C++程序 计算pow(x,n)
给定两个整数x和n,编写一个函数来计算xn。我们可以假设x和n很小,不会溢出。
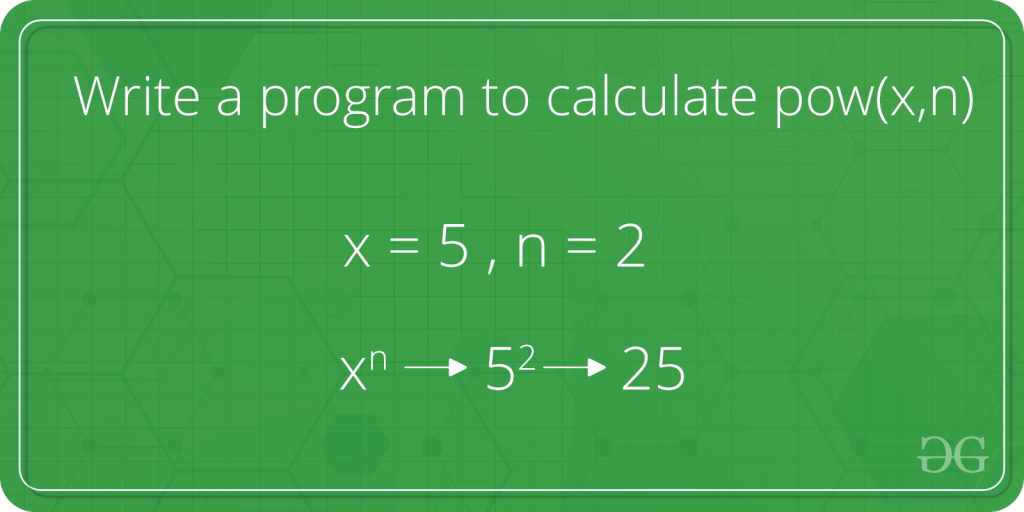
示例:
输入: x = 2,n = 3
输出: 8
输入: x = 7,n = 2
输出: 49
下面的解决方案将问题分为大为y/2的子问题,并递归调用子问题。
// C++ program to calculate pow(x,n)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class gfg
{
// Function to calculate x raised
// to the power y
public:
int power(int x, unsigned int y)
{
if (y == 0)
return 1;
else if (y % 2 == 0)
return (power(x, y / 2) *
power(x, y / 2));
else
return (x * power(x, y / 2) *
power(x, y / 2));
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
gfg g;
int x = 2;
unsigned int y = 3;
cout << g.power(x, y);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by SoM15242```
输出:
8
时间复杂度: O(n)
空间复杂度: O(1)
算法范式:分而治之。
上述功能可以通过仅计算power(x,y/2)一次并存储它来优化为O(logn)。
// Function to calculate x raised
// to the power y in O(logn)
int power(int x, unsigned int y)
{
int temp;
if( y == 0)
return 1;
temp = power(x, y / 2);
if (y % 2 == 0)
return temp * temp;
else
return x * temp * temp;
}
// This code is contributed by Shubhamsingh10```
优化后的解决方案时间复杂度: O(logn)
辅助空间: O(1)
让我们将pow函数扩展为适用于负y和浮点x。
// 扩展版的power函数
// 可以用于浮点x和
// 负y
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
float power(float x, int y)
{
float temp;
if(y == 0)
return 1;
temp = power(x, y / 2);
if (y % 2 == 0)
return temp * temp;
else
{
if(y > 0)
return x * temp * temp;
else
return (temp * temp) / x;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
float x = 2;
int y = -3;
cout << power(x, y);
return 0;
}
// This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra```
输出:
0.125000
时间复杂度: **辅助空间: O(1)
使用递归:
这种方法与迭代解决方案几乎相同。
// C++ program for the above
// approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int power(int x, int y)
{
// If x^0 return 1
if (y == 0)
return 1;
// If we need to find of 0^y
if (x == 0)
return 0;
// For all other cases
return x * power(x, y - 1);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x = 2;
int y = 3;
cout << (power(x, y));
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp```
输出:
8
时间复杂度: O(n)
辅助空间: O(1)
使用java的Math.pow()函数:
// C++程序如下
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int power(int x, int y)
{
// pow()函数的返回类型是double
return (int)pow(x, y);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x = 2;
int y = 3;
cout << (power(x, y));
}
// 代码由hemantraj712贡献```
输出:
8
时间复杂度: O(1)
辅助空间: O(1)
非递归方法:
这是一种非常适合新手的高效方法,他们很难理解迭代递归调用。此方法还需要 T(n)=O(log(n)) 的复杂度。
// C++程序如下
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int power(int x, int y)
{
int result = 1;
while (y > 0)
{
// y是偶数
if (y % 2 == 0)
{
x = x * x;
y = y / 2;
}
// y不是偶数
else
{
result = result * x;
y = y - 1;
}
}
return result;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x = 2;
int y = 3;
cout << (power(x, y));
return 0;
}
// 代码由Madhav Mohan贡献```
输出:
8
时间复杂度: O(log2y)
辅助空间: O(1)
使用二进制运算符:
在这里,我们使用右移运算符“>>”来找到一个数字的幂。
// 使用位操作来计算pow(x,n)的C++程序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int power(int x, int n)
{
int result = 1;
while (n > 0) {
if (n & 1 == 1) // y是奇数
{
result = result * x;
}
x = x * x;
n = n >> 1; // y=y/2;
}
return result;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int x = 2;
int n = 3;
// 调用函数
cout << (power(x, n));
return 0;
}
// 代码由Susobhan Akhuli贡献```
输出:
8
时间复杂度: O(log n)
辅助空间: O(1)
 极客教程
极客教程