如何用Python创建一个使用对数刻度的均匀间隔的数字列表
在这篇文章中,我们将使用对数尺度创建一个均匀间隔的数字列表。这意味着在对数尺度上,两个相邻的样本之间的差异是相同的。这个目标可以通过Python Numpy库中的两个不同的函数来实现。
使用到的函数:
- numpy.logspace。该函数返回以对数尺度均匀缩放的数字。
参数:
- start:序列的起始值是basestart
- stop: 如果端点是True,那么序列的结束值就是basestop。
- num(可选):指定要生成的样本数
- endpoint (可选):它可以是真或假,默认值为真
- base(可选):指定日志序列的基数。默认值是10。
- dtype(可选):指定输出阵列的类型
- axis(可选):结果中用于存储样本的轴。
返回:它返回在对数尺度上等距的样本阵列。
- numpy.geomspace。这个函数类似于logspace函数,唯一的区别是可以直接指定端点。在输出样本中,每个输出都是通过将之前的输出乘以相同的常数而得到的。
参数:
start:它是序列的起始值
stop: 如果endpoint是True,那么它就是序列的结束值。
num(可选):指定要生成的样本数
endpoint(可选):它可以是真或假,默认值为真
dtype(可选):指定输出阵列的类型
axis(可选):结果中用来存储样本的轴。
返回:它返回在对数尺度上等距的样本阵列。
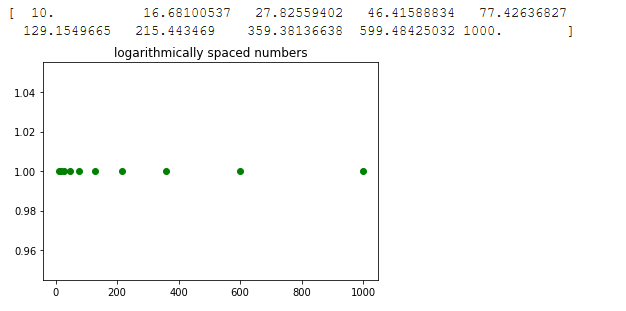
例子1:这个例子使用了logspace函数。在这个例子中,开始是1,停止是3,基数是10。所以序列的起点将是10**1=10,序列的终点将是10**3=1000。
# importing the library
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Initializing variable
y = np.ones(10)
# Calculating result
res = np.logspace(1, 3, 10, endpoint = True)
# Printing the result
print(res)
# Plotting the graph
plt.scatter(res, y, color = 'green')
plt.title('logarithmically spaced numbers')
plt.show()
输出:
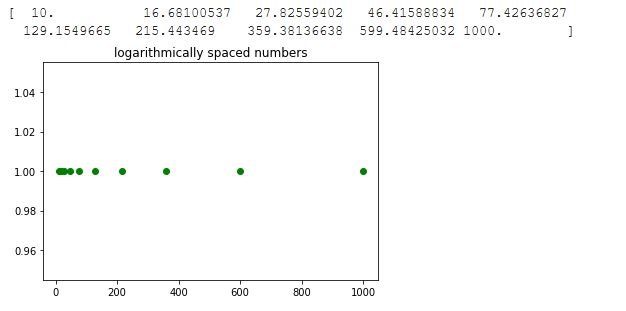
实例2:本例使用geomspace函数生成与上例相同的列表。这里我们直接传递10和1000作为起点和终点
# importing the library
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Initializing variable
y = np.ones(10)
# Calculating result
res = np.geomspace(10, 1000, 10, endpoint = True)
# Printing the result
print(res)
# Plotting the graph
plt.scatter(res, y, color = 'green')
plt.title('logarithmically spaced numbers')
plt.show()
输出:
例子3:在这个例子中,端点被设置为false,所以它将产生n+1个样本,只返回前n个样本,即停止不会被包括在序列中。
# importing the library
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Initializing variable
y = np.ones(10)
# Calculating result
res = np.logspace(1, 3, 10, endpoint = False)
# Printing the result
print(res)
输出:
[ 10. 15.84893192 25.11886432 39.81071706 63.09573445
100. 158.48931925 251.18864315 398.10717055 630.95734448]
 极客教程
极客教程