Python Pandas tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.rollforward
Dateoffsets是一种标准的日期增量,用于Pandas中的日期范围。在我们传入的关键字args方面,它的工作方式与relativedelta完全一样。DateOffsets的工作原理如下,每个偏移量指定一组符合DateOffset的日期。例如,Bday定义这个集合为工作日(M-F)的日期集合。DateOffsets可以被创建,以将日期向前移动一个给定的有效日期数量。例如,Bday(2)可以被添加到日期中,使其向前移动两个工作日。如果日期不是从一个有效的日期开始,首先它被移到一个有效的日期,然后创建偏移。Pandas tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.rollforward()函数只在不在偏移量上的情况下将提供的日期向前滚动到下一个偏移量。
语法: pandas.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.rollforward()
参数:dt : date
返回: rollforward
例子#1:使用pandas.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.rollforward()函数将提供的日期向前滚动到下一个偏移量,如果不在偏移量上。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating Timestamp
ts = pd.Timestamp('2019-10-10 11:15:00')
# Create an offset
bh = pd.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour(n = 5)
# Print the Timestamp
print(ts)
# Print the Offset
print(bh)
输出 :
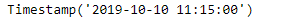
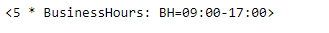
现在我们将在给定的时间戳对象上添加营业时间的偏移,以增加数据时间值。如果不在偏移量上,我们也将把提供的日期向前滚动到下一个偏移量。
# Adding the Business hour offset to the given timestamp
new_timestamp = ts + bh
# Print the updated timestamp
print(new_timestamp)
# roll forward the date if not
# on offset
result = bh.rollforward( pd.to_datetime('2010-02-13'))
# print the result
print(result)
输出:
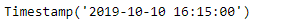
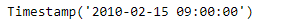
我们可以在输出中看到,我们已经成功地创建了一个偏移量并将其添加到给定的时间戳。我们也将提供的日期向前滚动到下一个偏移量。
例子2:使用pandas.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour.rollforward()函数将提供的日期向前滚动到下一个偏移量,如果不在偏移量上。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating Timestamp
ts = pd.Timestamp('2019-10-10 11:15:00')
# Create an offset
bh = pd.tseries.offsets.BusinessHour(offset = datetime.timedelta(hours = 1))
# Print the Timestamp
print(ts)
# Print the Offset
print(bh)
输出 :
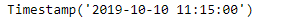

现在我们将在给定的时间戳对象上添加营业时间的偏移量来增加日期时间值。如果不在偏移量上,我们也会将提供的日期向前滚动到下一个偏移量。
# Adding the Business hour offset to the given timestamp
new_timestamp = ts + bh
# Print the updated timestamp
print(new_timestamp)
# roll forward the date if not
# on offset
result = bh.rollforward( pd.to_datetime('2010-02-12 11:00:00'))
# print the result
print(result)
输出 :
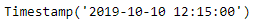
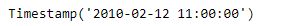
我们可以在输出中看到,我们已经成功创建了一个偏移量,并将其添加到给定的时间戳。通过的日期没有被向前滚动,因为它是在偏移上。
 极客教程
极客教程