MATLAB中的双积分
一个非负函数f(x, y)定义在平面内某一区域上的双积分告诉我们该图形下该区域的体积。一个双变量函数f(x, y)在区域R上的双积分可以表示如下:
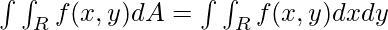
MATLAB允许用户使用integral2()方法来计算一个函数的双倍积分。integral2()方法的不同语法是:。
- F = integral2(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax)
- F = integral2(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax,Name,Value)
语法:
integral2(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax)
这个函数近似于任何函数f = fun(x,y)在xmin≤x≤xmax和ymin(x)≤y≤ymax(x)区域的积分。
示例 1:
% MATLAB Code to
% Create a function in x and y
% Function : y*sin(x) + x*cos(y)
f = @(x,y) y.*sin(x)+x.*cos(y);
disp("f(x,y) :");
disp(f);
% Double Integral of f(x)
% over pi≤x≤2*pi and 0≤y≤pi
d = integral2(f,pi,2*pi,0,pi);
disp("Double Integral of f(x) :");
disp(d);
输出 :

示例 2:
% MATLAB Code to
% Create a function in x and y
% Function : y*sin(x) + x*cos(y)
f = @(x,y) y.*sin(x)+x.*cos(y);
disp("f(x,y) :");
disp(f);
% Double Integral of f(x)
% over pi≤x≤2*pi and 0≤y≤x
ymax = @(x) x;
d = integral2(f,pi,2*pi,0,ymax);
disp("Double Integral of f(x) :");
disp(d);
输出 :

语法:
F = integral2(fun,xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax,Name,Value)
它用一个或多个Name, Value对参数来指定额外的选项。最常用的名称是 “方法”。
可能的值是。
- tiled。积分的界限必须是有限的,这个方法才能发挥作用。如果需要,它在将积分区转化为矩形后,将其细分为更简单的矩形区域。
- iterated。在这种方法中,采用的是迭代积分。它是指当函数由一个以上的变量组成时,对以前的积分结果进行反复积分的过程。在函数中。在这种方法中,积分极限可以是无限的。
- auto。auto “方法被作为默认值使用。它根据选择的极限值选择平铺或迭代。如果限制是无限的,那么它就选择 “迭代”,否则就使用 “平铺 “方法进行计算。
示例 3:
% MATLAB Code to
% Create a function in x and y
% Function : y*sin(x) + x*cos(y)
f = @(x,y) y.*sin(x)+x.*cos(y);
disp("f(x,y) :");
disp(f);
% Double Integral of f(x) using Tiled Method
% over pi≤x≤2*pi and 0≤y≤pi
d = integral2(f,pi,2*pi,0,pi,'Method','Tiled');
disp("Double Integral of f(x) :");
disp(d);
输出 :

示例 4:
% MATLAB code for iterated
% Create a function in x and y
% Function : x*y*e^-(x+y)
f = @(x,y) y.*x.*exp(-(x+y))
disp("f(x,y) :");
disp(f);
% Double Integral of f(x) using Iterated method
% over 0≤x≤Inf and 0≤y≤Inf
d = integral2(f,0,Inf,0,Inf,'Method','Iterated');
disp("Double Integral of f(x) :");
disp(d);
输出:

 极客教程
极客教程