Matplotlib 多图展示
在本章中,我们将学习如何在同一画布上创建多个子图。
subplot() 函数返回给定网格位置上的轴对象。该函数的调用签名为:-
plt.subplot(subplot(nrows, ncols, index)
在当前图中,该函数创建并返回一个Axes对象,该对象在一个nrows x ncols的网格中的位置索引处。索引从1到nrows * ncols,按行主序递增。如果nrows、ncols和index都小于10,则索引也可以作为单个、连接的三位数给出。
例如,subplot(2, 3, 3)和subplot(233)都在当前图的右上角创建一个Axes,占据图的高度的一半和宽度的三分之一。
创建subplot会删除与其重叠的任何现有subplot,除非它们共享边界。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# plot a line, implicitly creating a subplot(111)
plt.plot([1,2,3])
# now create a subplot which represents the top plot of a grid with 2 rows and 1 column.
#Since this subplot will overlap the first, the plot (and its axes) previously
created, will be removed
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(range(12))
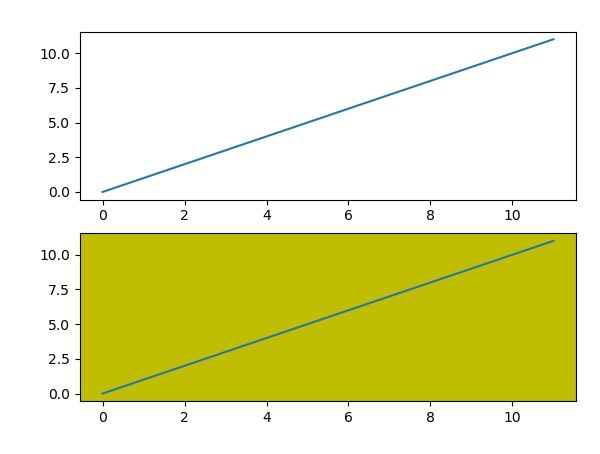
plt.subplot(212, facecolor='y') # creates 2nd subplot with yellow background
plt.plot(range(12))
以上代码生成以下输出 −
figure类的add_subplot()函数不会覆盖现有的图形-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax1.plot([1,2,3])
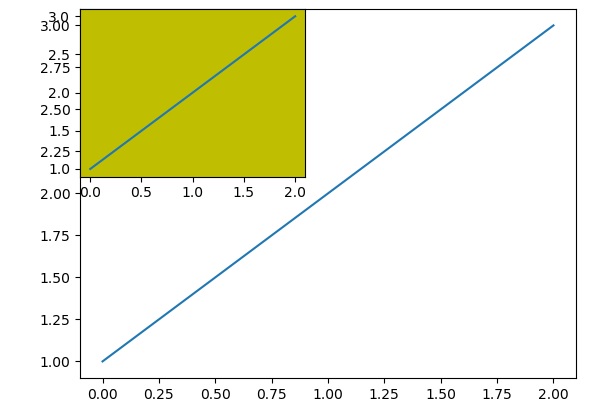
ax2 = fig.add_subplot(221, facecolor='y')
ax2.plot([1,2,3])
当上述代码行被执行时,会产生以下输出−
您可以通过在同一图形画布中添加另一个轴对象来添加插入图。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import math
x = np.arange(0, math.pi*2, 0.05)
fig=plt.figure()
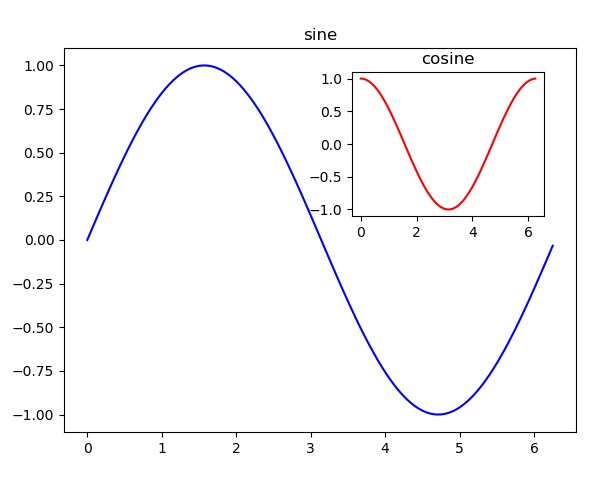
axes1 = fig.add_axes([0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8]) # main axes
axes2 = fig.add_axes([0.55, 0.55, 0.3, 0.3]) # inset axes
y = np.sin(x)
axes1.plot(x, y, 'b')
axes2.plot(x,np.cos(x),'r')
axes1.set_title('sine')
axes2.set_title("cosine")
plt.show()
在执行以上代码行时,将生成以下输出 –
 极客教程
极客教程