Matplotlib中使用set_clip_on()方法控制图形元素裁剪
参考:Matplotlib.artist.Artist.set_clip_on() in Python
Matplotlib是Python中最流行的数据可视化库之一,它提供了丰富的绘图功能和灵活的自定义选项。在Matplotlib中,Artist是所有可视化元素的基类,包括线条、文本、图像等。本文将深入探讨Artist类中的set_clip_on()方法,这是一个强大的工具,用于控制图形元素是否被裁剪到其所在的轴域内。
1. set_clip_on()方法简介
set_clip_on()是Matplotlib中Artist类的一个方法,用于设置是否对图形元素进行裁剪。当设置为True时,图形元素会被限制在其所在的轴域内;当设置为False时,图形元素可以超出轴域的边界。
1.1 基本语法
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
artist = ax.plot([0, 1], [0, 1])[0]
artist.set_clip_on(True) # 或 False
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个简单的线条,并使用set_clip_on()方法设置其裁剪状态。
1.2 方法参数
set_clip_on()方法接受一个布尔值参数:
- True:启用裁剪(默认值)
- False:禁用裁剪
2. 为什么使用set_clip_on()?
使用set_clip_on()方法可以让我们更灵活地控制图形元素的显示范围。这在以下情况下特别有用:
- 创建超出常规绘图区域的视觉效果
- 绘制跨越多个子图的元素
- 实现特殊的图表设计
- 调试图形元素的位置和大小
3. 在不同类型的Artist上使用set_clip_on()
set_clip_on()方法可以应用于各种类型的Artist对象。让我们逐一探讨它在不同图形元素上的应用。
3.1 线条(Line2D)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
line, = ax.plot(x, np.sin(x))
line.set_clip_on(False)
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, 0.5)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Line2D with clip_on=False")
plt.show()
Output:
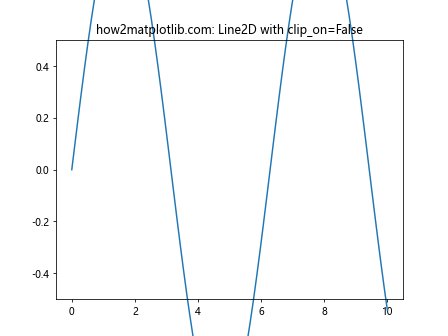
在这个例子中,我们绘制了一个正弦曲线,并将其clip_on属性设置为False。这样,即使我们将y轴的范围限制在-0.5到0.5之间,整条曲线仍然可见。
3.2 文本(Text)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax.set_ylim(0, 10)
text = ax.text(5, 5, "how2matplotlib.com", fontsize=20)
text.set_clip_on(False)
plt.title("Text with clip_on=False")
plt.show()
Output:
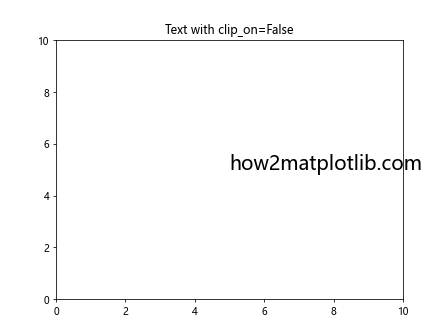
这个例子展示了如何使用set_clip_on()方法来允许文本超出轴域的边界。即使文本的位置或大小导致它超出了轴的范围,它仍然会完整显示。
3.3 散点图(scatter)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.random.rand(50)
y = np.random.rand(50)
scatter = ax.scatter(x, y, s=1000)
scatter.set_clip_on(False)
ax.set_xlim(0.3, 0.7)
ax.set_ylim(0.3, 0.7)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Scatter plot with clip_on=False")
plt.show()
Output:
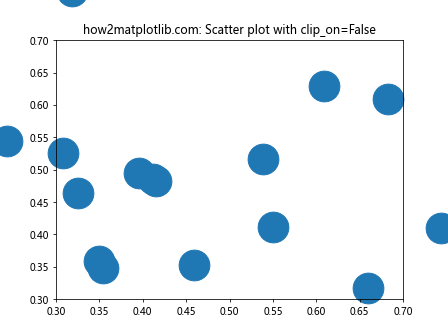
在这个散点图示例中,我们故意将点的大小设置得很大,并将轴的范围限制在一个较小的区域。通过设置clip_on=False,我们可以看到完整的散点,即使它们超出了轴的范围。
3.4 柱状图(bar)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.arange(5)
y = np.random.rand(5)
bars = ax.bar(x, y)
for bar in bars:
bar.set_clip_on(False)
ax.set_ylim(0, 0.5)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Bar plot with clip_on=False")
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何在柱状图中使用set_clip_on()。通过将每个柱子的clip_on属性设置为False,我们可以看到完整的柱子,即使它们的高度超过了y轴的上限。
4. set_clip_on()的高级应用
除了基本用法,set_clip_on()还可以用于创建一些有趣的视觉效果和高级图表设计。
4.1 创建图例外的元素
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
line, = ax.plot(x, np.sin(x), label="Sine wave")
ax.legend()
annotation = ax.annotate("how2matplotlib.com", xy=(5, 1.5), xytext=(5, 2),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
annotation.set_clip_on(False)
ax.set_ylim(-1, 1)
plt.title("Annotation outside plot area")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个注释,并将其放置在图表的外部。通过设置clip_on=False,我们可以确保注释完全可见,即使它位于轴域之外。
4.2 跨越多个子图的元素
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 4))
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
ax1.plot(x, np.sin(x))
ax2.plot(x, np.cos(x))
# 创建一个跨越两个子图的文本
text = fig.text(0.5, 0.95, "how2matplotlib.com", ha='center', va='top', fontsize=16)
text.set_clip_on(False)
plt.suptitle("Text spanning multiple subplots")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何创建一个跨越多个子图的文本元素。通过将clip_on设置为False,我们可以确保文本不会被任何子图的边界裁剪。
4.3 创建自定义图例
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
ax.plot(x, np.sin(x), label="Sine")
ax.plot(x, np.cos(x), label="Cosine")
# 创建自定义图例
legend = ax.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5))
for text in legend.get_texts():
text.set_clip_on(False)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Custom legend")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个位于图表右侧的自定义图例。通过将图例中的文本元素的clip_on属性设置为False,我们可以确保它们在图例框外也能完全显示。
5. set_clip_on()与其他属性的交互
set_clip_on()方法通常与其他属性和方法结合使用,以实现更复杂的视觉效果。
5.1 与zorder属性的结合
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
background = ax.fill_between(x, 0, 1, color='lightgray')
line, = ax.plot(x, 0.5 + 0.4 * np.sin(x), 'r', linewidth=3)
line.set_clip_on(False)
line.set_zorder(10)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Combining clip_on and zorder")
plt.show()
Output:
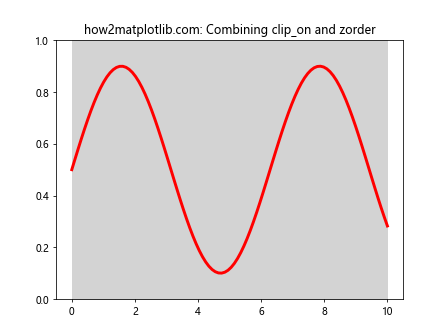
在这个例子中,我们结合使用了set_clip_on()和set_zorder()方法。通过将线条的clip_on设置为False并增加其zorder,我们可以创建一个看起来位于图表上层的线条,即使它超出了y轴的范围。
5.2 与alpha属性的结合
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
ax.fill_between(x, y1, y2, alpha=0.3)
ax.plot(x, y1, 'r', alpha=0.7)
ax.plot(x, y2, 'b', alpha=0.7)
for artist in ax.get_children():
if isinstance(artist, plt.Line2D) or isinstance(artist, plt.PolyCollection):
artist.set_clip_on(False)
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, 0.5)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Combining clip_on and alpha")
plt.show()
这个例子展示了如何结合使用set_clip_on()和alpha属性。通过将所有线条和填充区域的clip_on属性设置为False,并使用alpha来控制透明度,我们可以创建一个独特的视觉效果,即使在轴域之外也能看到部分图形元素。
6. set_clip_on()的性能考虑
虽然set_clip_on()是一个强大的工具,但在使用时也需要考虑性能问题。
6.1 大量元素时的性能
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
n = 1000
x = np.random.rand(n)
y = np.random.rand(n)
scatter = ax.scatter(x, y, s=50)
scatter.set_clip_on(False) # 对于大量点,这可能会影响性能
ax.set_xlim(0.3, 0.7)
ax.set_ylim(0.3, 0.7)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Performance with many elements")
plt.show()
Output:
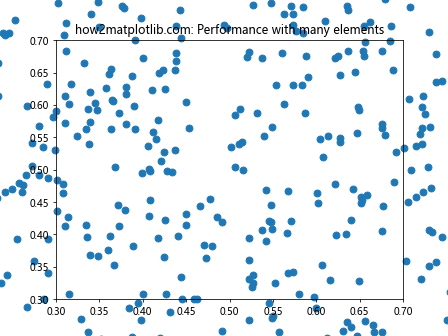
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个包含大量点的散点图。当处理大量元素时,将clip_on设置为False可能会影响渲染性能,因为Matplotlib需要绘制所有点,即使它们在可见区域之外。
6.2 动态图表中的使用
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
line, = ax.plot([], [], lw=2)
line.set_clip_on(False)
ax.set_xlim(0, 2*np.pi)
ax.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
def init():
line.set_data([], [])
return line,
def animate(i):
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x + i/10.0)
line.set_data(x, y)
return line,
anim = FuncAnimation(fig, animate, init_func=init, frames=200, interval=20, blit=True)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Animation with clip_on=False")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个动画示例中,我们创建了一个正弦波动画,并将线条的clip_on属性设置为False。这允许线条在动画过程中超出y轴的范围。然而,在复杂的动画中,禁用裁剪可能会影响性能,特别是当有大量元素需要重新绘制时。
7. set_clip_on()的常见问题和解决方案
使用set_clip_on()方法时,可能会遇到一些常见问题。以下是一些问题及其解决方案。
7.1 元素不可见
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
line, = ax.plot(x, np.sin(x))
ax.set_ylim(-0.5, 0.5)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Element visibility issue")
plt.show()
Output:
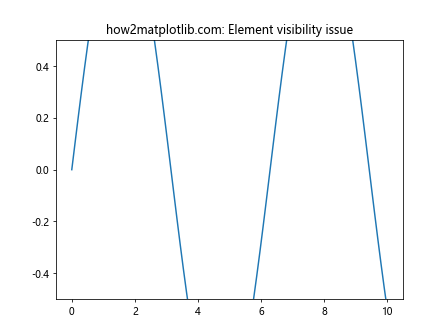
在这个例子中,由于y轴的范围限制,部分正弦波不可见。要解决这个问题,可以使用set_clip_on(False):
line.set_clip_on(False)
7.2 图例位置问题
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
ax.plot(x, np.sin(x), label="Sine")
ax.plot(x, np.cos(x), label="Cosine")
legend = ax.legend(loc='center left', bbox_to_anchor=(1, 0.5))
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Legend position issue")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,图例可能被部分裁剪。要解决这个问题,可以对图例中的文本应用set_clip_on(False):
for text in legend.get_texts():
text.set_clip_on(False)
7.3 子图重叠问题
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 4))
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
ax1.plot(x, np.sin(x))
ax2.plot(x, np.cos(x))
text = fig.text(0.5, 0.95, "how2matplotlib.com", ha='center', va='top', fontsize=16)
plt.title("Subplots overlap issue")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,添加的文本可能与子图重叠。要解决这个问题,可以使用set_clip_on(False)并调整布局:
text.set_clip_on(False)
plt.tight_layout(rect=[0, 0, 1, 0.95])
8. set_clip_on()在不同类型图表中的应用
set_clip_on()方法可以在各种类型的图表中使用,以创建独特的视觉效果。
8.1 在饼图中的应用
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
sizes = [30, 20, 25, 15, 10]
labels = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
explode = (0.1, 0, 0, 0, 0)
wedges, texts, autotexts = ax.pie(sizes, explode=explode, labels=labels, autopct='%1.1f%%',
startangle=90)
for text in texts + autotexts:
text.set_clip_on(False)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Pie chart with clip_on=False for labels")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个饼图示例中,我们将标签和百分比文本的clip_on属性设置为False,确保它们在饼图边缘也能完全显示。
8.2 在热力图中的应用
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
data = np.random.rand(10, 10)
im = ax.imshow(data, cmap='hot')
for i in range(10):
for j in range(10):
text = ax.text(j, i, f"{data[i, j]:.2f}", ha="center", va="center", color="w")
text.set_clip_on(False)
plt.colorbar(im)
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com: Heatmap with clip_on=False for text")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个热力图示例中,我们将每个单元格的数值文本的clip_on属性设置为False,确保即使文本超出单元格边界也能完全显示。
8.3 在3D图中的应用
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
y = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap='viridis')
text = ax.text(0, 0, 2, "how2matplotlib.com", fontsize=16)
text.set_clip_on(False)
plt.title("3D surface plot with clip_on=False for text")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个3D图示例中,我们将文本的clip_on属性设置为False,允许它显示在3D图的任何位置,即使超出了轴的范围。
9. set_clip_on()与其他Matplotlib功能的结合
set_clip_on()方法可以与Matplotlib的其他功能结合使用,以创建更复杂和有趣的可视化效果。
9.1 与自定义边界框结合
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
circle = patches.Circle((0.5, 0.5), 0.4, fill=False)
ax.add_patch(circle)
text = ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "how2matplotlib.com", ha='center', va='center', fontsize=12)
text.set_clip_on(False)
text.set_clip_path(circle)
ax.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
plt.title("Text clipped to circle boundary")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们结合使用了set_clip_on()和set_clip_path()方法。文本不会被轴的边界裁剪,但会被圆形路径裁剪。
9.2 与变换结合
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
line, = ax.plot(x, y)
trans = ax.get_xaxis_transform()
text = ax.text(5, 0.5, "how2matplotlib.com", transform=trans)
text.set_clip_on(False)
ax.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
plt.title("Text with custom transform and clip_on=False")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们使用自定义变换将文本放置在x轴上方,并通过set_clip_on(False)确保它不会被y轴范围裁剪。
9.3 与动画结合
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
line, = ax.plot(x, np.sin(x))
text = ax.text(np.pi, 1.5, "how2matplotlib.com", ha='center')
text.set_clip_on(False)
ax.set_ylim(-1, 1)
def update(frame):
line.set_ydata(np.sin(x + frame/10))
return line,
ani = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=100, interval=50, blit=True)
plt.title("Animation with non-clipped text")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个动画示例中,我们创建了一个移动的正弦波,同时在图表上方显示一个不被裁剪的文本。
10. 总结
Matplotlib的set_clip_on()方法是一个强大而灵活的工具,可以帮助我们创建更丰富、更有创意的数据可视化。通过控制图形元素是否被裁剪,我们可以:
- 创建超出常规绘图区域的视觉效果
- 实现跨越多个子图的元素
- 自定义图例和注释的位置
- 解决元素可见性和重叠问题
- 在各种类型的图表中创建独特的设计
然而,在使用set_clip_on()时,我们也需要注意以下几点:
- 性能影响:对大量元素禁用裁剪可能会影响渲染性能
- 布局考虑:禁用裁剪可能需要调整图表布局以避免重叠
- 可读性:确保禁用裁剪不会影响图表的整体可读性
通过深入理解和灵活运用set_clip_on()方法,我们可以在Matplotlib中创建出更加精美和富有表现力的数据可视化作品。无论是制作学术论文的插图,还是创建商业报告的图表,掌握这个方法都将为我们的可视化工作增添新的维度和可能性。
 极客教程
极客教程