Pandas的系统取样
抽样是一种方法,人们可以从给定的数据中抽取子集(样本),并对样本进行调查,而不对数据中的每一件事进行调查。例如,假设在一所大学里,有人想检查在该学院学习的学生的平均身高。一种方法是收集所有学生的数据并进行计算,但这项工作非常耗时。因此,要使用抽样调查。因此,解决方案是,在课间休息时,从食堂随机选择学生,测量他们的身高,然后从这个学生的子集中计算出平均身高。
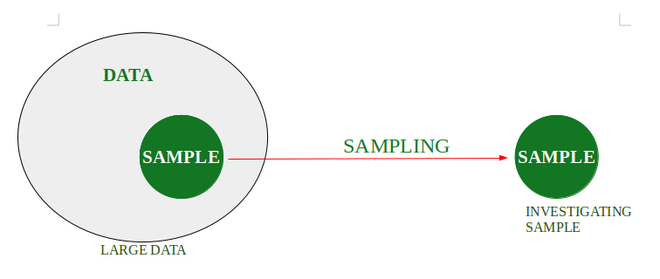
取样类型:
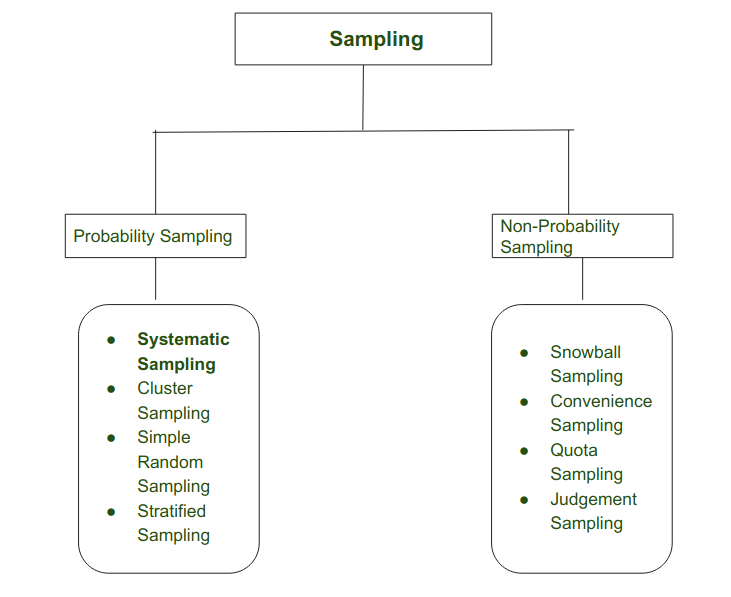
Sampling
系统取样
系统抽样被定义为概率抽样的类型,研究者可以从大量的数据中研究一个目标数据。目标数据是通过选择随机的起点,并在一定的时间间隔后选择下一个元素作为样本。在这种情况下,一个小的子集(样本)被从大数据中提取出来。
假设数据的大小是D,N是我们要选择的样本大小。因此,根据系统抽样法。
Interval = (D/N)
假设(D/N)=J
因此,当我们从数据中选择第一个随机元素E时,样本的下一个元素将是(E+J)。
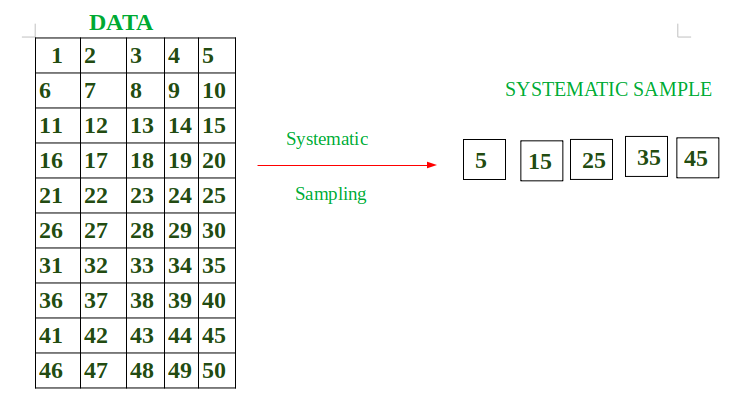
例如:数据总大小=50(1到50)。
我们希望样本中的元素=5
间隔=50/5=10。
这意味着在一个样本中,我们要系统地找出10个元素的缺口。
假设我先随机选择元素,样本元素=5
所以接下来将是5+10=15
15+10= 25
25+ 10 =35
35+10 = 45
So,
样本 = { 5,15,25,35,45 }
Diagrammatically,
步骤:
- 采取数据。
- 从大数据中提取系统性的样本。
- 打印样本数据的平均值。
代码:
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Define total number of students
number_of_students = 15
# Create data dictionary
data = {'Id': np.arange(1, number_of_students+1).tolist(),
'height': [159, 171, 158, 162, 162, 177, 160, 175,
168, 171, 178, 178, 173, 177, 164]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
display(df)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(0, len(df), step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
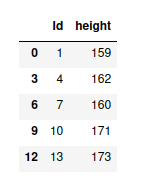
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, 3)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
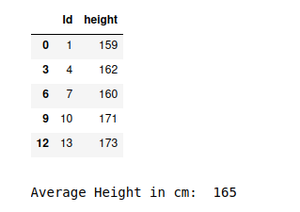
输出:
例子:打印样本数据的平均值
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Define total number of students
number_of_students = 15
# Create data dictionary
data = {'Id': np.arange(1, number_of_students+1).tolist(),
'height': [159, 171, 158, 162, 162, 177, 160, 175,
168, 171, 178, 178, 173, 177, 164]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(0, len(df), step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, 3)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
# Empty Print Statement for new line
print()
# Save the sample data in a separate variable
systematic_data = round(systematic_sample['height'].mean())
print("Average Height in cm: ", systematic_data)
输出:
系统性抽样的类型
系统性抽样有三种类型,如下图所示。
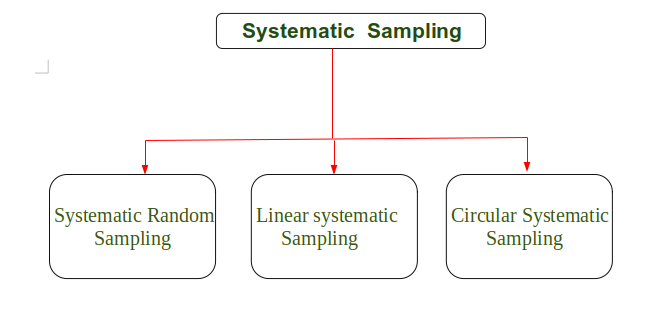
系统性抽样的类型
系统性随机抽样:
在系统随机抽样中,选择随机起点,然后从该随机起点开始进行系统抽样。
步骤:
- Get data
- 选择一个随机的起始点
- 应用系统的方法处理数据
- 按计划进行操作
示例:
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import random
# Define total number of house
number_of_house = 30
# Create data dictionary
data = {'house_number': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30],
'number_of_children': [2, 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 4, 1, 3, 5, 4, 3, 5,
3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 2, 2, 2,
2, 3, 2, 1]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Defining Size of Systematic Sample
size_of_systematic_sample = 6
# Defining Interval(gap) in order to get required data.
interval = (number_of_house // size_of_systematic_sample)
# Choosing Random Number
random_number = random.randint(1, 30)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(random_number, len(df), step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, interval)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
# Empty Print Statement for new line
print()
# Save the sample data in a separate variable
systematic_data = round(systematic_sample['number_of_children'].mean())
# Printing Average Number of Children
print("Average Number Of Childrens in Locality: ", systematic_data)
输出:

线性系统抽样 :
线性系统抽样是系统抽样的一种类型,样本的选择采用线性方法。线性方法的意思是,在特定的时间间隔后,从大数据中选择样本,然后对所选样本进行操作。
这些元素在starting_random_number到last_element-1的范围内选择。
步骤:
- Get data
- 从数据集中选择特定时间间隔后的数据
- 按计划进行操作
示例:
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import random
# Define total number of boxes
number_of_boxes = 30
# Create data dictionary
data = {'Box_Number': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26,
27, 28, 29, 30],
'Defective_Bulbs': [2, 2, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 5, 4, 3, 5, 3,
0, 1, 2, 0, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 2, 0, 3, 2, 0,
5, 4]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Size of Systematic Sample
size_systematic_sample = 5
# Interval (Gap) taken
interval = (number_of_boxes // size_systematic_sample)
# Choosing Random Starting Point
random_number = random.randint(1, 30)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(random_number, len(df)-1, step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, interval)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
# Empty Print Statement for new line
print()
# Save the sample data in a separate variable
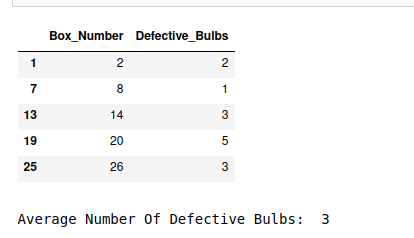
systematic_data = round(systematic_sample['Defective_Bulbs'].mean())
# Printing Average Number of Defective Bulbs
print("Average Number Of Defective Bulbs: ", systematic_data)
输出:
圆形的系统抽样
在循环系统抽样中,一个样本在结束后再次从同一点开始。基本上,在系统地选择样本时,当达到结束元素时,再次选择样本将从开始开始,直到样本的所有元素被选中。这意味着对所有使用循环系统取样的数据都进行了操作。
步骤:
- Get data
- 系统地选择样本
- 一旦达到终点,重新启动
- 按计划进行操作
代码:
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import random
# Define total number of house
number_of_house = 30
# Create data dictionary
data = {'house_number': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30],
'number_of_Adults': [2, 2, 5, 3, 2, 8, 4, 7, 8, 5, 4, 9, 5,
4, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 4, 5, 4, 2, 6,
2, 3, 2, 2]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Defining Size of Systematic Sample
size_of_systematic_sample = 6
# Defining Interval(gap) in order to get required data.
interval = (number_of_house // size_of_systematic_sample)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(0, len(df), step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, interval)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
# Empty Print Statement for new line
print()
# Save the sample data in a separate variable
systematic_data = round(systematic_sample['number_of_Adults'].mean())
# Printing Average Number of Children
print("Average Number Of Adults in Locality: ", systematic_data)
输出:

 极客教程
极客教程