R语言 非线性最小二乘法
在对回归分析的真实世界数据建模时,我们观察到模型的方程很少是一个线性方程从而给出一个线性图形的情况。大多数情况下,真实世界数据模型的方程涉及到更高次数的数学函数,例如3次方程或正弦函数。在这种情况下,模型的图形呈曲线而不是直线。线性回归和非线性回归的目标都是调整模型参数的值,找到最接近数据的直线或曲线。通过找到这些值,我们将能够具有很高的准确度估算响应变量。
在最小二乘回归中,我们建立一个回归模型,其中不同点到回归曲线的垂直距离的平方和最小化。通常我们从一个定义好的模型开始,假设系数的一些值。然后我们使用R的 nls() 函数获得更准确的值以及置信区间。
语法
在R中创建非线性最小二乘法测试的基本语法为−
nls(formula, data, start)
以下是使用的参数的描述 –
- formula 是一个包含变量和参数的非线性模型公式。
-
data 是用于评估公式中的变量的数据框。
-
start 是一个具有起始估计值的命名列表或命名数值向量。
示例
我们将考虑一个非线性模型,并假设其系数的初始值。 接下来,我们将看到这些假设值的置信区间,以便我们可以判断这些值在模型中的拟合程度。
因此,让我们考虑以下方程:
a = b1*x^2+b2
假设初始系数为1和3,并将这些值拟合到nls()函数中。
xvalues <- c(1.6,2.1,2,2.23,3.71,3.25,3.4,3.86,1.19,2.21)
yvalues <- c(5.19,7.43,6.94,8.11,18.75,14.88,16.06,19.12,3.21,7.58)
# Give the chart file a name.
png(file = "nls.png")
# Plot these values.
plot(xvalues,yvalues)
# Take the assumed values and fit into the model.
model <- nls(yvalues ~ b1*xvalues^2+b2,start = list(b1 = 1,b2 = 3))
# Plot the chart with new data by fitting it to a prediction from 100 data points.
new.data <- data.frame(xvalues = seq(min(xvalues),max(xvalues),len = 100))
lines(new.data$xvalues,predict(model,newdata = new.data))
# Save the file.
dev.off()
# Get the sum of the squared residuals.
print(sum(resid(model)^2))
# Get the confidence intervals on the chosen values of the coefficients.
print(confint(model))
当我们执行上面的代码时,它会产生以下结果 –
[1] 1.081935
Waiting for profiling to be done...
2.5% 97.5%
b1 1.137708 1.253135
b2 1.497364 2.496484
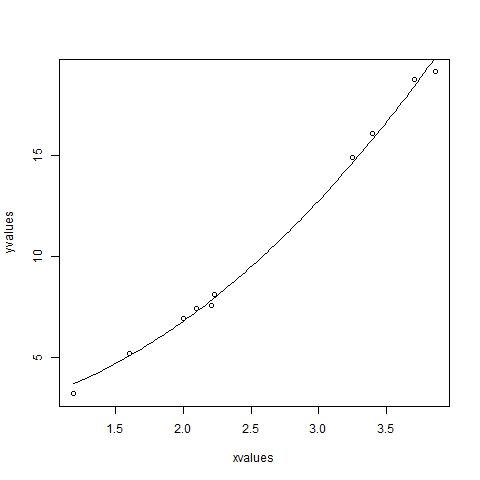
 极客教程
极客教程