Matplotlib.axes.axes.get_position()
Matplotlib是Python中的一个库,它是NumPy库的数值-数学扩展。Axes包含了大多数图形元素:Axis、Tick、Line2D、Text、Polygon等,并设置坐标系。Axes的实例通过callbacks属性支持回调。
函数:Matplotlib.axes.axes.get_position()
在matplotlib库的Axes模块中的Axes.set_position()函数用于获得一个作为框的Axes rectangle的副本。
Axes.get_position(self, original=False)
参数:
- original:如果为true,该参数用于返回原始位置。否则返回活动位置。
返回值:该方法将坐标轴矩形的副本作为Bbox返回。
下面的例子演示了matplotlib.axes.axes.get_position()函数在matplotlib.axes中的作用:
示例1
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.arange(10)
y = [2, 4, 6, 14, 15, 16, 17, 16, 18, 20]
y2 = [10, 11, 12, 13, 8, 10, 12, 14, 18, 19]
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax1.plot(x, y, "go-", label ='Line 1', )
ax1.plot(x, y2, "o-", label ='Line 2')
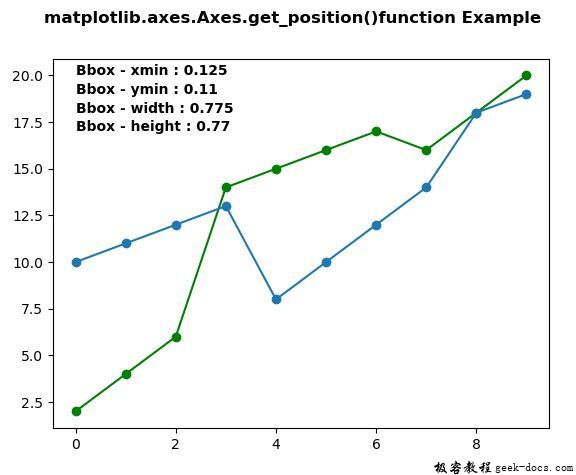
chartBox = ax1.get_position()
x, y, w, h = chartBox.x0, chartBox.y0, chartBox.width, chartBox.height
ax1.text(0, 20, "Bbox - xmin : "+str(x),
fontweight ="bold")
ax1.text(0, 19, "Bbox - ymin : "+str(round(y, 2)),
fontweight ="bold")
ax1.text(0, 18, "Bbox - width : "+str(w),
fontweight ="bold")
ax1.text(0, 17, "Bbox - height : "+str(h),
fontweight ="bold")
fig.suptitle('matplotlib.axes.Axes.get_position()\
function Example\n', fontweight ="bold")
plt.show()
输出:
示例2
# Implementation of matplotlib function
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import LogNorm
Z = np.random.rand(6, 30)
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax1.pcolor(Z)
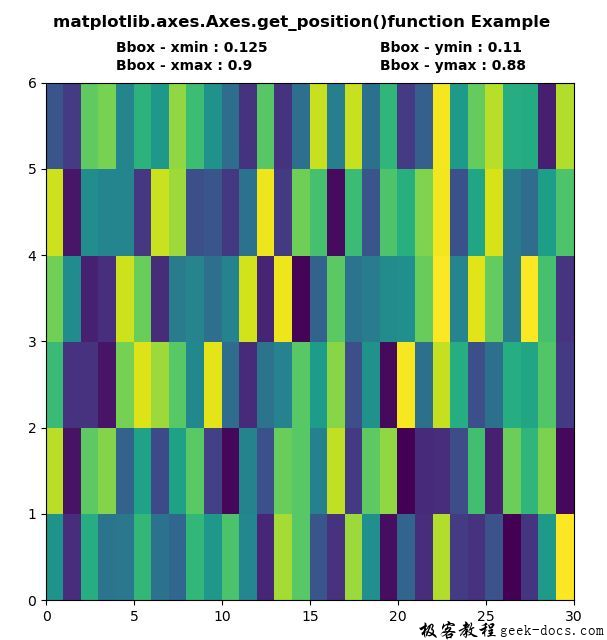
chartBox = ax1.get_position()
x, y, x1, y1 = chartBox.x0, chartBox.y0, chartBox.x1, chartBox.y1
ax1.text(4, 6.35, "Bbox - xmin : "+str(x),
fontweight ="bold")
ax1.text(19, 6.35, "Bbox - ymin : "+str(round(y, 2)),
fontweight ="bold")
ax1.text(4, 6.15, "Bbox - xmax : "+str(x1),
fontweight ="bold")
ax1.text(19, 6.15, "Bbox - ymax : "+str(y1),
fontweight ="bold")
fig.suptitle('matplotlib.axes.Axes.get_position()\
function Example\n', fontweight ="bold")
plt.show()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程