Python Pandas Series.dt.tz_localize
Series.dt可以用来访问系列的数据时间值,并返回几个属性。Pandas Series.dt.tz_localize()函数将无时区的Datetime Array/Index定位为有时区意识的Datetime Array/Index。这个方法接收一个无时区(tz)的Datetime数组/索引对象,并使其具有时区意识。它不会将时间转移到另一个时区。
语法: Series.dt.tz_localize(*args, **kwargs)
参数:
tz :时区来转换时间戳。
返回:与自身类型相同
例子#1:使用Series.dt.tz_localize()函数,将系列中的tz-naive日期时间值本地化为tz-aware。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(['2012-12-31', '2019-1-1 12:30', '2008-02-2 10:30',
'2010-1-1 09:25', '2019-12-31 00:00'])
# Creating the index
idx = ['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3', 'Day 4', 'Day 5']
# set the index
sr.index = idx
# Convert the underlying data to datetime
sr = pd.to_datetime(sr)
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
现在我们将使用Series.dt.tz_localize()函数将给定的tz-naive系列本地化为 “美国/东部”。
# localize to 'US / Eastern'
result = sr.dt.tz_localize(tz = 'US / Eastern')
# print the result
print(result)
输出 :

正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.dt.tz_localize()函数已经成功地将给定的tz-naive数据时间系列定位为tz-aware。
示例#2 : 使用Series.dt.tz_localize()函数,将给定的系列对象作为本地python日期时间对象的数组返回。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the Series
sr = pd.Series(pd.date_range('2012-12-31 00:00', periods = 5, freq = 'D'))
# Creating the index
idx = ['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3', 'Day 4', 'Day 5']
# set the index
sr.index = idx
# Print the series
print(sr)
输出 :
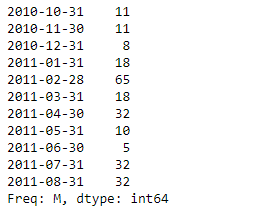
现在我们将使用Series.dt.tz_localize()函数将给定的tz-naive系列本地化为 “欧洲/柏林”。
# localize to 'Europe / Berlin'
result = sr.dt.tz_localize(tz = 'Europe / Berlin')
# print the result
print(result)
输出 :
正如我们在输出中看到的,Series.dt.tz_localize()函数已经成功地将给定的tz-naive数据时间系列定位为tz-aware。
 极客教程
极客教程