R语言 改变图例的位置和外观
图例对于为图表添加更多信息和增强用户的可读性非常有用。它涉及到创建标题、索引、绘图框的位置,以便对绘制的图形有更好的理解。内置的R函数legend()可以用来为绘图添加一个图例。散点图、线形图和块状图可用于在R中轻松实现数据的可视化。在这篇文章中,改变R中图形图例的位置和外观
语法: legend(x, y, legend)
参数 :
- x和y:用于定位图例的x和y坐标。它也可以接受字符串作为参数,如右上角、左下角等。
- legend:向量,提供关于图表中每个类别的信息。
例1: 改变图例的位置
整数值可以被分配给x和y坐标,图例框直接与这些坐标对齐。在这种情况下,有必要提供两个坐标。
代码
# declaring the data to plot
# x coordinate is a vector of
# integers from 1 to 10
x <- 1 : 10
y = x^1/2
z = x^2
# plotting x and y coordinate line
plot(x, y, col = "blue")
# adding another line on
# the coordinates involving y and z
lines(z, y ,col = "red")
# Adding a legend to the graph
#defining the lines
legend(2, 4, legend=c("Equation 1", "Equation 2"),
fill = c("blue","red"))
输出
例2: 放置图例,对齐方式为正方形。
x坐标甚至可以包含一个带有对齐的位置的字符串。这个字符串是一个关键词的组合,其合理的值被定义为bottom right, bottom, bottomleft, left, topleft, top, topright, right, center。这种情况下就不需要定义y坐标的值了。
代码
# declaring the data to plot
# x coordinate is a vector of
# integers from 1 to 10
x <- 1 : 10
y = x^1/2
z = x^2
# plotting x and y coordinate
# line
plot(x, y, col = "blue")
# adding another line on the
# coordinates involving y and z
lines(z, y , col = "red")
# Adding a legend to the graph
# defining the lines
legend(x = "topleft", legend=c(
"Equation 1", "Equation 2"),
fill = c("blue","red"))
输出
例子3: 留出空白和对齐的理由
如果我们以关键字的形式指定位置参数,图例框就会出现与相应的轴相连。为了解决这个问题,可以在这个方法中定义inset参数。这个参数指定了与边缘的距离,是绘图区域的一部分。
代码
# declaring the data to plot
# x coordinate is a vector of
# integers from 1 to 10
x <- 1:10
y = x^1/2
z = x^2
# plotting x and y coordinate line
plot(x, y, col = "blue")
# adding another line on the
# coordinates involving y and z
lines(z, y ,col = "red")
# Adding a legend to the graph
# defining the lines
legend(x="topleft", legend=c(
"Equation 1", "Equation 2"),
fill = c("blue","red"), inset = 0.05)
输出
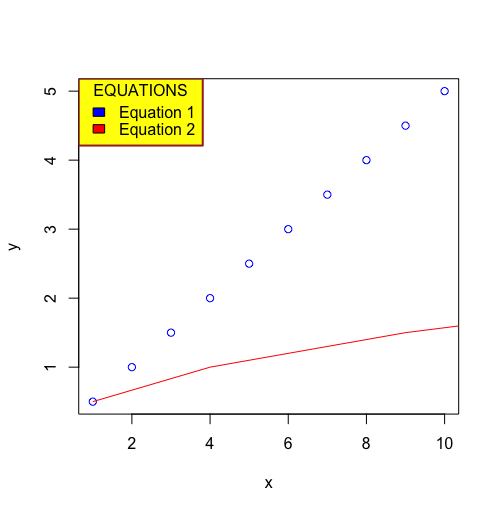
例4: 图例的颜色外观
图中的图例框可以根据要求进行定制,以传达更多信息,提供更好的视觉效果。以下参数可以用来定制。
- title: 可以声明的图例框的标题,以了解指示的索引是什么
- bty(默认值:o): 包围图例的盒子的类型。可以使用不同类型的字母,其中盒子的形状等同于字母的形状。例如,”n “可以用来表示没有方框。
- bg: 可以为图例框指定一个背景颜色。
- box.lwd : 图例框的线宽指示器
- box.lty : 图例框的线型指示器
- box.col : 图例框的线条颜色指示器
代码
# declaring the data to plot
# x coordinate is a vector of
# integers from 1 to 10
x <- 1:10
y = x^1/2
z = x^2
# plotting x and y coordinate line
plot(x, y, col = "blue")
# adding another line on the
# coordinates involving y and z
lines(z, y , col = "red")
# Adding a legend to the graph
# defining the lines
legend(x = "topleft", box.col = "brown",
bg ="yellow", box.lwd = 2 , title="EQUATIONS",
legend=c("Equation 1", "Equation 2"),
fill = c("blue","red"))
输出
 极客教程
极客教程