JavaScript 如何获取元素的渲染高度
要获取元素的高度,在JavaScript中有五种常见方法。让我们看看每种方法的区别以及何时使用它们。只有最后一种方法给出了正确的渲染高度,而不是布局高度。
- style.height
- jQuery(height, innerHeight, outerHeight)
- clientHeight,offsetHeight,scrollHeight
- getComputedStyle
- getBoundingClientRect().height
渲染高度是元素在应用了所有样式和变换后最终得到的高度。例如,一个元素的高度为100px,然后获得了transform:scale(0.5)的属性。它的渲染高度为50px(变换后),布局高度为100px。
style.height
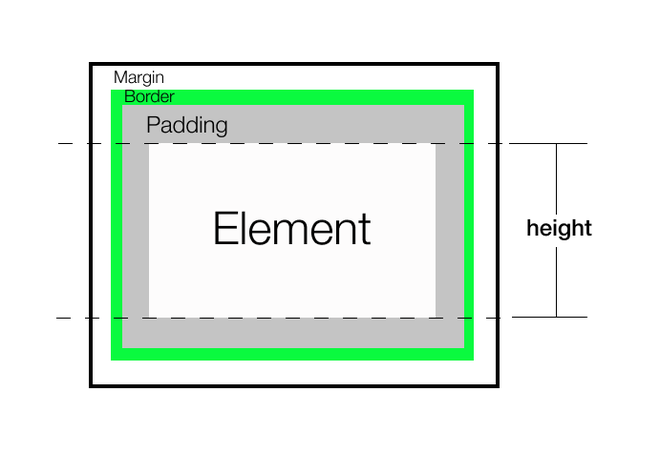
我们可以在任何选定的元素上使用style.height,并返回其高度。不包括padding,border或margin。它始终返回具有特定单位的高度。
注意: 只有在HTML中使用style属性显式设置高度时才起作用。
语法:
let height = document.getElementById("someId").style.height;
示例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
div {
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: green;
}
#div1 {
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<h1>
style.height without
inline style
</h1>
</div>
<div id="div2" style="height: 100px;">
<h1>style.height with inline style</h1>
</div>
<button onclick="alertHeight()">
Get Height
</button>
<script>
function alertHeight() {
alert(document.getElementById
("div1").style.height);
alert(document.getElementById
("div2").style.height);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出: 对于“div1”,返回空字符串;对于“div2”,返回“100px”
- 对于“div1”:

-
对于“div2”:
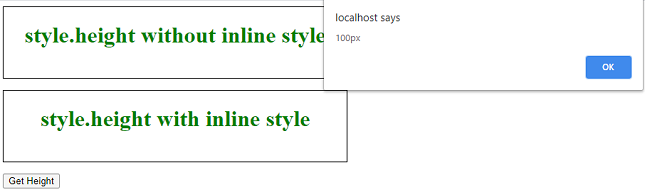
结论: 只返回使用内联样式属性指定的高度。它不考虑任何变换,比如缩放。它不可靠,不应作为内联样式不理想的替代品
jQuery(height, innerHeight, outerHeight)
height()
返回元素的当前高度。不包括 padding 、 border 或 margin 。始终返回一个无单位的像素值。
注意: 无论CSS的 box-sizing 属性的值如何,height()总是返回内容高度。
语法:
let height = $("#div1").height();
示例2:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
div {
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: green;
}
#div1 {
height: 100px;
}
</style>
<script src=
"https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.0.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<h1>(".class").height</h1>
</div>
<button onclick="alertHeight()">
Get Height
</button>
<script>
function alertHeight() {
alert(("#div1").height());
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
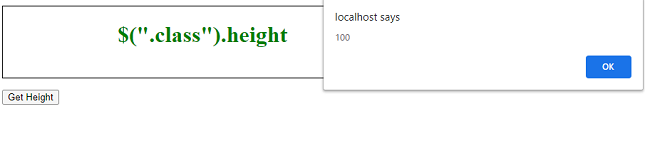
输出: 它返回一个无单位的像素值为100。
输出:
innerHeight()
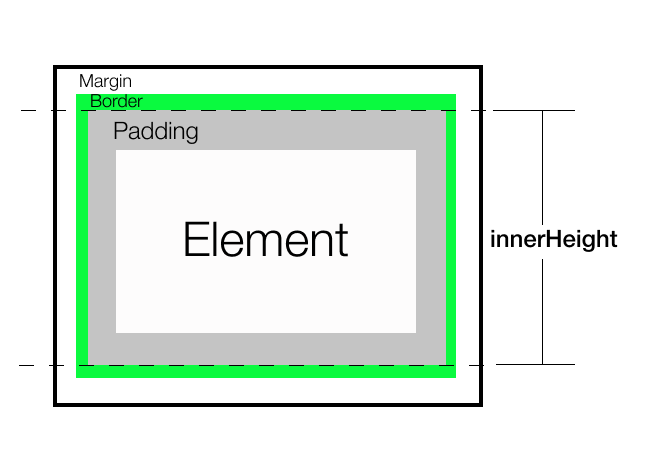
它返回包括顶部和底部padding但不包括border的元素的当前高度。 它总是返回一个无单位的像素值。
语法:
let height = $("#div1").innerHeight();
示例3:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
div {
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: green;
}
#div1 {
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
}
</style>
<script src=
"https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.0.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<h1>(".class").innerHeight</h1>
</div>
<button onclick="alertHeight()">
Get Height
</button>
<script>
function alertHeight() {
alert(("#div1").innerHeight());
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出: 它返回120,这是(10(顶部填充)+ 100(内容高度)+ 10(底部填充))

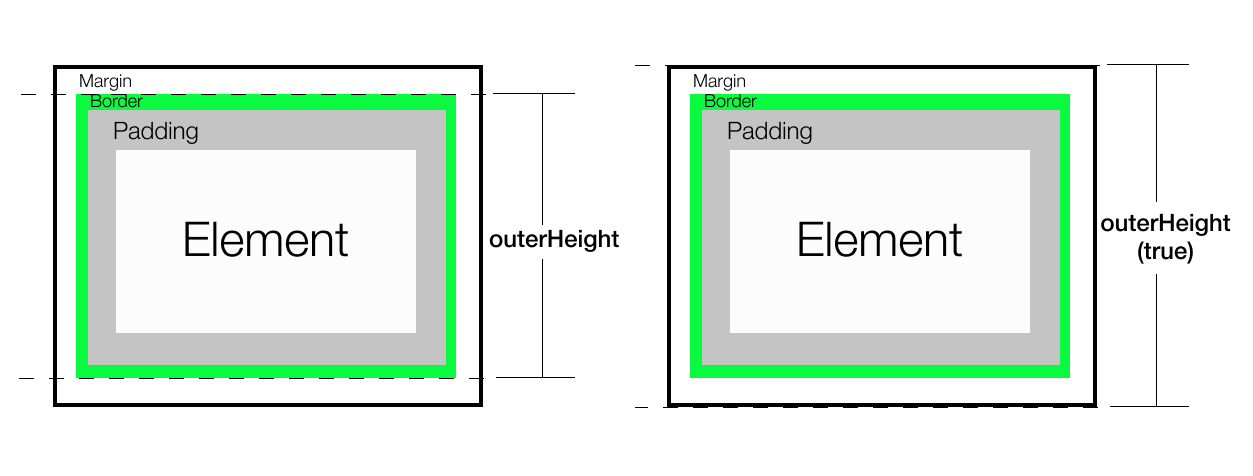
outerHeight()
它返回当前元素的高度,包括 padding , border 和 margin ,可选地。它总是返回一个无单位的像素值。
语法:
let height = ("#div1").outerHeight();
let height =("#div1").outerHeight();
示例 4:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
div {
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: green;
}
#div1 {
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
margin: 5px;
}
</style>
<script src=
"https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.0.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<h1>(".class").outerHeight</h1>
</div>
<button onclick="alertHeight()">
Get Height
</button>
<script>
function alertHeight() {
alert(("#div1").outerHeight());
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
(1(顶边框)+ 10(顶边距)+ 100(内容高度)+10(底边距)+ 1(底边框)

注意: height()、innerHeight()和outerHeight()报告的数值在元素或其父级元素隐藏时不能保证准确。为了获取准确的结果,请确保在使用这些方法之前元素是可见的。jQuery会尝试临时显示然后重新隐藏元素以测量其尺寸,但这种方法不可靠,即使准确也会极大地影响页面性能。这种显示和隐藏测量功能可能会在未来的jQuery版本中移除。
结论:
// If you need height of div excluding margin/padding/border
('#div1').height();
// If you need height of div with padding but without border + margin('#div1').innerHeight();
// If you need height of div including padding and border
('#div1').outerHeight();
// For including border + margin + padding, can use('#div1').outerHeight(true);
所有这些仅返回布局高度,而不是渲染高度。
clientHeight, offsetHeight, scrollHeight
clientHeight()
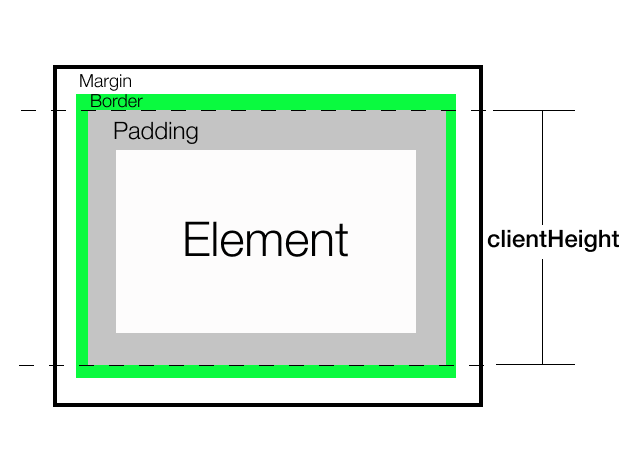
它返回元素中显示内容的高度(包括垂直填充,但不包括边框、外边距或滚动条)。它总是以像素的整数值返回。如果元素被隐藏,则返回0。如果它是一个可滚动的元素,则仅返回可见部分的高度。
语法:
let height = document.getElementById("div1").clientHeight;
示例5:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
div {
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: green;
}
#div1 {
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
<script src=
"https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.0.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<h1>.clientHeight</h1>
</div>
<button onclick="alertHeight()">
Get Height
</button>
<script>
function alertHeight() {
alert(document.getElementById
("div1").clientHeight);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
它返回120,即(10(上边距)+ 100(内容高度)+ 10(下边距))

总结: 如果我们想要找到实际显示内容的高度,请使用clientHeight。它返回元素当前可见部分的布局高度,即使结果是一个小数也会四舍五入为整数值。
offsetHeight()
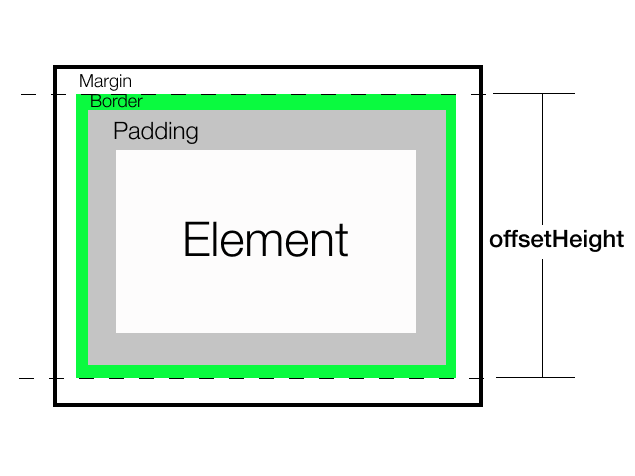
它返回元素占用的高度,包括垂直内边距、边框和滚动条(如果有)。它不包括外边距。它始终返回以像素为单位的整数值。如果元素隐藏,则返回0。
注意: 不包括伪元素(如::after或::before)的高度
语法:
let height = document.getElementById("div1").offsetHeight;
示例6:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
div {
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: green;
}
#div1 {
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<h1>.offsetHeight</h1>
</div>
<button onclick="alertHeight()">
Get Height
</button>
<script>
function alertHeight() {
alert(document.getElementById
("div1").offsetHeight);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
它返回122,即(1(上边框) + 10(上内边距) + 100(内容高度) + 10(下内边距) + 1(下边框))

结论: 如果您需要知道一个元素占用的总高度,包括可见内容的宽度、滚动条(如果有)、内边距和边框,我们可以使用offsetWidth。它返回当前可见部分的布局高度,以整数值四舍五入。
scrollHeight()
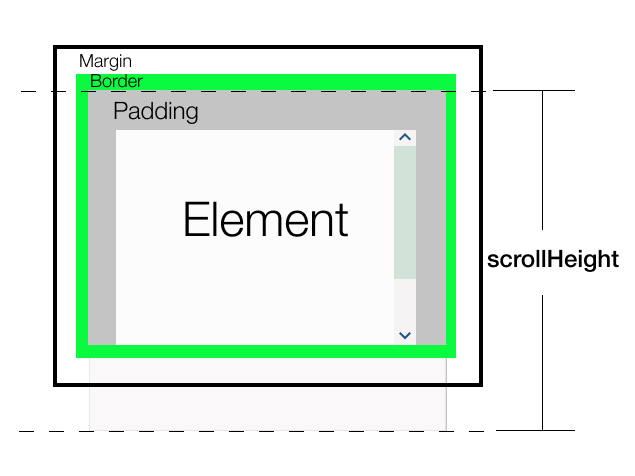
它返回元素整个内容的高度,即使由于滚动条只有部分内容可见。它始终以像素为单位返回整数值。如果元素是隐藏的,则返回0。
它类似于clientHeight,它包括元素及其内边距,但不包括边框、外边距或水平滚动条(如果存在)。它还可以包括伪元素(如::before或::after)的高度。如果元素的内容可以适应而不需要垂直滚动条,它的scrollHeight等于clientHeight。
语法:
let height = document.getElementById("div1").scrollHeight
示例7:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
div {
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: green;
}
.div0 {
height: 50px;
}
#div1 {
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
overflow: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<h1>.offsetHeight</h1>
As the placement season is back
so are we to help you ace the
interview.We have selected some
most commonly asked and must do
practice problems for you. You
can also take part in our mock
placement contests which will
help you learn different topics
and practice at the same time,
simulating the feeling of a
real placement test environment.
There are many important things
that should be taken care of,
like user friendliness,modularity,
security, maintainability, etc.
Why to worry about performance?
The answer to this is simple, we
can have all the above things
only if we have performance. So
performance is like currency through
which we can buy all the above things.
Another reason for studying performance
is – speed is fun! To summarize,
performance == scale. Imagine a text
editor that can load 1000 pages,
but can spell check 1 page per minute
OR an image editor that takes 1 hour
to rotate your image 90 degrees left
OR … you get it. If a software feature
can not cope with the scale of tasks
users need to perform – it is as good
as dead.
</div>
<button onclick="alertHeight()">
Get Height</button>
<script>
function alertHeight() {
alert(document.getElementById
("div1").scrollHeight);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
(1(上边框) + 10(上内边距) + 整个内容(可见和不可见) + 10(下内边距) + 1(下边框))

结论: 如果您需要知道内容的实际大小,不管有多少内容当前可见,请使用 scrollHeight 。它包括元素的 padding ,但不包括 margin,border 或 scrollbar (如果有的话)。如果高度是小数,则返回四舍五入的整数。
getComputedStyle()方法
getComputedStyle()方法基本上允许我们检索不同属性的解析CSS值。它返回一个CSSStyleDeclaration对象。计算样式用于在应用了多个源的“样式”后显示元素。
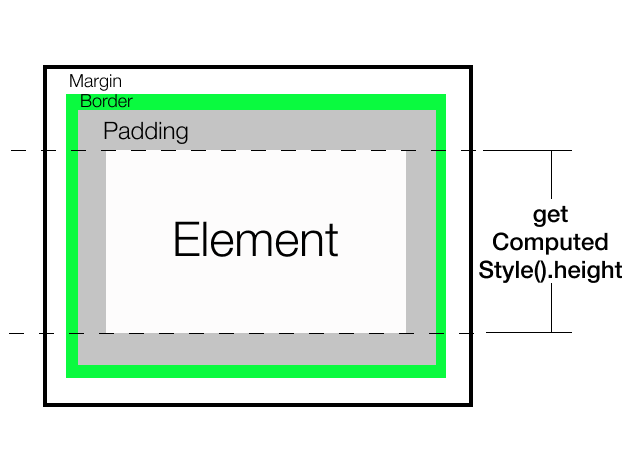
getComputedStyle().height 它将返回指定的布局高度而不是渲染高度。它返回小数像素值。它是一个解析值,因此如果我们使用100%,它将返回等效的解析像素值。它只给出内容高度。如果需要,我们可以逐个访问每个CSS属性,如 margin-top,margin-bottom,padding-top,padding-bottom,border-top,border-bottom 并按需添加它们。
语法:
let height = getComputedStyle(document.getElementById("div1")).height;
或
let height = getComputedStyle(document.getElementById("div1"))
.getPropertyValue("height");
let marginTop = getComputedStyle(document.getElementById("div1"))
.getPropertyValue("margin-top");
let borderBottom = getComputedStyle(document.getElementById("div1"))
.getPropertyValue("border-bottom");
示例8:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
div {
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: green;
}
#div1 {
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<h1>.getComputedStyle(el).height</h1>
</div>
<button onclick="alertHeight()">
Get Height</button>
<script>
function alertHeight() {
alert(getComputedStyle(
document.getElementById("div1"))
.getPropertyValue("height"));
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
100像素

结论: 它允许完全控制所选内容,但只返回布局尺寸。它不会导致任何变换。如果需要,我们还可以通过在getComputedStyle()中传递第二个参数来针对伪元素并获取其特定样式。
注意: getComputedStyle()函数的不同属性在不同浏览器中具有不同的支持。
getBoundingClientRect()方法
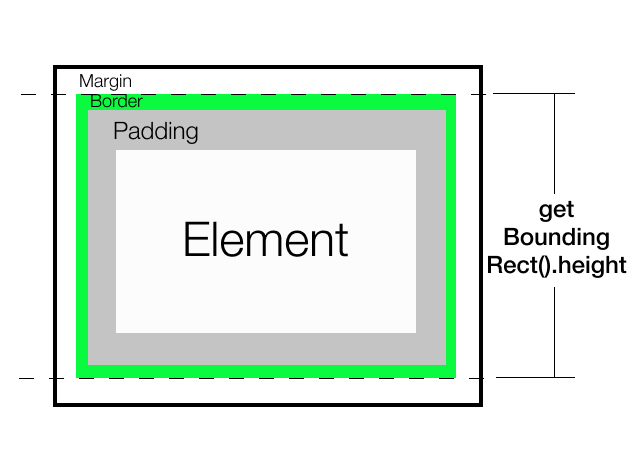
getBoundingClientRect()。height返回元素占用的高度,包括垂直填充、边框和滚动条(如果有)。它不包括边距。它类似于offsetHeight,但返回的是一个小数值,而且显示的是渲染的高度而不是布局高度。
语法:
let height = document.getElementById("div1")
.getBoundingClientRect().height;
示例9:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
div {
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
color: green;
}
#div1 {
height: 100px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<h1>.getBoundingClientRect().height</h1>
</div>
<button onclick="alertHeight()">
Get Height
</button>
<script>
function alertHeight() {
alert(document.getElementById("div1").
getBoundingClientRect().height);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
输出:
它返回122,这是(1(上边框) + 10(上填充) + 100(内容高度) + 10(下填充) + 1(下边框))

结论: 它与 offsetHeight 相似,但返回的是分数值。它还提供了渲染的高度而不是布局的高度。如果应用了transform的缩放,返回的值现在将不同。
使用 getBoundingCLientRect().height 如果您需要最终的渲染高度。否则,根据要求您可以使用除 style.height 之外的所有其他方法。
 极客教程
极客教程