如何使用纯Typescript类创建Mongo模式
TypeScript 是一种面向对象的编程语言,它是JavaScript的超集,并包含所有JavaScript元素。通过使用TSC(TypeScript编译器),我们可以将Typescript代码(.ts文件)转换为JavaScript(.js文件)。它是开源的,其代码更容易阅读和理解。
MongoDB 是一种通用的广泛使用的基于文档的NoSQL数据库。一个集合可以容纳大量文档。我们可以将集合看作RDBMS技术中的表,但集合中不需要强实体关系。mongoose模式相当于一个集合。我们可以在Mongoose模式中包含不同的数据以创建MongoDB中的集合。在本文中,让我们看看如何从纯Typescript类创建Mongo模式。Typescript文件的扩展名是.ts,通常从Angular框架项目中,我们使用Typescript类来详细了解。为了与MongoDB交互,我们需要Mongoose。
项目设置和模块安装:
步骤1: 我们将使用Typescript类,使用以下命令初始化项目。
yarn init (或 npm init)
当提示时,将入口点设置为以下文件。
src/server.ts。
步骤2: 使用以下命令安装所需的模块。
# 连接到mongodb的依赖项
# 模式和连接mongodb
yarn add express mongoose
# 创建Typescript文件的依赖项
# 执行这些文件的依赖项
# 加速开发的依赖项
yarn add -D nodemon typescript ts-node
@types/express @types/mongoose @types/node
# 全局依赖项
npm i -g typescript ts-node
package.json: 我们的 package.json 文件将如下所示。
{
"name": "mongo-typescript",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "src/server.ts",
"license": "MIT",
"scripts": {
"start": "node --inspect=5858 -r ts-node/register ./src/server.ts",
"dev": "nodemon",
"build": "tsc",
"script": "cd src/scripts && ts-node"
},
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.17.1",
"mongoose": "^5.9.7"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/express": "^4.17.6",
"@types/mongoose": "^5.7.10",
"@types/node": "^13.11.1",
"nodemon": "^2.0.3",
"ts-node": "^8.8.2",
"typescript": "^3.8.3"
}
}
tsconfig.json: 该文件必须在根目录中创建,它会告诉编译器TypeScript文件的位置,并允许我们使用ES6的导入/导出语法。
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es6",
"module": "commonjs",
"outDir": "dist",
"sourceMap": true
},
"include": ["src/**/*.ts"],
"exclude": ["node_modules", ".vscode"]
}
连接到数据库: 为了进行数据库连接,使用以下命令创建一个单独的文件夹。
mkdir src
cd src
mkdir database
touch database.ts
项目结构: 它将如下所示。
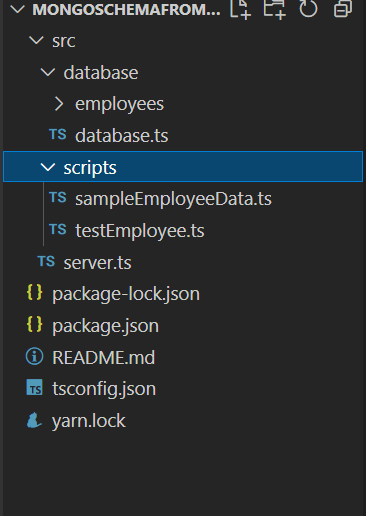
示例:
import * as Mongoose from 'mongoose';
import { EmployeeModel } from './employees/employees.model';
let database: Mongoose.Connection;
export const connect = () => {
// 在下面添加自己的URI,这里使用的是本地的MongoDB,
// 数据库名为UserDB
const uri =
'mongodb://localhost:27017/UserDB';
if (database) {
return;
}
// 连接数据库时需要使用以下设置来解决所有的弃用警告
Mongoose.connect(uri, {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useFindAndModify: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
useCreateIndex: true,
});
database = Mongoose.connection;
// 在数据库可用且成功连接时输出消息
database.once('open', async () => {
console.log('成功连接数据库');
});
// 连接错误时
database.on('error', () => {
console.log(`连接数据库发生错误。请检查MongoDB是否已安装,或尝试使用开源的Mongo Atlas数据库`);
});
return {
EmployeeModel
};
};
// 安全断开连接的方式
export const disconnect = () => {
if (!database) {
return;
}
Mongoose.disconnect();
};
import * as express from "express";
import { connect } from "./database/database";
const app = express();
// 可用的端口号,不应被其他服务使用
const port = 5002;
connect();
// 启动项目时输出控制台消息
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`服务器启动于 http://localhost:${port}`);
});
创建模型
TypeScript文件有助于创建MongoDB的模式。它由MongoDB模型的三个部分组成(模式、静态方法和实例方法),第四个部分用于存储TypeScript接口,第五个部分用于将所有内容组合在一起。
在 src/database/
- $lt;collectionname >.schema.ts:定义Mongoose模式,有助于确定MongoDB文档的结构。
- $lt;collectionname >.statics.ts:添加并在模型本身上调用所需的静态方法。
- $lt;collectionname >.methods.ts:模型的实例方法,可以在单个模型实例上调用的函数。
- $lt;collectionname >.types.ts:存储在其他文件中使用的类型。
- $lt;collectionname >.model.ts:用于将所有内容组合在一起。
我们可以使用以下命令创建文件夹和文件。
# 进入scr文件夹并创建database文件夹
cd src
mkdir database
# 进入database文件夹并创建employees文件夹
cd database
mkdir employees
# 进入employees文件夹并创建文件
cd employees
touch employees.schema.ts employees.statics.ts
touch employees.methods.ts employees.types.ts employees.model.ts
// 主模式文件,在此处我们可以定义所需的属性
import * as Mongoose from "mongoose";
const EmployeeSchema = new Mongoose.Schema({
firstName: String,
lastName: String,
age: Number,
dateOfJoining: {
type: Date,
default: new Date(),
},
lastUpdated: {
type: Date,
default: new Date(),
},
gender: String,
department: String,
// 应在此处给出所有其他必需的属性
});
export default EmployeeSchema;
- IEmployeeDocument: 包含我们的字段和标准Mongoose文档的其他元素。
- IEmployeeModel: 标准Mongoose模型的表示,包含我们的 IEmployeeDocument 类型的文档。
import { Document, Model } from "mongoose";
// 这些字段表示集合的字段,集合的名称为“Employee”
export interface IEmployee {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
age: number;
dateOfEntry?: Date;
lastUpdated?: Date;
gender: String;
department: String;
}
export interface IEmployeeDocument extends IEmployee, Document { }
export interface IEmployeeModel extends Model<IEmployeeDocument> { }
import { model } from "mongoose";
import { IEmployeeDocument } from "./employees.types";
import EmployeeSchema from "./employees.schema";
export const EmployeeModel = model<IEmployeeDocument>("employee",
EmployeeSchema
)
创建下面两个静态方法:
- findOneOrCreate: 检查条目是否存在,如果不存在,则创建新的条目。
- findByAge: 根据提供的年龄范围返回一个员工数组。
类似地,我们可以根据需求定义方法,比如findByGender、findByDepartment等,最终符合我们的要求
import { IEmployeeDocument, IEmployeeModel } from "./employees.types";
// 检查条目是否存在,如果不存在,则创建一个
export async function findOneOrCreate(
this: IEmployeeModel,
{
firstName,
lastName,
age,
gender,
department,
}: {
firstName: string; lastName: string; age: number;
gender: string; department: string
}
): Promise<IEmployeeDocument> {
const employeeRecord = await this.findOne({
firstName,
lastName, age, gender, department
});
if (employeeRecord) {
return employeeRecord;
} else {
return this.create({
firstName, lastName,
age, gender, department
});
}
}
export async function findByAge(
this: IEmployeeModel,
min?: number,
max?: number
): Promise<IEmployeeDocument[]> {
return this.find({ age: { gte: min || 0,lte: max || Infinity } });
}
// 根据需求添加其余方法
import { Document } from "mongoose";
import { IEmployeeDocument } from "./employees.types";
export async function setLastUpdated(
this: IEmployeeDocument): Promise<void> {
const now = new Date();
if (!this.lastUpdated || this.lastUpdated < now) {
this.lastUpdated = now;
await this.save();
}
}
export async function sameLastName(
this: IEmployeeDocument): Promise<Document[]> {
return this.model("employee")
.find({ lastName: this.lastName });
}
import * as Mongoose from "mongoose";
import { findOneOrCreate, findByAge } from "./employees.statics";
import { setLastUpdated, sameLastName } from "./employees.methods";
const EmployeeSchema = new Mongoose.Schema({
firstName: String,
lastName: String,
age: Number,
dateOfJoining: {
type: Date,
default: new Date(),
},
lastUpdated: {
type: Date,
default: new Date(),
},
gender: String,
department: String,
// All other required attributes should be given here
});
EmployeeSchema.statics.findOneOrCreate = findOneOrCreate;
EmployeeSchema.statics.findByAge = findByAge;
EmployeeSchema.methods.setLastUpdated = setLastUpdated;
EmployeeSchema.methods.sameLastName = sameLastName;
export default EmployeeSchema;
import { Document, Model } from "mongoose";
export interface IEmployee {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
age: number;
dateOfJoining?: Date;
lastUpdated?: Date;
gender: String;
department: String;
}
export interface IEmployeeDocument extends IEmployee, Document {
setLastUpdated: (this: IEmployeeDocument) => Promise<void>;
sameLastName: (this: IEmployeeDocument) => Promise<Document[]>;
}
export interface IEmployeeModel extends Model<IEmployeeDocument> {
findOneOrCreate: (
this: IEmployeeModel,
{
firstName,
lastName,
age,
gender,
department,
}: { firstName: string; lastName: string; age: number;
gender: string; department: string; }
) => Promise<IEmployeeDocument>;
findByAge: (
this: IEmployeeModel,
min?: number,
max?: number
) => Promise<IEmployeeDocument[]>;
}
import { EmployeeModel } from "../database/employees/employees.model";
import { connect, disconnect } from "../database/database";
(async () => {
connect();
// 通过 "sampleEmployeeData.ts" 可以向 Mongoose 架构添加数据
// 我们的架构名称是 employees
const employees = [
{
firstName: "Rachel", lastName: "Green", age: 25,
gender: "女性", department: "设计"
},
{
firstName: "Monica", lastName: "Geller", age: 25,
gender: "女性", department: "餐饮"
},
{
firstName: "Phebe", lastName: "Phebe", age: 25,
gender: "女性", department: "Masus"
},
{
firstName: "Ross", lastName: "Geller", age: 30,
gender: "男性", department: "古生物学"
},
{
firstName: "Chandler", lastName: "Bing", age: 30,
gender: "男性", department: "IT"
},
{
firstName: "Joey", lastName: "Joey", age: 30,
gender: "男性", department: "戏剧家"
},
];
try {
for (const employee of employees) {
await EmployeeModel.create(employee);
console.log(`创建员工 {employee.firstName}
{employee.lastName}`);
}
disconnect();
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
})();
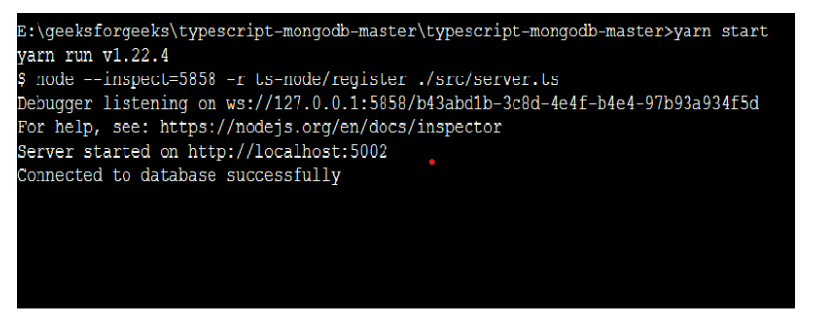
运行应用程序的步骤: 使用以下命令启动服务器。
yarn start
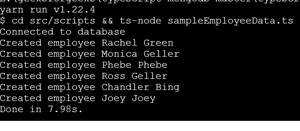
下一步是我们需要使用 Mongoose 架构创建集合。使用以下命令填充数据:
yarn script sampleEmployeeData.ts
输出:
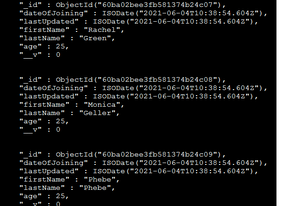
在 Mongo shell 中,我们可以进行验证。在 UserDB 数据库中,查询 db.employees.find().pretty() ,我们可以看到输出:
结论: TypeScript 文件非常好用,具有 JavaScript 的高级功能,并且通过使用 mongoose、Express,我们可以轻松地使用 TypeScript 文件创建 MongoDB 架构。
阅读更多:JavaScript 教程
 极客教程
极客教程