Matplotlib.axes.axes.get_xbound()
Matplotlib是Python中的一个库,它是NumPy库的数值-数学扩展。Axes包含了大多数图形元素:Axis、Tick、Line2D、Text、Polygon等,并设置坐标系。Axes的实例通过callbacks属性支持回调。
matplotlib.axes.axes.get_xbound()函数
matplotlib库的Axes模块中的Axes.get_xbound()函数用于按递增顺序返回x轴的数值下界和上界
语法:Axes.get_xbound(self)
参数:该方法不接受任何参数。
该方法返回以下内容
- lower, upper:返回当前的x轴上下边界。
注意:这个函数可以在各种情况下代替get_xlim。
下面的例子演示了matplotlib.axes.axes.get_xbound()函数在matplotlib.axes中的作用:
示例1
# Implementation of matplotlib function
from matplotlib.widgets import Cursor
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, [ax, ax1] = plt.subplots(2, 1)
t = 4*(np.random.rand(2, 100) - .5)
x = np.cos(2 * np.pi * t)
y = np.sin(2 * np.pi * t)
ax.plot(x, y, 'g')
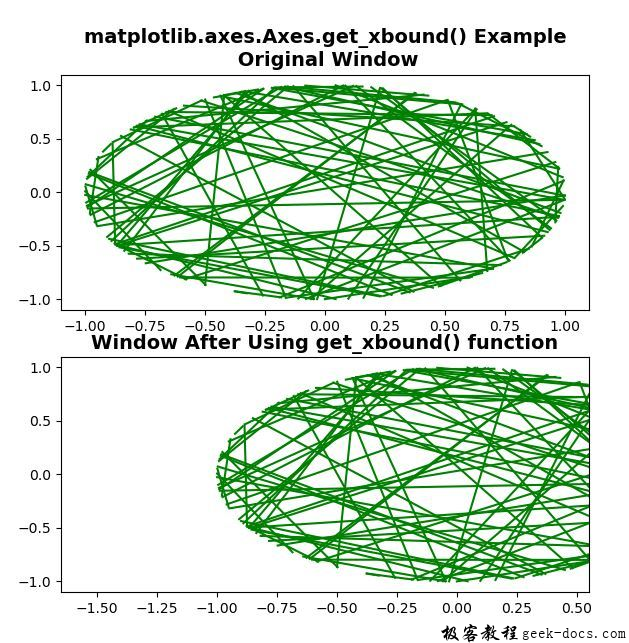
lower, upper = ax.get_xbound()
ax.set_title('matplotlib.axes.Axes.get_xbound()\
Example\n Original Window',
fontsize = 14, fontweight ='bold')
ax1.plot(x, y, 'g')
ax1.set_xbound(1.5 * lower, 0.5 * upper)
ax1.set_title('Window After Using get_xbound() function',
fontsize = 14, fontweight ='bold')
plt.show()
输出:
示例2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Fixing random state for
# reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
# the random data
x = np.random.randn(1000)
y = np.random.randn(1000)
# definitions for the axes
left, width = 0.1, 0.65
bottom, height = 0.1, 0.65
spacing = 0.005
rect_scatter = [left, bottom,
width, height]
rect_histx = [left,
bottom + height + spacing,
width, 0.2]
rect_histy = [left + width + spacing,
bottom, 0.2, height]
# start with a rectangular Figure
plt.figure()
ax_scatter = plt.axes(rect_scatter)
ax_scatter.tick_params(direction ='in',
bottom = True,
right = True)
ax_histx = plt.axes(rect_histx)
ax_histx.tick_params(direction ='in',
labeltop = True)
ax_histy = plt.axes(rect_histy)
ax_histy.tick_params(direction ='in',
labelleft = True)
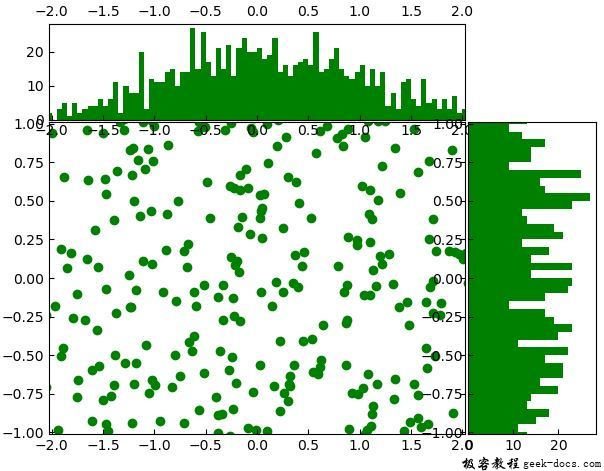
# the scatter plot:
ax_scatter.scatter(2 * x, y * 2, color ="green")
# now determine nice limits by hand:
binwidth = 0.05
lim = np.ceil(np.abs([x, y]).max() / binwidth) * binwidth
ax_scatter.set_xbound((-0.5 * lim, 0.5 * lim))
ax_scatter.set_ybound((-0.25 * lim, 0.25 * lim))
bins = np.arange(-lim, lim + binwidth, binwidth)
ax_histx.hist(x, bins = bins,
color ="green")
ax_histy.hist(y, bins = bins,
color ="green",
orientation ='horizontal')
ax_histx.set_xbound(ax_scatter.get_xbound())
ax_histy.set_ybound(ax_scatter.get_ybound())
plt.show()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程