Python numpy.polyint()
numpy.polyint(p, m) :评估一个指定阶数的多项式的反导数。
多项式’p’的反导数’P’满足如下条件
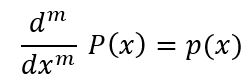
参数 :
p :[array_like or poly1D] 多项式系数按照幂的递减顺序给出。如果第二个参数(根)被设置为True,那么数组值就是多项式方程的根。例如,poly1d(3, 2, 6) = 3x 2+ 2x + 6
m :[int, optional] 反衍生物的顺序。默认为1。
返回:多项式的反导数。
代码 #1:
# Python code explaining
# numpy.polyint()
# importing libraries
import numpy as np
# Constructing polynomial
p1 = np.poly1d([1, 2])
p2 = np.poly1d([4, 9, 5, 4])
print ("P1 : ", p1)
print ("\n p2 : \n", p2)
# Solve for x = 2
print ("\n\np1 at x = 2 : ", p1(2))
print ("p2 at x = 2 : ", p2(2))
a = np.polyint(p1, 1)
b = np.polyint(p2, 1)
print ("\n\nUsing polyint")
print ("p1 anti-derivative of order = 1 : \n", a)
print ("p2 anti-derivative of order = 1 : \n", b)
a = np.polyint(p1, 2)
b = np.polyint(p2, 2)
print ("\n\nUsing polyint")
print ("p1 anti-derivative of order = 2 : \n", a)
print ("p2 anti-derivative of order = 2 : \n", b)
输出 :
P1 :
1 x + 2
p2 :
3 2
4 x + 9 x + 5 x + 4
p1 at x = 2 : 4
p2 at x = 2 : 82
Using polyint
p1 anti-derivative of order = 1 :
2
0.5 x + 2 x
p2 anti-derivative of order = 1 :
4 3 2
1 x + 3 x + 2.5 x + 4 x
代码 #2:
# Python code explaining
# numpy.polyint()
# importing libraries
import numpy as np
# Constructing polynomial
p1 = np.poly1d([1, 2])
p2 = np.poly1d([4, 9, 5, 4])
a = np.polyint(p1, 2)
b = np.polyint(p2, 2)
print ("\n\nUsing polyint")
print ("p1 anti-derivative of order = 2 : \n", a)
print ("p2 anti-derivative of order = 2 : \n", b)
输出 :
Using polyint
p1 anti-derivative of order = 2 :
3 2
0.1667 x + 1 x
p2 anti-derivative of order = 2 :
5 4 3 2
0.2 x + 0.75 x + 0.8333 x + 2 x
 极客教程
极客教程