PyTorch – 线性回归
在本章中,我们将重点介绍使用TensorFlow实现线性回归的基本例子。Logistic回归或线性回归是一种有监督的机器学习方法,用于对顺序离散的类别进行分类。我们在本章的目标是建立一个模型,用户可以通过这个模型来预测预测变量和一个或多个自变量之间的关系。
这两个变量之间的关系被认为是线性的,也就是说,如果y是因变量,x被认为是自变量,那么两个变量的线性回归关系将看起来像下面提到的方程
Y = Ax+b
接下来,我们将设计一个线性回归的算法,使我们能够理解下面给出的两个重要概念—
- 成本函数
- 梯度下降算法
线性回归的示意图如下所述
解释结果
Y=ax+b
- a 的值是斜率。
-
b 的值是 y-截距。
-
r 是 相关系数。
-
r2是 相关系数。
线性回归方程的图解如下
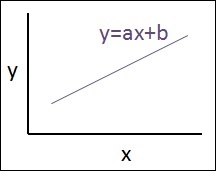
以下是使用PyTorch实现线性回归的步骤。
第1步
使用以下代码导入必要的软件包,以便在PyTorch中创建线性回归
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
%matplotlib inline
sns.set_style(style = 'whitegrid')
plt.rcParams["patch.force_edgecolor"] = True
第2步
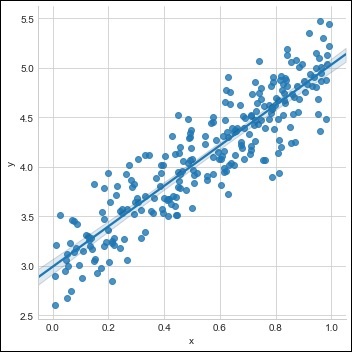
用现有的数据集创建一个单一的训练集,如下图所示
m = 2 # slope
c = 3 # interceptm = 2 # slope
c = 3 # intercept
x = np.random.rand(256)
noise = np.random.randn(256) / 4
y = x * m + c + noise
df = pd.DataFrame()
df['x'] = x
df['y'] = y
sns.lmplot(x ='x', y ='y', data = df)
第3步
用PyTorch库实现线性回归,如下所述-
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
x_train = x.reshape(-1, 1).astype('float32')
y_train = y.reshape(-1, 1).astype('float32')
class LinearRegressionModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim):
super(LinearRegressionModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.linear(x)
return out
input_dim = x_train.shape[1]
output_dim = y_train.shape[1]
input_dim, output_dim(1, 1)
model = LinearRegressionModel(input_dim, output_dim)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
[w, b] = model.parameters()
def get_param_values():
return w.data[0][0], b.data[0]
def plot_current_fit(title = ""):
plt.figure(figsize = (12,4))
plt.title(title)
plt.scatter(x, y, s = 8)
w1 = w.data[0][0]
b1 = b.data[0]
x1 = np.array([0., 1.])
y1 = x1 * w1 + b1
plt.plot(x1, y1, 'r', label = 'Current Fit ({:.3f}, {:.3f})'.format(w1, b1))
plt.xlabel('x (input)')
plt.ylabel('y (target)')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
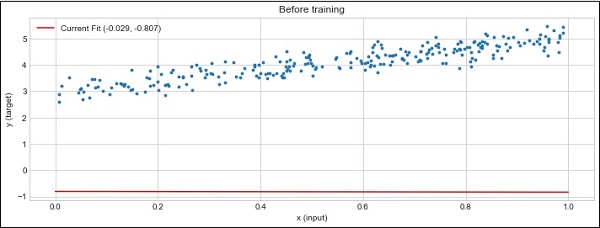
plot_current_fit('Before training')
生成的曲线图如下 −
 极客教程
极客教程