Python random.triangular()
triangular()是随机模块的一个内置方法。它用于返回一个范围内的随机浮点数,并偏向一个极端。
语法:Random.triangular(low, high, mode)。
参数:
low:随机数的下限
high:随机数的上限
mode:附加偏置;low < mode < high ,如果参数是(10,100,20),那么由于偏差,产生的大多数随机数会更接近于10,而不是100。
返回:一个随机的浮动数
例1:
# import the random module
import random
# determining the values of the parameters
low = 10
high = 100
mode = 20
# using the triangular() method
print(random.triangular(low, high, mode))
输出:
22.614510550239572
例2:如果我们多次生成这个数字,我们就可以大概确定其偏差。
# import the random module
import random
# determining the values of the parameters
low = 10
high = 100
mode = 20
# running the triangular method with the
# same parameters multiple times
for i in range(10):
print(random.triangular(low, high, mode))
输出:
58.645768016894735
46.690692250503226
33.57590419190895
52.331804090351305
33.09451214875767
12.03845752596168
32.816080679206294
20.4739124559502
82.49208123077557
63.511062284733015
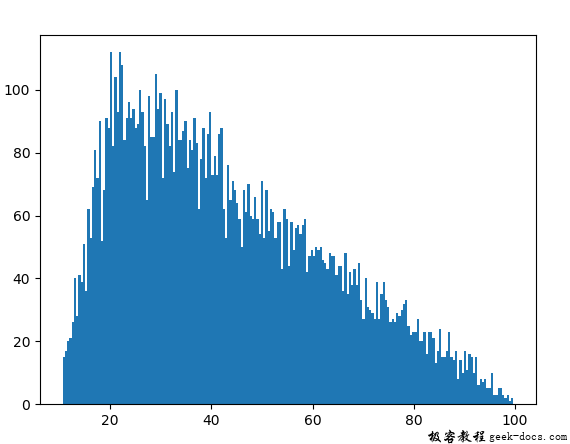
例3:我们可以通过绘制图表来直观地看到三角形模式。
# import the required libraries
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# store the random numbers in a list
nums = []
low = 10
high = 100
mode = 20
for i in range(10000):
temp = random.triangular(low, high, mode)
nums.append(temp)
# plotting a graph
plt.hist(nums, bins = 200)
plt.show()
输出:
 极客教程
极客教程