数组和映射的区别
数组
数组 是存储在连续的内存位置的项目的集合。其原理是将同一类型的多个项目存储在一起。这使得计算每个元素的位置更加容易,只需将偏移量加到一个基值上,即数组中第一个元素的内存位置(一般用数组的名称表示)。
下面给出了数组的示意图-
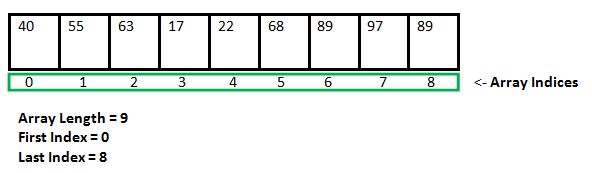
程序1:
下面是一个一维数组的图示 –
// C++ program to illustrate 1D array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given array
int arr[] = { 6, 10, 5, 0 };
// Print the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Java示例:
// Java program to illustrate 1D array
class YiibaiDemo{
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given array
int arr[] = { 6, 10, 5, 0 };
// Print the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
运行结果:
6 10 5 0
程序2:
下面是一个二维数组的图示 –
// C++ program to illustrate 1D array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// A 2D array with 3 rows and
// 2 columns
int x[3][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 2, 3 }, { 4, 5 } };
// Print each array element value
// Traverse row
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// Traverse column
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
// Print element
cout << "Element at x[" << i<< "][" << j << "]: ";
cout << x[i][j] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Java示例代码:
// Java program to illustrate 1D array
import java.util.*;
class YiibaiDemo{
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// A 2D array with 3 rows and
// 2 columns
int x[][] = { { 0, 1 }, { 2, 3 }, { 4, 5 } };
// Print each array element value Traverse row
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
// Traverse column
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
// Print element
System.out.print("Element at x[" + i +"][" + j + "]: ");
System.out.print(x[i][j] + "n");
}
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
Element at x[0][0]: 0
Element at x[0][1]: 1
Element at x[1][0]: 2
Element at x[1][1]: 3
Element at x[2][0]: 4
Element at x[2][1]: 5
映射
映射是一个关联的容器,它以映射的方式存储元素。每个元素都有一个键值和一个映射值。没有两个映射值的键值是相同的。下面给出了映射的示意图 –
程序1:
下面是一个映射的代码 –
// C++ program to illustrate Map
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Empty map container
map<int, int> gquiz1;
// Insert elements in Map
gquiz1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 40));
gquiz1.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 30));
gquiz1.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 60));
// Iterator to iterate Map
map<int, int>::iterator itr;
cout << "The map gquiz1 is : ";
cout << "tKEYtELEMENTn";
// Print map gquiz1
for (itr = gquiz1.begin();
itr != gquiz1.end(); ++itr) {
cout << 't' << itr->first << 't' << itr->second << 'n';
}
return 0;
}
Java示例代码 –
// Java program to illustrate Map
import java.util.*;
class YiibaiDemo{
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Empty map container
HashMap<Integer,
Integer> gquiz1 = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
// Insert elements in Map
gquiz1.put(1, 40);
gquiz1.put(2, 30);
gquiz1.put(3, 60);
// Iterator to iterate Map
Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> itr = gquiz1.entrySet().iterator();
System.out.print("The map gquiz1 is : n");
System.out.print("KEYtELEMENTn");
// Print map gquiz1
while(itr.hasNext())
{
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry = itr.next();
System.out.print('t' + entry.getKey() + "t" + entry.getValue()+ "n");
}
}
}
运行结果:
The map gquiz1 is :
KEY ELEMENT
1 40
2 30
3 60
数组和映射的区别 –
| 数组 | 映射 |
|---|---|
| 数组是相同数据类型的元素的集合。 | 映射是一个键和值对的散列结构。 |
| 数组的索引是从0开始的整数 | Map的键可以是任何数据类型。 |
| 元素通过索引被访问。 | 元素通过键值被访问。 |
| 输入的元素的顺序被保持。 | 不保证保持顺序。 |
| 数组可以是一维、二维或多维 映射可以是多图、无序多图、无序地图等。数组的大小必须在阵列声明时指定。 | 映射的大小是动态的。 |
 极客教程
极客教程