WebRTC 文本演示
在这一章节中,我们将构建一个客户端应用程序,允许两个使用WebRTC的独立设备上的用户彼此发送消息。我们的应用程序将有两个页面。一个页面用于登录,另一个页面用于向另一个用户发送消息。
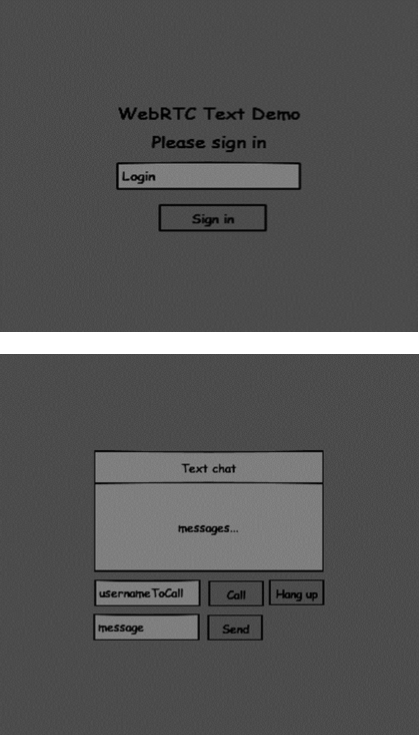
这两个页面将使用div标签。大部分输入是通过简单的事件处理程序完成的。
信令服务器
为了创建一个WebRTC连接,客户端必须能够在不使用WebRTC对等连接的情况下传输消息。这就是我们将使用HTML5 WebSockets的地方——一个双向的套接字连接,连接两个端点——一个Web服务器和一个Web浏览器。现在让我们开始使用WebSocket库。创建server.js文件并插入以下代码 –
//require our websocket library
var WebSocketServer = require('ws').Server;
//creating a websocket server at port 9090
var wss = new WebSocketServer({port: 9090});
//when a user connects to our sever
wss.on('connection', function(connection) {
console.log("user connected");
//when server gets a message from a connected user
connection.on('message', function(message) {
console.log("Got message from a user:", message);
});
connection.send("Hello from server");
});
第一行需要 WebSocket 库,我们已经安装好了。然后我们在端口号为 9090 的地方创建了一个 socket 服务器。接下来,我们监听连接事件。当用户通过 WebSocket 连接到服务器时,这段代码将被执行。然后我们监听用户发送的任何消息。最后,我们向已连接的用户发送一条回应,内容是“Hello from server”。
在我们的信令服务器中,每个连接都将使用基于字符串的用户名,以便我们知道将消息发送到何处。让我们稍微改变一下连接处理程序 –
connection.on('message', function(message) {
var data;
//accepting only JSON messages
try {
data = JSON.parse(message);
} catch (e) {
console.log("Invalid JSON");
data = {};
}
});
这样我们只接受 JSON 消息。接下来,我们需要将所有连接的用户存放在某个地方。我们将使用一个简单的 JavaScript 对象来实现。更改我们文件的顶部 –
//require our websocket library
var WebSocketServer = require('ws').Server;
//creating a websocket server at port 9090
var wss = new WebSocketServer({port: 9090});
//all connected to the server users
var users = {};
我们将为来自客户端的每个消息添加一个type字段。例如,如果用户想要登录,他会发送一个login类型的消息。让我们来定义一下 –
connection.on('message', function(message) {
var data;
//accepting only JSON messages
try {
data = JSON.parse(message);
} catch (e) {
console.log("Invalid JSON");
data = {};
}
//switching type of the user message
switch (data.type) {
//when a user tries to login
case "login":
console.log("User logged:", data.name);
//if anyone is logged in with this username then refuse
if(users[data.name]) {
sendTo(connection, {
type: "login",
success: false
});
} else {
//save user connection on the server
users[data.name] = connection;
connection.name = data.name;
sendTo(connection, {
type: "login",
success: true
});
}
break;
default:
sendTo(connection, {
type: "error",
message: "Command no found: " + data.type
});
break;
}
});
如果用户发送一条登录类型的消息,我们 −
- 检查是否有其他用户已经使用过这个用户名登录。
- 如果是这样,告诉用户他没有成功登录。
- 如果没有人使用这个用户名,我们将用户名添加为连接对象的一个键。
- 如果一条命令不能被识别,我们发送一个错误。
以下代码是一个帮助函数,用于向连接发送消息。将其添加到 server.js 文件中 −
function sendTo(connection, message) {
connection.send(JSON.stringify(message));
}
当用户断开连接时,我们应该清理其连接。当触发关闭事件时,我们可以删除用户。将以下代码添加到连接处理程序中:
connection.on("close", function() {
if(connection.name) {
delete users[connection.name];
}
});
成功登录后,用户想要呼叫另一个用户。他应该向另一个用户发出一个提议来实现这个目标。添加 提议 处理程序−
case "offer":
//for ex. UserA wants to call UserB
console.log("Sending offer to: ", data.name);
//if UserB exists then send him offer details
var conn = users[data.name];
if(conn != null){
//setting that UserA connected with UserB
connection.otherName = data.name;
sendTo(conn, {
type: "offer",
offer: data.offer,
name: connection.name
});
break;
首先,我们获取我们要拨打电话的用户的连接。如果它存在,我们向他发送报价的详细信息。我们还将 otherName 添加到连接对象中。这是为了以后能够简单地找到它。 回应该响应的方式与我们在报价处理程序中使用的模式类似。我们的服务器只是将所有消息作为答案传递给另一个用户。在 报价处理程序之后添加以下代码-
case "answer":
console.log("Sending answer to: ", data.name);
//for ex. UserB answers UserA
var conn = users[data.name];
if(conn != null) {
connection.otherName = data.name;
sendTo(conn, {
type: "answer",
answer: data.answer
});
}
break;
最后一部分是处理用户之间的 ICE candidate。我们使用相同的技术,只是在用户之间传递消息。主要的区别是每个用户可能会多次以任何顺序发送候选者消息。添加候选者处理程序 −
case "candidate":
console.log("Sending candidate to:",data.name);
var conn = users[data.name];
if(conn != null) {
sendTo(conn, {
type: "candidate",
candidate: data.candidate
});
}
break;
为了让我们的用户能够与另一个用户断开连接,我们应该实现挂断功能。它还将通知服务器删除所有用户引用。添加 离开 处理程序 −
case "leave":
console.log("Disconnecting from", data.name);
var conn = users[data.name];
conn.otherName = null;
//notify the other user so he can disconnect his peer connection
if(conn != null) {
sendTo(conn, {
type: "leave"
});
}
break;
这也会向其他用户发送离开事件,以便他可以相应地断开他的对等连接。我们还应该处理当用户从信令服务器断开连接的情况。让我们修改我们的关闭处理程序:
connection.on("close", function() {
if(connection.name) {
delete users[connection.name];
if(connection.otherName) {
console.log("Disconnecting from ", connection.otherName);
var conn = users[connection.otherName];
conn.otherName = null;
if(conn != null) {
sendTo(conn, {
type: "leave"
});
}
}
}
});
以下是我们的信令服务器的全部代码:
//require our websocket library
var WebSocketServer = require('ws').Server;
//creating a websocket server at port 9090
var wss = new WebSocketServer({port: 9090});
//all connected to the server users
var users = {};
//when a user connects to our sever
wss.on('connection', function(connection) {
console.log("User connected");
//when server gets a message from a connected user
connection.on('message', function(message) {
var data;
//accepting only JSON messages
try {
data = JSON.parse(message);
} catch (e) {
console.log("Invalid JSON");
data = {};
}
//switching type of the user message
switch (data.type) {
//when a user tries to login
case "login":
console.log("User logged", data.name);
//if anyone is logged in with this username then refuse
if(users[data.name]) {
sendTo(connection, {
type: "login",
success: false
});
} else {
//save user connection on the server
users[data.name] = connection;
connection.name = data.name;
sendTo(connection, {
type: "login",
success: true
});
}
break;
case "offer":
//for ex. UserA wants to call UserB
console.log("Sending offer to: ", data.name);
//if UserB exists then send him offer details
var conn = users[data.name];
if(conn != null) {
//setting that UserA connected with UserB
connection.otherName = data.name;
sendTo(conn, {
type: "offer",
offer: data.offer,
name: connection.name
});
}
break;
case "answer":
console.log("Sending answer to: ", data.name);
//for ex. UserB answers UserA
var conn = users[data.name];
if(conn != null) {
connection.otherName = data.name;
sendTo(conn, {
type: "answer",
answer: data.answer
});
}
break;
case "candidate":
console.log("Sending candidate to:",data.name);
var conn = users[data.name];
if(conn != null) {
sendTo(conn, {
type: "candidate",
candidate: data.candidate
});
}
break;
case "leave":
console.log("Disconnecting from", data.name);
var conn = users[data.name];
conn.otherName = null;
//notify the other user so he can disconnect his peer connection
if(conn != null) {
sendTo(conn, {
type: "leave"
});
}
break;
default:
sendTo(connection, {
type: "error",
message: "Command not found: " + data.type
});
break;
}
});
//when user exits, for example closes a browser window
//this may help if we are still in "offer","answer" or "candidate" state
connection.on("close", function() {
if(connection.name) {
delete users[connection.name];
if(connection.otherName) {
console.log("Disconnecting from ", connection.otherName);
var conn = users[connection.otherName];
conn.otherName = null;
if(conn != null) {
sendTo(conn, {
type: "leave"
});
}
}
}
});
connection.send("Hello world");
});
function sendTo(connection, message) {
connection.send(JSON.stringify(message));
}
客户端应用程序
测试此应用程序的一种方法是打开两个浏览器选项卡,并尝试相互发送消息。
首先,我们需要安装bootstrap库。Bootstrap是用于开发Web应用程序的前端框架。您可以在http://getbootstrap.com/了解更多信息。 创建一个名为“textchat”的文件夹。这将是我们的根应用程序文件夹。在此文件夹中创建一个名为package.json的文件(用于管理npm依赖项),并添加以下内容-
{
"name": "webrtc-textochat",
"version": "0.1.0",
"description": "webrtc-textchat",
"author": "Author",
"license": "BSD-2-Clause"
}
然后运行 npm install bootstrap 。这将在 textchat/node_modules 文件夹中安装bootstrap库。
现在我们需要创建一个基本的HTML页面。在根文件夹中创建一个 index.html 文件,并添加以下代码−
<html>
<head>
<title>WebRTC Text Demo</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "node_modules/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"/>
</head>
<style>
body {
background: #eee;
padding: 5% 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<div id = "loginPage" class = "container text-center">
<div class = "row">
<div class = "col-md-4 col-md-offset-4">
<h2>WebRTC Text Demo. Please sign in</h2>
<label for = "usernameInput" class = "sr-only">Login</label>
<input type = "email" id = "usernameInput"
class = "form-control formgroup" placeholder = "Login"
required = "" autofocus = "">
<button id = "loginBtn" class = "btn btn-lg btn-primary btnblock">
Sign in</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div id = "callPage" class = "call-page container">
<div class = "row">
<div class = "col-md-4 col-md-offset-4 text-center">
<div class = "panel panel-primary">
<div class = "panel-heading">Text chat</div>
<div id = "chatarea" class = "panel-body text-left"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class = "row text-center form-group">
<div class = "col-md-12">
<input id = "callToUsernameInput" type = "text"
placeholder = "username to call" />
<button id = "callBtn" class = "btn-success btn">Call</button>
<button id = "hangUpBtn" class = "btn-danger btn">Hang Up</button>
</div>
</div>
<div class = "row text-center">
<div class = "col-md-12">
<input id = "msgInput" type = "text" placeholder = "message" />
<button id = "sendMsgBtn" class = "btn-success btn">Send</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src = "client.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
这个页面对你应该很熟悉。我们添加了 bootstrap 的 css 文件。我们还定义了两个页面。最后,我们创建了几个文本字段和按钮,用于从用户那里获取信息。在“chat”页面上,您应该看到带有“chatarea” ID 的 div 标签,其中将显示所有我们的消息。请注意,我们添加了一个指向 client.js 文件的链接。
现在我们需要与我们的信令服务器建立连接。在根目录下创建 client.js 文件,代码如下:
//our username
var name;
var connectedUser;
//connecting to our signaling server
var conn = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:9090');
conn.onopen = function () {
console.log("Connected to the signaling server");
};
//when we got a message from a signaling server
conn.onmessage = function (msg) {
console.log("Got message", msg.data);
var data = JSON.parse(msg.data);
switch(data.type) {
case "login":
handleLogin(data.success);
break;
//when somebody wants to call us
case "offer":
handleOffer(data.offer, data.name);
break;
case "answer":
handleAnswer(data.answer);
break;
//when a remote peer sends an ice candidate to us
case "candidate":
handleCandidate(data.candidate);
break;
case "leave":
handleLeave();
break;
default:
break;
}
};
conn.onerror = function (err) {
console.log("Got error", err);
};
//alias for sending JSON encoded messages
function send(message) {
//attach the other peer username to our messages
if (connectedUser) {
message.name = connectedUser;
}
conn.send(JSON.stringify(message));
};
现在通过 node server 运行我们的信令服务器。然后,在根文件夹中运行 static 命令,并在浏览器中打开页面。您应该会看到以下控制台输出:
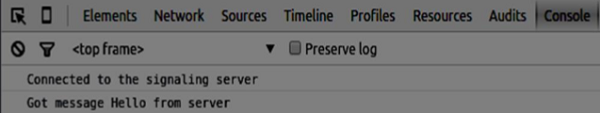
下一步是使用唯一用户名实现用户登录。我们只需要将用户名发送到服务器,然后服务器会告诉我们这个用户名是否已被使用。将以下代码添加到你的 client.js 文件中 −
//******
//UI selectors block
//******
var loginPage = document.querySelector('#loginPage');
var usernameInput = document.querySelector('#usernameInput');
var loginBtn = document.querySelector('#loginBtn');
var callPage = document.querySelector('#callPage');
var callToUsernameInput = document.querySelector('#callToUsernameInput');
var callBtn = document.querySelector('#callBtn');
var hangUpBtn = document.querySelector('#hangUpBtn');
callPage.style.display = "none";
// Login when the user clicks the button
loginBtn.addEventListener("click", function (event) {
name = usernameInput.value;
if (name.length > 0) {
send({
type: "login",
name: name
});
}
});
function handleLogin(success) {
if (success === false) {
alert("Ooops...try a different username");
} else {
loginPage.style.display = "none";
callPage.style.display = "block";
//**********************
//Starting a peer connection
//**********************
}
};
首先,我们选择一些页面元素的参考。然后,我们隐藏呼叫页面。然后,在登录按钮上添加一个事件监听器。当用户点击它时,我们将他的用户名发送到服务器。最后,我们实现handleLogin回调函数。如果登录成功,我们显示呼叫页面,建立一个对等连接,并创建一个数据通道。 为了通过数据通道启动对等连接,我们需要: - 创建RTCPeerConnection对象 - 在我们的RTCPeerConnection对象中创建一个数据通道 将以下代码添加到“UI选择器块”中:
var msgInput = document.querySelector('#msgInput');
var sendMsgBtn = document.querySelector('#sendMsgBtn');
var chatArea = document.querySelector('#chatarea');
var yourConn;
var dataChannel;
修改 handleLogin 函数−
function handleLogin(success) {
if (success === false) {
alert("Ooops...try a different username");
} else {
loginPage.style.display = "none";
callPage.style.display = "block";
//**********************
//Starting a peer connection
//**********************
//using Google public stun server
var configuration = {
"iceServers": [{ "url": "stun:stun2.1.google.com:19302" }]
};
yourConn = new webkitRTCPeerConnection(configuration, {optional: [{RtpDataChannels: true}]});
// Setup ice handling
yourConn.onicecandidate = function (event) {
if (event.candidate) {
send({
type: "candidate",
candidate: event.candidate
});
}
};
//creating data channel
dataChannel = yourConn.createDataChannel("channel1", {reliable:true});
dataChannel.onerror = function (error) {
console.log("Ooops...error:", error);
};
//when we receive a message from the other peer, display it on the screen
dataChannel.onmessage = function (event) {
chatArea.innerHTML += connectedUser + ": " + event.data + "<br />";
};
dataChannel.onclose = function () {
console.log("data channel is closed");
};
}
};
如果登录成功,应用程序将创建RTCPeerConnection对象并设置onicecandidate处理程序,该处理程序将所有找到的icecandidates发送给其他对等方。它还创建一个dataChannel。注意,当创建RTCPeerConnection对象时,构造函数中的第二个参数[{RtpDataChannels: true}]是可选的,但如果您使用的是Chrome或Opera浏览器,则是强制性的。下一步是向其他对等方创建一个offer。一旦用户收到offer,他就会创建一个answer并开始交换ICE candidates。将以下代码添加到client.js文件中:
如果登录成功,应用程序将创建RTCPeerConnection对象并设置onicecandidate处理程序,该处理程序将所有找到的icecandidates发送给其他对等方。它还创建一个dataChannel。注意,当创建RTCPeerConnection对象时,构造函数中的第二个参数[{RtpDataChannels: true}]是可选的,但如果您使用的是Chrome或Opera浏览器,则是强制性的。下一步是向其他对等方创建一个offer。一旦用户收到offer,他就会创建一个answer并开始交换ICE candidates。将以下代码添加到client.js文件中−
//initiating a call
callBtn.addEventListener("click", function () {
var callToUsername = callToUsernameInput.value;
if (callToUsername.length > 0) {
connectedUser = callToUsername;
// create an offer
yourConn.createOffer(function (offer) {
send({
type: "offer",
offer: offer
});
yourConn.setLocalDescription(offer);
}, function (error) {
alert("Error when creating an offer");
});
}
});
//when somebody sends us an offer
function handleOffer(offer, name) {
connectedUser = name;
yourConn.setRemoteDescription(new RTCSessionDescription(offer));
//create an answer to an offer
yourConn.createAnswer(function (answer) {
yourConn.setLocalDescription(answer);
send({
type: "answer",
answer: answer
});
}, function (error) {
alert("Error when creating an answer");
});
};
//when we got an answer from a remote user
function handleAnswer(answer) {
yourConn.setRemoteDescription(new RTCSessionDescription(answer));
};
//when we got an ice candidate from a remote user
function handleCandidate(candidate) {
yourConn.addIceCandidate(new RTCIceCandidate(candidate));
};
我们向Call按钮添加了一个点击事件处理程序,它会发起一个请求。然后我们实现了一些onmessage处理程序所需要的其他处理程序。它们会被异步处理,直到两个用户都建立了连接。
下一步是实现挂断功能。这将停止传输数据,并告诉另一个用户关闭数据通道。添加以下代码−
//hang up
hangUpBtn.addEventListener("click", function () {
send({
type: "leave"
});
handleLeave();
});
function handleLeave() {
connectedUser = null;
yourConn.close();
yourConn.onicecandidate = null;
};
当用户点击挂断按钮 –
- 将向对方发送一个“离开”消息。
- 它会关闭RTCPeerConnection和数据通道。
最后一步是向另一个对等方发送一条消息。将“点击”事件处理程序添加到“发送消息”按钮中 –
//when user clicks the "send message" button
sendMsgBtn.addEventListener("click", function (event) {
var val = msgInput.value;
chatArea.innerHTML += name + ": " + val + "<br />";
//sending a message to a connected peer
dataChannel.send(val);
msgInput.value = "";
});
现在运行代码。您应该能够使用两个浏览器标签登录到服务器。然后,您可以与其他用户建立对等连接,并给他发送消息,同时通过点击“挂断”按钮关闭数据通道。
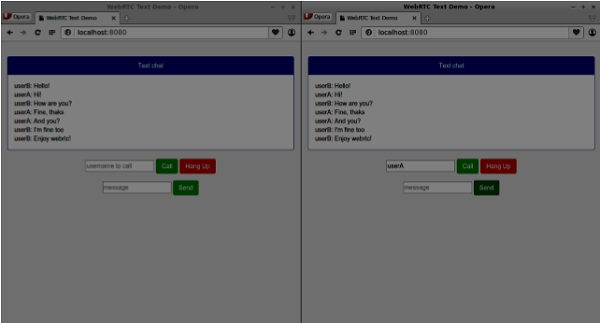
//our username
var name;
var connectedUser;
//connecting to our signaling server
var conn = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:9090');
conn.onopen = function () {
console.log("Connected to the signaling server");
};
//when we got a message from a signaling server
conn.onmessage = function (msg) {
console.log("Got message", msg.data);
var data = JSON.parse(msg.data);
switch(data.type) {
case "login":
handleLogin(data.success);
break;
//when somebody wants to call us
case "offer":
handleOffer(data.offer, data.name);
break;
case "answer":
handleAnswer(data.answer);
break;
//when a remote peer sends an ice candidate to us
case "candidate":
handleCandidate(data.candidate);
break;
case "leave":
handleLeave();
break;
default:
break;
}
};
conn.onerror = function (err) {
console.log("Got error", err);
};
//alias for sending JSON encoded messages
function send(message) {
//attach the other peer username to our messages
if (connectedUser) {
message.name = connectedUser;
}
conn.send(JSON.stringify(message));
};
//******
//UI selectors block
//******
var loginPage = document.querySelector('#loginPage');
var usernameInput = document.querySelector('#usernameInput');
var loginBtn = document.querySelector('#loginBtn');
var callPage = document.querySelector('#callPage');
var callToUsernameInput = document.querySelector('#callToUsernameInput');
var callBtn = document.querySelector('#callBtn');
var hangUpBtn = document.querySelector('#hangUpBtn');
var msgInput = document.querySelector('#msgInput');
var sendMsgBtn = document.querySelector('#sendMsgBtn');
var chatArea = document.querySelector('#chatarea');
var yourConn;
var dataChannel;
callPage.style.display = "none";
// Login when the user clicks the button
loginBtn.addEventListener("click", function (event) {
name = usernameInput.value;
if (name.length > 0) {
send({
type: "login",
name: name
});
}
});
function handleLogin(success) {
if (success === false) {
alert("Ooops...try a different username");
} else {
loginPage.style.display = "none";
callPage.style.display = "block";
//**********************
//Starting a peer connection
//**********************
//using Google public stun server
var configuration = {
"iceServers": [{ "url": "stun:stun2.1.google.com:19302" }]
};
yourConn = new webkitRTCPeerConnection(configuration, {optional: [{RtpDataChannels: true}]});
// Setup ice handling
yourConn.onicecandidate = function (event) {
if (event.candidate) {
send({
type: "candidate",
candidate: event.candidate
});
}
};
//creating data channel
dataChannel = yourConn.createDataChannel("channel1", {reliable:true});
dataChannel.onerror = function (error) {
console.log("Ooops...error:", error);
};
//when we receive a message from the other peer, display it on the screen
dataChannel.onmessage = function (event) {
chatArea.innerHTML += connectedUser + ": " + event.data + "<br />";
};
dataChannel.onclose = function () {
console.log("data channel is closed");
};
}
};
//initiating a call
callBtn.addEventListener("click", function () {
var callToUsername = callToUsernameInput.value;
if (callToUsername.length > 0) {
connectedUser = callToUsername;
// create an offer
yourConn.createOffer(function (offer) {
send({
type: "offer",
offer: offer
});
yourConn.setLocalDescription(offer);
}, function (error) {
alert("Error when creating an offer");
});
}
});
//when somebody sends us an offer
function handleOffer(offer, name) {
connectedUser = name;
yourConn.setRemoteDescription(new RTCSessionDescription(offer));
//create an answer to an offer
yourConn.createAnswer(function (answer) {
yourConn.setLocalDescription(answer);
send({
type: "answer",
answer: answer
});
}, function (error) {
alert("Error when creating an answer");
});
};
//when we got an answer from a remote user
function handleAnswer(answer) {
yourConn.setRemoteDescription(new RTCSessionDescription(answer));
};
//when we got an ice candidate from a remote user
function handleCandidate(candidate) {
yourConn.addIceCandidate(new RTCIceCandidate(candidate));
};
//hang up
hangUpBtn.addEventListener("click", function () {
send({
type: "leave"
});
handleLeave();
});
function handleLeave() {
connectedUser = null;
yourConn.close();
yourConn.onicecandidate = null;
};
//when user clicks the "send message" button
sendMsgBtn.addEventListener("click", function (event) {
var val = msgInput.value;
chatArea.innerHTML += name + ": " + val + "<br />";
//sending a message to a connected peer
dataChannel.send(val);
msgInput.value = "";
});
 极客教程
极客教程