从元素上获取NumPy数组值的幂
NumPy是一个强大的N维数组对象,它在线性代数、傅里叶变换和随机数能力中的应用。它提供了一个比传统Python列表快得多的数组对象。numpy.power()用于计算元素的幂。它将第一个数组的元素从第二个数组中提升到幂,从元素上看。
语法: numpy.power(arr1, arr2, out = None, where = True, casting = ‘same_kind’, order = ‘K’, dtype = None)
参数 :
arr1 : [array_like]输入数组或对象,可作为基数。
arr2 : [array_like]输入数组或对象,作为指数工作。
out : [ndarray, optional]输出数组,其尺寸与输入数组相同。摆放的结果。
**kwargs :允许你向一个函数传递关键字的可变长度的参数。
当我们想在一个函数中处理命名的参数时,它就会被使用。
where : [array_like, optional]真值意味着要计算出普遍性。函数(ufunc)的位置,假值意味着离开仅在输出中的值。
因此,让我们来讨论一些与数组的获取能力有关的例子。
例子1:计算一个具有不同元素明智值的数组的功率。
# import required modules
import numpy as np
# creating the array
sample_array1 = np.arange(5)
sample_array2 = np.arange(0, 10, 2)
print("Original array ")
print("array1 ", sample_array1)
print("array2 ", sample_array2)
# calculating element-wise power
power_array = np.power(sample_array1, sample_array2)
print("power to the array1 and array 2 : ", power_array)
输出:
Original array
array1 [0 1 2 3 4]
array2 [0 2 4 6 8]
power to the array1 and array 2 : [ 1 1 16 729 65536]
例子2:对数组中的每个元素都计算相同的功率。
# import required module
import numpy as np
# creating the array
array = np.arange(8)
print("Original array")
print(array)
# computing the power of array
print("power of 3 for every element-wise:")
print(np.power(array, 3))
输出:
Original array
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
power of 3 for every element-wise:
[ 0 1 8 27 64 125 216 343]
例子3:计算小数点的功率。
# import required modules
import numpy as np
# creating the array
sample_array1 = np.arange(5)
# initialization the decimal number
sample_array2 = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 2.0]
print("Original array ")
print("array1 ", sample_array1)
print("array2 ", sample_array2)
# calculating element-wise power
power_array = np.power(sample_array1, sample_array2)
print("power to the array1 and array 2 : ", power_array)
输出:
Original array
array1 [0 1 2 3 4]
array2 [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 3.0, 2.0]
power to the array1 and array 2 : [ 0. 1. 8. 27. 16.]
注意:你不能计算负功率。
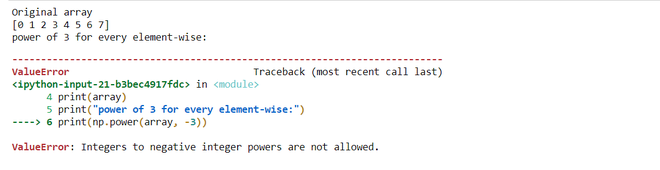
示例 4:
# importing module
import numpy as np
# creating the array
array = np.arange(8)
print("Original array")
print(array)
print("power of 3 for every element-wise:")
# computing the negative power element
print(np.power(array, -3))
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程