变量集2的估计
与可变性指标有关的术语:
-> Deviation
-> Variance
-> Standard Deviation
-> Mean Absolute Deviation
-> Median Absolute Deviation
-> Order Statistics
-> Range
-> Percentile
-> Inter-quartile Range
- 中位数绝对偏差。平均绝对偏差、方差和标准偏差(在上一节中讨论过)对极端值和异常值并不健全。我们对偏离中位数的偏差之和进行平均。
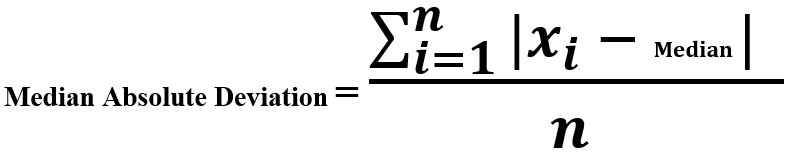
- 示例 :
Sequence : [2, 4, 6, 8]
Mean = 5
Deviation around mean = [-3, -1, 1, 3]
Mean Absolute Deviation = (3 + 1 + 1 + 3)/ 4
# Median Absolute Deviation
import numpy as np
def mad(data):
return np.median(np.absolute(
data - np.median(data)))
Sequence = [2, 4, 10, 6, 8, 11]
print ("Median Absolute Deviation : ", mad(Sequence))
输出 :
Median Absolute Deviation : 3.0
- 顺序统计。这种变异性测量方法是基于排列(排序)数据的传播。
- 范围。它是属于秩序统计的最基本的测量。它是数据集的最大和最小值之间的差异。它对了解数据的分布很有好处,但它对离群值非常敏感。我们可以通过删除极端值来使它变得更好。
示例 :
Sequence : [2, 30, 50, 46, 37, 91]
Here, 2 and 91 are outliers
Range = 91 - 2 = 89
Range without outliers = 50 - 30 = 20
- 百分位数:这是一个非常好的测量方法,可以测量数据的可变性,避免离群值。数据中的第P个百分位数是指至少有P%或更少的数值小于它,至少有(100-P)%的数值大于P。
中位数是数据的第50个百分点。
示例 :
Sequence : [2, 30, 50, 46, 37, 91]
Sorted : [2, 30, 37, 46, 50, 91]
50th percentile = (37 + 46) / 2 = 41.5
- 代码 –
# Percentile
import numpy as np
Sequence = [2, 30, 50, 46, 37, 91]
print ("50th Percentile : ", np.percentile(Sequence, 50))
print ("60th Percentile : ", np.percentile(Sequence, 60))
输出 :
50th Percentile : 41.5
60th Percentile : 46.0
- 四分位数间范围(IQR)。它适用于排名(排序的数据)。它有三个四分位数来划分数据–Q1(25分位数)、Q2(50分位数)和Q3(75分位数)。四分位数范围是Q3和Q1之间的差异。
示例 :
Sequence : [2, 30, 50, 46, 37, 91]
Q1 (25th percentile) : 31.75
Q2 (50th percentile) : 41.5
Q3 (75th percentile) : 49
IQR = Q3 - Q1 = 17.25
- 代码 – 1
# Inter-Quartile Range
import numpy as np
from scipy.stats import iqr
Sequence = [2, 30, 50, 46, 37, 91]
print ("IQR : ", iqr(Sequence))
输出 :
IQR : 17.25
- 代码 – 2
import numpy as np
# Inter-Quartile Range
iqr = np.subtract(*np.percentile(Sequence, [75, 25]))
print ("\nIQR : ", iqr)
输出 :
IQR : 17.25
 极客教程
极客教程