Python numpy.std()
numpy.std(arr, axis = None) :计算给定数据(数组元素)沿指定轴(如果有的话)的标准偏差。.
Standard Deviation (SD)是指在给定的数据集中的数据分布的扩散。
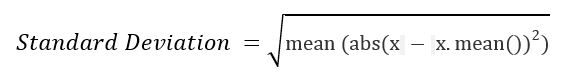
例如: :
x = 1 1 1 1 1
Standard Deviation = 0 .
y = 9, 2, 5, 4, 12, 7, 8, 11, 9, 3, 7, 4, 12, 5, 4, 10, 9, 6, 9, 4
第1步 :分布的平均值4 = 7
第2步 : (x – x.mean())**2的总和 = 178
第3步 : 找到平均数 = 178 /20 = 8.9
这个结果是方差。
第4步 :标准偏差=sqrt(Variance) = sqrt(8.9) = 2.983.
参数 :
arr :[array_like]输入阵列。
axis :[int或int的tuples]轴,我们想沿着这个轴计算标准差。否则,它将认为arr是平坦的(对所有轴都有效)。 axis = 0表示沿列的SD, axis = 1表示沿行的SD。
out :[ndarray, optional]不同的数组,我们想把结果放在其中。该数组必须具有与预期输出相同的尺寸。
dtype :[data-type, optional]我们在计算SD时希望的类型。
结果 :数组的标准偏差(如果坐标轴为零,则为标量值),或者带有沿指定坐标轴的标准偏差值的数组。
代码 #1:
# Python Program illustrating
# numpy.std() method
import numpy as np
# 1D array
arr = [20, 2, 7, 1, 34]
print("arr : ", arr)
print("std of arr : ", np.std(arr))
print ("\nMore precision with float32")
print("std of arr : ", np.std(arr, dtype = np.float32))
print ("\nMore accuracy with float64")
print("std of arr : ", np.std(arr, dtype = np.float64))
输出 :
arr : [20, 2, 7, 1, 34]
std of arr : 12.576167937809991
More precision with float32
std of arr : 12.576168
More accuracy with float64
std of arr : 12.576167937809991
代码 #2:
# Python Program illustrating
# numpy.std() method
import numpy as np
# 2D array
arr = [[2, 2, 2, 2, 2],
[15, 6, 27, 8, 2],
[23, 2, 54, 1, 2, ],
[11, 44, 34, 7, 2]]
# std of the flattened array
print("\nstd of arr, axis = None : ", np.std(arr))
# std along the axis = 0
print("\nstd of arr, axis = 0 : ", np.std(arr, axis = 0))
# std along the axis = 1
print("\nstd of arr, axis = 1 : ", np.std(arr, axis = 1))
输出 :
std of arr, axis = None : 15.3668474320532
std of arr, axis = 0 : [ 7.56224173 17.68473918 18.59267329 3.04138127 0. ]
std of arr, axis = 1 : [ 0. 8.7772433 20.53874388 16.40243884]
 极客教程
极客教程