使用HTML CSS和JavaScript的滑动窗口可视化工具
窗口滑动技术在数组问题中被广泛使用,在子数组相关问题中也经常使用,比如子数组和等。在本文中,我们将了解滑动窗口可视化工具的工作原理,以及可视化工具的基本实现。
窗口滑动技术是一种在具有固定大小窗口的数组中计算和解决连续元素问题的高效方法。窗口滑动技术在子数组问题和需要关注特定窗口的问题中使用。理解这个算法非常重要,因为它涉及到一些主要的问题陈述。
预备知识: HTML,CSS,JavaScript
当我们需要处理一组元素时,我们可以使用窗口滑动技术,这组元素可以是数组、字符串或任何其他结构,我们需要从特定结构(如数组、字符串等)中获取一个具有固定大小窗口的输出。
例如使用数组:
/* K is the size of the window and we need
to find the maximum sum in that window */
Input : arr[] = {100, 200, 300, 400}, k = 2
Output : 700
Input : arr[] = {1, 4, 2, 10, 23, 3, 1, 0, 20}, k = 4
Output : 39
/* We get maximum sum by adding subarray
{4, 2, 10, 23} of size 4 */
Input : arr[] = {2, 3}, k = 3
Output : Invalid
/* There is no subarray of size 3 as
size of whole array is 2 */
例如,使用字符串:
/* Find the sum 299 in ASCII values
in contiguous form fixed sized */
window of 3 inside a string
string s : abadfg
sum : 299;
Output : Found
窗口滑动技术的基本思想是删除在新的窗口中不应该存在的元素,并添加新的元素到窗口中来创建新的窗口。
可视化器的逐步实施: 为了创建可视化器,我们将按照以下步骤进行操作:
第一步: 我们需要理解HTML部分,了解我们如何在HTML中创建容器,为了实现划分,我们创建了一个容器来保存所有的元素,如显示器容器,该容器包含要显示在屏幕上的元素,接下来我们有模式和模式文本,它们是用来显示数组和保存消息(如最大总和、当前总和)的div标签,我们还有一个开始按钮,当点击时开始算法可视化。
- index.html
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content=
"width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link href=
"https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Open+Sans:wght@300&display=swap"
rel="stylesheet" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<script src="script.js"></script>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>
<span class="1">S</span>liding
<span class="2">W</span>indow
<span class="3">T</span>echnique
<span>Visualizer</span>
</h1>
<div id="message">
We will find the maximum sum in array using
sliding window technique in certain sized
window when window size is 4
</div>
<div id="container">
<div id="displayer">
<div id="pattern"></div>
<div id="pattern_text"></div>
</div>
<div id="start">Begin</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
第二步: 我们将使用黑色背景,因此我们将每个元素的文本颜色设置为白色,以便它们可见,然后对于span,我们必须使其发光,因此我们给出了一个text-shadow,设置了我们的HTML的背景颜色和字体族。现在,对于body,我们确保一切保持居中,并设置flex-direction为center,对于容器也是如此。此外,我们给它一些位置,容器也是如此,我们给它一个字母间距,这样看起来整洁。我们创建了一个瓷砖,并确保每个显示的元素都是对称的。我们将其设置为悬停,并将颜色更改为青色,然后为每个元素设置其位置样式。当我们迭代数组元素时,我们确保数组元素迭代器的颜色显示为不同的颜色,即红色,当将元素添加到窗口时,我们用绿色突出显示,而突出显示要删除的元素时使用红色。窗口显示为白色。
- style.css
CSS
* {
color: white;
font-family: "Open sans", sans-serif;
}
html {
background-color: black;
}
body {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
height: 100vmin;
}
h1 span {
font-size: 6vmin;
font-weight: normal;
text-shadow: 0 0 20px cyan,
0 0 40px cyan,
0 0 80px cyan;
}
#container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
height: 80%;
width: 80%;
}
#displayer {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
width: 100%;
height: 90%;
}
#pattern,
#message {
width: 100%;
height: 7vmin;
margin: 3vmin;
font-size: 5vmin;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
#message {
color: cyan;
font-size: 2vmin;
}
#pattern_text {
width: 100%;
height: 5vmin;
margin: 3vmin;
font-size: 5vmin;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
color: g;
}
#pattern_text {
width: 100%;
height: 5vmin;
margin: 3vmin;
font-size: 5vmin;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
color: g;
}
.tile {
width: 6vmin;
height: 6vmin;
margin: 10px;
text-align: center;
height: fit-content;
border: 2px pink;
}
#start {
align-self: center;
background-color: black;
font-size: 3vmin;
box-sizing: border-box;
padding: 1vmin;
color: white;
cursor: pointer;
border: none;
margin-top: 2vmin;
transition: 0.5s ease-in-out;
font-weight: bold;
letter-spacing: 4px;
}
#start:hover {
transform: scale(1.5);
text-shadow: 0 0 10px cyan,
0 0 20px cyan,
0 0 40px cyan;
}
h1 {
margin-top: 0;
text-align: center;
padding: 1vmin;
margin-bottom: 1vmin;
width: 100%;
font-size: 5vmin;
font-weight: normal;
letter-spacing: 2px;
border-bottom: 1px solid white;
}
第三步: 在JavaScript中,当我们首次加载窗口时,我们看到“开始”按钮以启动可视化。之后,我们有一个名为max_sum和current_sum的数组,窗口大小显示为白色,迭代器显示为红色。 max_sum和current_sum在数组下方被计算并显示出来。我们使用async await来通过创建延迟平滑地显示实际可视化。首先,我们比较第一个窗口计算总和,然后将max_sum保持为current_sum。现在,对于第二个窗口,我们找到第二个窗口的current_sum并将其与max_sum进行比较,如果第二个窗口的current_sum大于max_sum,则将max_sum赋值为第二个窗口的current_sum,依此类推,直到完成所有迭代。在这种情况下,我们得到了固定大小为4的窗口的max_sum。
- script.js:
Javascript
function id(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
var count = 0;
var pattern, text, Psize, Tsize;
var idcountrater = 0;
var conti = 0;
const slidingWindowTech = async (pattern, Psize, sum, k) => {
console.log("hola")
var max_sum = 0;
let maxi = document.createElement('div');
maxi.id = "message";
maxi.classList.add("message");
maxi.innerText = `MaximumSum is {max_sum}`
console.log(maxi)
id("pattern_text").appendChild(maxi);
let current_sum = 0;
let current = document.createElement('div');
current.id = "message";
current.classList.add("message");
current.innerText = `CurrentSum is{current_sum}`
id("pattern_text").appendChild(current);
for (let i = 0; i < Psize - k + 1; i++) {
await new Promise((resolve) =>
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 1000)
)
console.log(i + " " + (i + k - 1));
id(i).style.borderLeft = "2px solid white"
id(i).style.borderTop = "2px solid white"
id(i).style.borderBottom = "2px solid white"
id(i + 1).style.borderBottom = "2px solid white"
id(i + 1).style.borderTop = "2px solid white"
id(i + 2).style.borderTop = "2px solid white"
id(i + 2).style.borderBottom = "2px solid white"
id((i + k - 1)).style.borderRight = "2px solid white";
id(i + k - 1).style.borderTop = "2px solid white"
id(i + k - 1).style.borderBottom = "2px solid white"
if (i != 0) {
// current_sum=current_sum-pattern[i-1]
id(i - 1).style.color = "Red"
await new Promise((resolve) =>
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 1000)
)
current_sum = current_sum - pattern[i - 1]
current.innerText =
`CurrentSum after subtracting {i - 1}th ` +
`element from{i} window is {current_sum}`
id(i - 1).style.color = "white"
await new Promise((resolve) =>
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 1000)
)
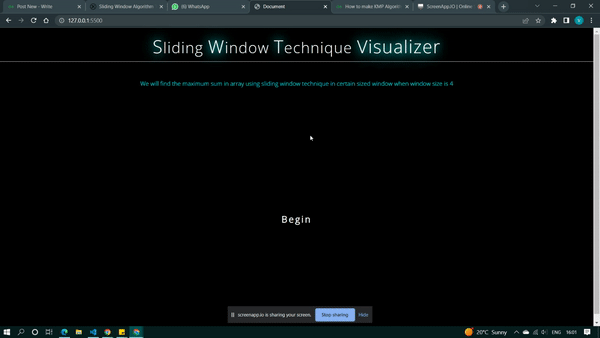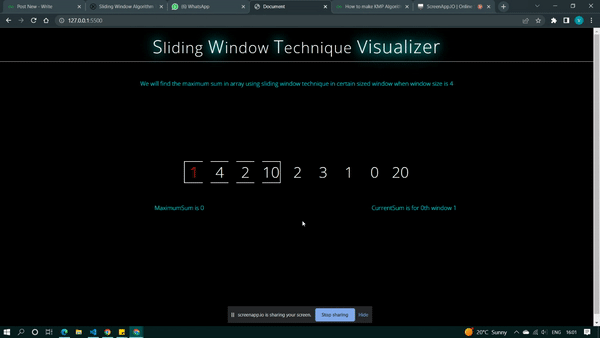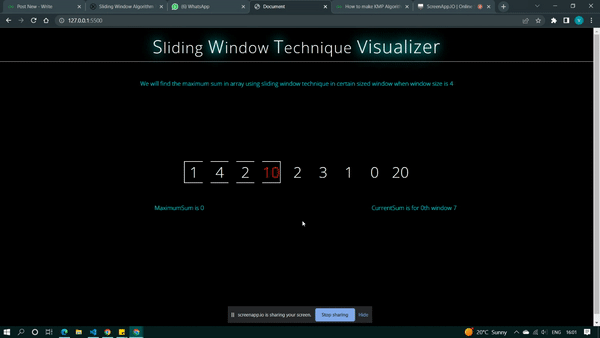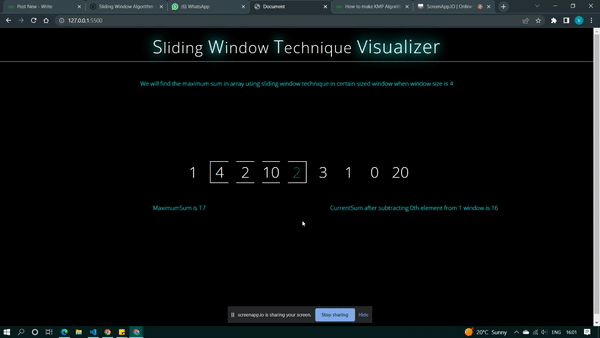
id(i + k - 1).style.color = "green"
await new Promise((resolve) =>
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 1000)
)
current_sum = current_sum + pattern[i + k - 1]
current.innerText =
`CurrentSum after adding{i + k - 1}th in {i} window is{current_sum}`
id(i + k - 1).style.color = "white"
await new Promise((resolve) =>
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 1000)
)
}
else {
for (let j = 0; j < k; j++) {
console.log("hola 1 " + current_sum)
id((i + j)).style.color = "Red"
await new Promise((resolve) =>
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 1000)
)
current_sum = current_sum + pattern[i + j];
current.innerText =
`CurrentSum is for {i}th window{current_sum}`
await new Promise((resolve) =>
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 1000)
)
id((i + j)).style.color = "white"
}
}
id(i).style.borderLeft = "none"
id(i).style.borderTop = "none"
id(i).style.borderBottom = "none"
id(i + 1).style.borderBottom = "none"
id(i + 1).style.borderTop = "none"
id(i + 2).style.borderTop = "none"
id(i + 2).style.borderBottom = "none"
id((i + k - 1)).style.borderRight = "none";
id(i + k - 1).style.borderTop = "none"
id(i + k - 1).style.borderBottom = "none"
console.log(current_sum)
// Update result if required.
// max_sum = max(current_sum, max_sum);
if (current_sum > max_sum) max_sum = current_sum;
maxi.innerText = `MaximumSum is ${max_sum}`
}
current.style.display = "none"
}
let idcount = 0;
window.onload = async () => {
id("displayer").style.display = "none";
id("start").addEventListener('click', () => {
id("start").style.display = "none"
id("displayer").style.display = "flex";
pattern = [1, 4, 2, 10, 2, 3, 1, 0, 20]
Psize = 9
sum = 24
let idcount1 = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < Psize; i++) {
let tile = document.createElement('span');
tile.id = idcount;
tile.classList.add("tile");
tile.innerText = pattern[i];
id("pattern").appendChild(tile);
idcount++;
}
slidingWindowTech(pattern, Psize, sum, 4)
})
}
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程