。
 极客教程
极客教程