在Ubuntu服务器上配置Django WebSocket应用程序
本教程将指导你详细了解如何在_Ubuntu 20.10服务器上配置你的Django websocket应用程序的每个步骤。本文假设你对Django很熟悉,并且有一台ubuntu远程服务器正在运行。要了解更多关于Django的信息,请查看 – Django教程
首先,让我们看看我们将用什么来把它投入生产。
1.Nginx – 网络和代理服务器
2.Daphne – 我们的ASGI(异步服务器网关接口)服务器,它将为我们的Django应用程序提供服务。
3.Redis后端服务器 – 它将处理我们的网络套接字连接 ( ws:// )
Nginx 配置
安装Nginx和监督员
$ sudo apt install nginx supervisor
在你的/etc/nginx/sites-available/文件夹中创建你的服务器并添加以下内容。
upstream redis_backend_server{
server localhost:6379;
}
upstream app_server {
server localhost:9090;
}
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
keepalive_timeout 700;
ssl_certificate <path to your cert>;
ssl_certificate_key <path to your key>;
server_name foo.com www.foo.com;
access_log <path to your access logs>;
error_log <path to your error logs>;
add_header X-Frame-Options SAMEORIGIN;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "frame-ancestors self https://foo.com";
location /static/ {
root /var/www/staticfiles/;
}
if (scheme = http) {
return 301 https://server_namerequest_uri;
}
location / {
include proxy_params;
proxy_pass http://app_server;
}
location /ws {
proxy_pass http://redis_backend_server;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgradehttp_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_ssl_certificate <path to your cert>;
proxy_ssl_certificate_key <path to your key>;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IPremote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Hostserver_name;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}
注意 – 用你的IP或你的域名代替foo。
现在保存配置并重启Nginx。
$ sudo service nginx reload
检查配置是否正确,如下所示。

一旦完成了这些,让我们转向我们的实际应用服务器。
Daphne 配置
Install Daphne
$ pip3 install daphne
测试事情是否在运作。
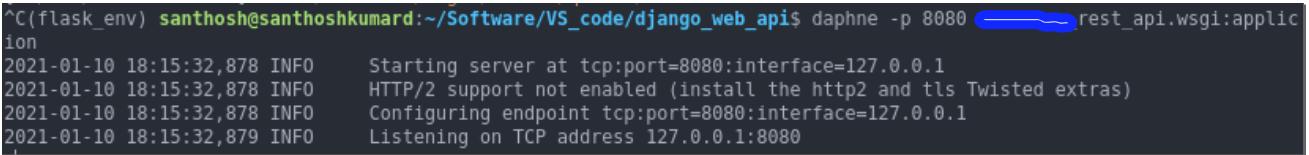
$ daphne -p 8001 project.asgi:application
你应该在你的终端看到类似的东西。
在/etc/supervisor/conf.d/文件夹中创建django_server并添加以下内容。
[fcgi-program:django_server]
# TCP socket used by Nginx backend upstream
socket=tcp://localhost:9090
# Directory where your site's project files are located
directory= <path>
# Each process needs to have a separate socket file, so we use process_num
# Make sure to update "mysite.asgi" to match your project name
command=<path to daphne> -u /run/daphne/daphne%(process_num)d.sock --endpoint fd:fileno=0 --access-log - --proxy-headers project.asgi:application
# Number of processes to startup, roughly the number of CPUs you have
numprocs=1
# Give each process a unique name so they can be told apart
process_name=asgi%(process_num)d
# Automatically start and recover processes
autostart=true
autorestart=true
# Choose where you want your log to go
stdout_logfile=<path to your asgi logs>
redirect_stderr=true
注意 – 用你的项目名称替换项目
一旦完成,我们就必须为我们的插座创建一个目录来运行。
$ sudo mkdir /run/daphne/
重新启动并更新监督器的配置。
$ sudo supervisorctl reread
$ sudo supervisorctl update
我知道这有很多东西需要接受,我们只需再走一步就能让我们的服务器启动和运行。所以,请跟着我。
Redis后端服务器配置
这台服务器将处理Daphne服务器转发的所有网络套接字连接。
安装redis服务器
$ sudo apt install redis-server
编辑Redis的配置,使其以服务的形式运行在我们的systemd上
$ sudo nano /etc/redis/redis.conf
将配置文件中的 “supervised no “改为 “supervised systemd”。
$ sudo systemctl restart redis.service
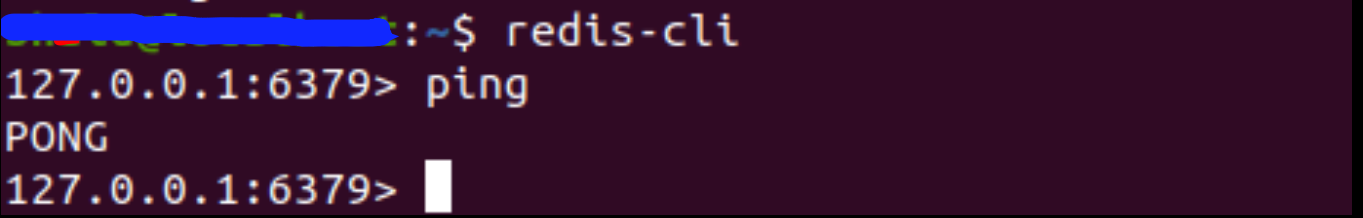
检查服务器是否处于活跃和运行状态
sudo systemctl status redis
你应该得到以下回应
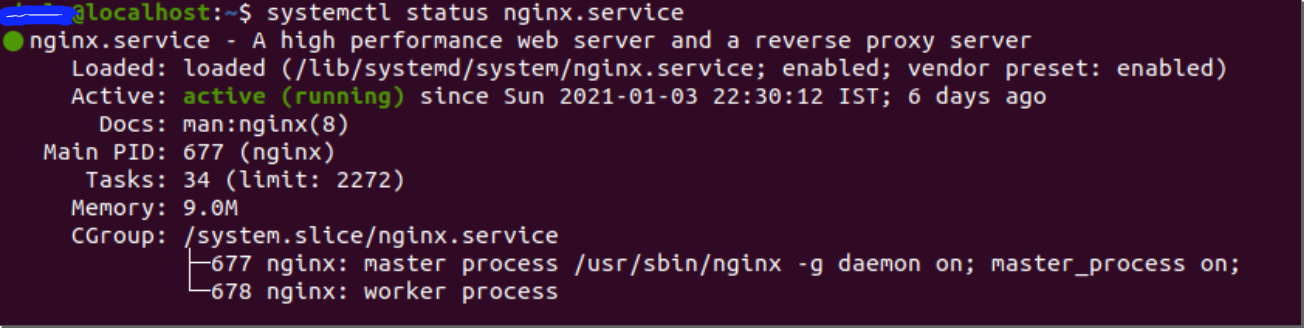
最后,在所有的地方和运行中,你应该看到你的应用程序在你的服务器上启动和运行。
 极客教程
极客教程