使用django的Python表单验证
Django是以MVT模式工作的。所以有必要创建数据模型(或表)。对于每个表,都要创建一个模型类。
假设有一个表单,将用户名、性别和文本作为用户的输入,任务是验证数据并保存。
在django中可以这样做,如下所示。
from django.db import models
# model named Post
class Post(models.Model):
Male = 'M'
FeMale = 'F'
GENDER_CHOICES = (
(Male, 'Male'),
(FeMale, 'Female'),
)
# define a username filed with bound max length it can have
username = models.CharField( max_length = 20, blank = False,
null = False)
# This is used to write a post
text = models.TextField(blank = False, null = False)
# Values for gender are restricted by giving choices
gender = models.CharField(max_length = 6, choices = GENDER_CHOICES,
default = Male)
time = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add = True)
在创建数据模型后,需要在数据库中反映这些变化,为此运行以下命令。
python manage.py makemigrations
这样做是为了编译模型,如果没有发现任何错误,就会在迁移文件夹中创建一个文件。随后运行下面的命令,最终将保存在迁移文件中的变化反映到数据库中。
python manage.py migrate
现在可以创建一个表单了。假设用户名长度不应小于5,帖子长度应大于10。然后,我们定义类PostForm,其需要的验证规则如下。
from django.forms import ModelForm
from django import forms
from formValidationApp.models import *
# define the class of a form
class PostForm(ModelForm):
class Meta:
# write the name of models for which the form is made
model = Post
# Custom fields
fields =["username", "gender", "text"]
# this function will be used for the validation
def clean(self):
# data from the form is fetched using super function
super(PostForm, self).clean()
# extract the username and text field from the data
username = self.cleaned_data.get('username')
text = self.cleaned_data.get('text')
# conditions to be met for the username length
if len(username) < 5:
self._errors['username'] = self.error_class([
'Minimum 5 characters required'])
if len(text) <10:
self._errors['text'] = self.error_class([
'Post Should Contain a minimum of 10 characters'])
# return any errors if found
return self.cleaned_data
到现在为止,数据模型和表单类已经被定义。现在,重点将放在如何实际使用上面定义的这些模块。
首先,通过这个命令在localhost上运行
python manage.py runserver
在浏览器中打开http://localhost:8000/,然后它将在urls.py文件中搜索,寻找”路径
urls.py文件如下所示。
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.home, name ='index'),
]
基本上,这将”网址与一个定义在views.py文件中的函数_home _联系起来。
views.py文件 。
from .models import Post
from .forms import PostForm
from .import views
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse, render, redirect
def home(request):
# check if the request is post
if request.method =='POST':
# Pass the form data to the form class
details = PostForm(request.POST)
# In the 'form' class the clean function
# is defined, if all the data is correct
# as per the clean function, it returns true
if details.is_valid():
# Temporarily make an object to be add some
# logic into the data if there is such a need
# before writing to the database
post = details.save(commit = False)
# Finally write the changes into database
post.save()
# redirect it to some another page indicating data
# was inserted successfully
return HttpResponse("data submitted successfully")
else:
# Redirect back to the same page if the data
# was invalid
return render(request, "home.html", {'form':details})
else:
# If the request is a GET request then,
# create an empty form object and
# render it into the page
form = PostForm(None)
return render(request, 'home.html', {'form':form})
home.html模板文件
{% load bootstrap3 %}
{% bootstrap_messages %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head >
<title>Basic Form</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js">
</script>
<script src="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body style="padding-top: 60px;background-color: #f5f7f8 !important;">
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4 col-md-offset-4">
<h2>Form</h2>
<form action="" method="post"><input type='hidden'/>
{%csrf_token %}
{% bootstrap_form form %}
<!-This is the form variable which we are passing from the function
of home in views.py file. That's the beauty of Django we
don't need to write much codes in this it'll automatically pass
all the form details in here
->
<div class="form-group">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-default ">
Submit
</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
在浏览器中打开http://localhost:8000/,显示如下。
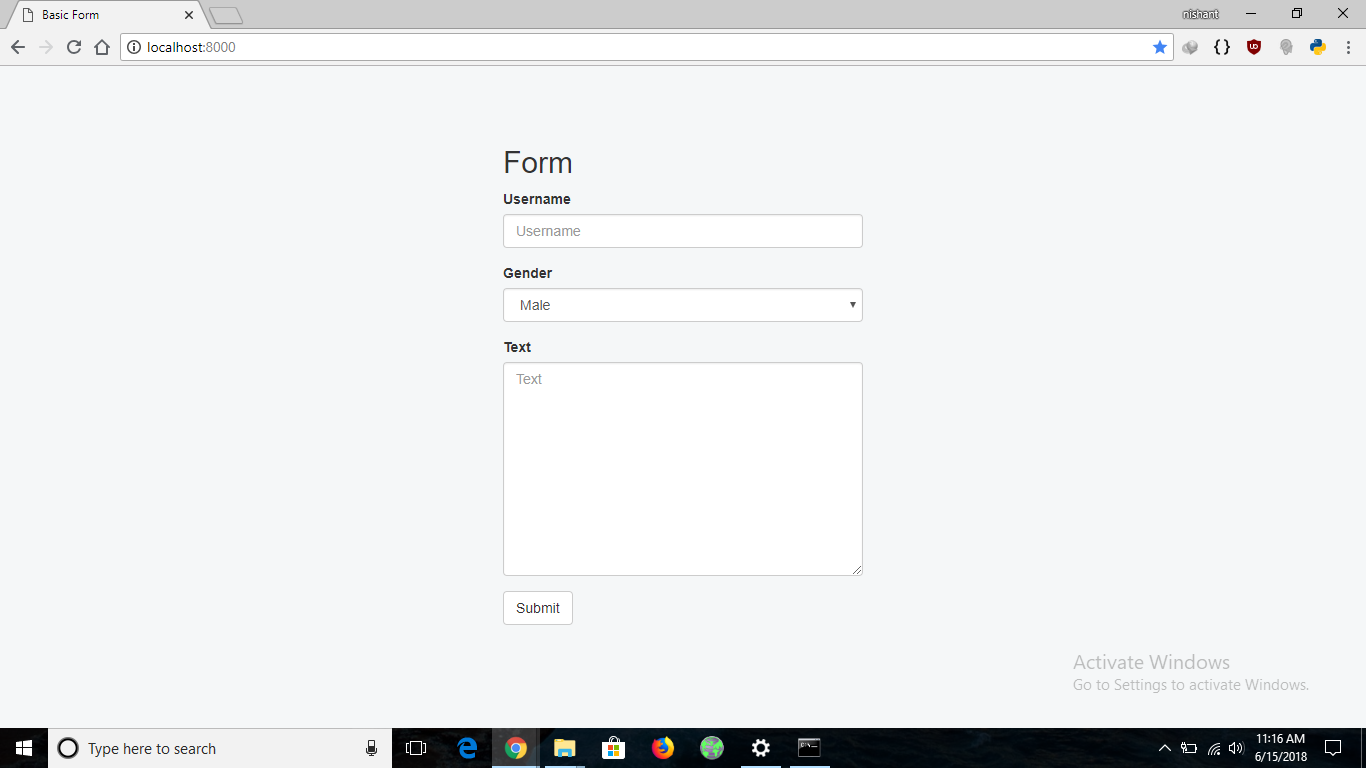
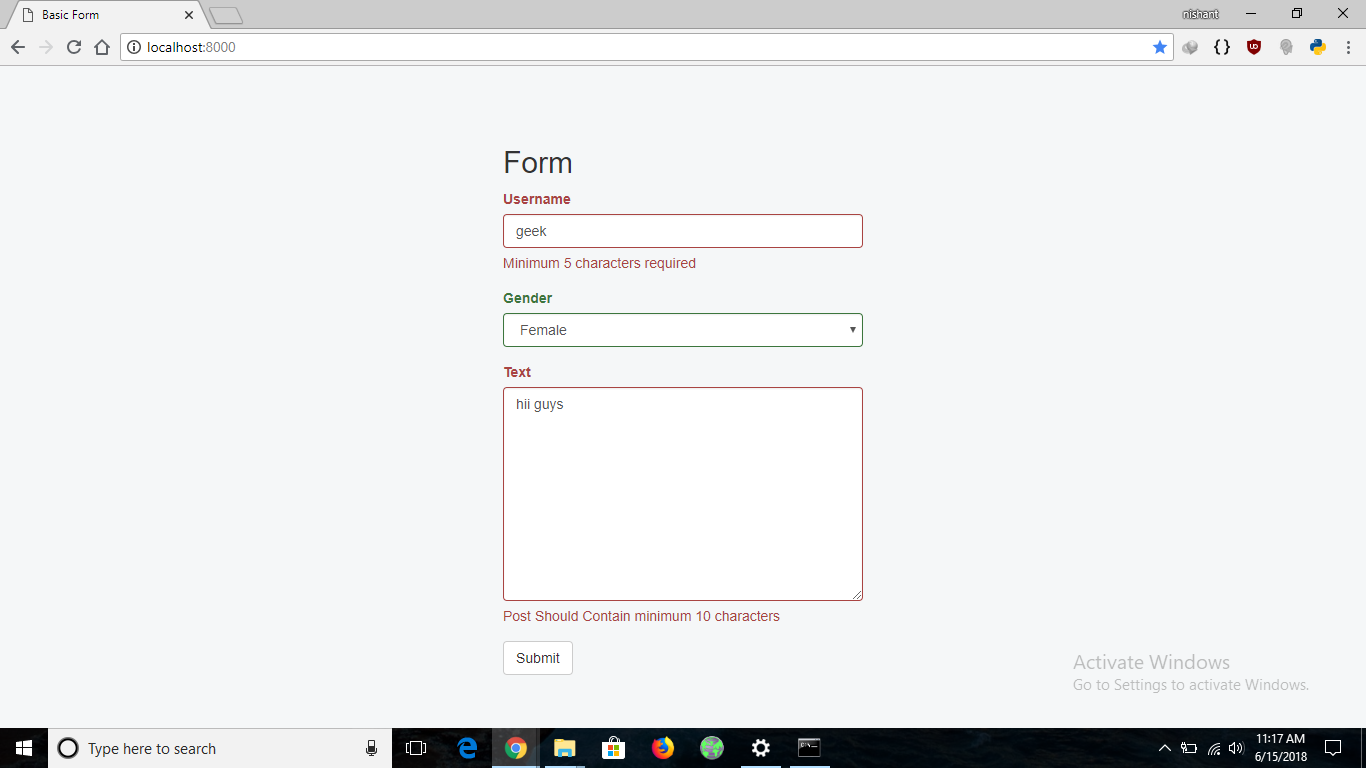
如果提交了一个长度小于5的用户名的表单,在提交时就会出现错误,同样的,在填写Post Text时也是如此。下面的图片显示了提交无效表单数据时表单的表现。
 极客教程
极客教程