Pandas 序列(Series)是pandas中的一维数据结构,类似于python中的列表和Numpy中的Ndarray对象,在 Series 中包含的数据类型可以是整数,浮点数,字符串,python对象等。
pandas.Series
Pandas Series构造函数如下:
pandas.Series( data, index, dtype, copy)
构造函数的参数说明如下
| 编号 | 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | data |
支持多种数据类型,如:ndarray,list,constants |
| 2 | index |
索引值必须是唯一的,与data的长度相同,默认为np.arange(n) |
| 3 | dtype |
数据类型 |
| 4 | copy |
是否复制数据,默认为false |
创建一个空的Series
#import the pandas library and aliasing as pd
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series()
print (s)
执行结果如下:
Series([], dtype: float64)
从ndarray创建一个Series
如果数据是ndarray,则传递的索引必须具有相同的长度。 如果没有传递索引值,那么默认的索引范围将是range(n),其中n是数组长度,即[0,1,2,3…. range(len(array))-1] - 1]。
#import the pandas library and aliasing as pd
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = np.array(['a','b','c','d'])
s = pd.Series(data)
print (s)
输出结果如下:
0 a
1 b
2 c
3 d
dtype: object
这里没有传递索引,采用默认索引值是 0 到 len(data)-1,即 0 到 3
示例:传递索引值
#import the pandas library and aliasing as pd
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = np.array(['a','b','c','d'])
s = pd.Series(data,index=[100,101,102,103])
print (s)
输出结果如下:
100 a
101 b
102 c
103 d
dtype: object
从字典创建一个Series
字典(dict)可以作为输入传递,如果没有指定索引,则按排序从字典中取得键值作为索引。 如果传递了索引,索引中与标签对应的数据中的值将被拉出。
示例:字典键值作为索引
# import the pandas library and aliasing as pd
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = {'a' : 0., 'b' : 1., 'c' : 2.}
s = pd.Series(data)
print (s)
输出结果如下:
a 0.0
b 1.0
c 2.0
dtype: float64
示例:传递索引
# import the pandas library and aliasing as pd
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = {'a' : 0., 'b' : 1., 'c' : 2.}
s = pd.Series(data,index=['b','c','d','a'])
print (s)
输出结果如下:
b 1.0
c 2.0
d NaN
a 0.0
dtype: float64
索引顺序保持不变,缺少的元素使用NaN(不是数字)填充。
从标量创建一个Series
如果数据是标量类型,则必须提供索引。重复该值以匹配索引的长度。
# import the pandas library and aliasing as pd
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
s = pd.Series(5, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
print (s)
输出结果如下:
0 5
1 5
2 5
3 5
dtype: int64
通过位置访问Series数据
Series中的数据可以使用类似于访问ndarray中的数据来访问。
示例1:检索第一个元素,当前索引从0开始计数
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
#retrieve the first element
print (s[0])
输出结果如下:
1
示例2:检索Series中的前三个元素
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
#retrieve the first three element
print (s[:3])
输出结果如下:
a 1
b 2
c 3
dtype: int64
s[a :] : 将提取该索引之后的所有数据
s[a : b] : 将提取 a 和 b 之间的所有数据
示例:检索最后三个元素
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
#retrieve the last three element
print (s[-3:])
输出结果如下:
c 3
d 4
e 5
dtype: int64
通过索引访问Series数据
Series 就像一个固定大小的字典,可以通过索引获取数据。
示例1:使用索引获取单个元素。
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
#retrieve a single element
print (s['a'])
输出结果如下:
1
示例2:使用索引获取多个元素。
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
#retrieve multiple elements
print (s[['a','c','d']])
输出结果如下:
a 1
c 3
d 4
dtype: int64
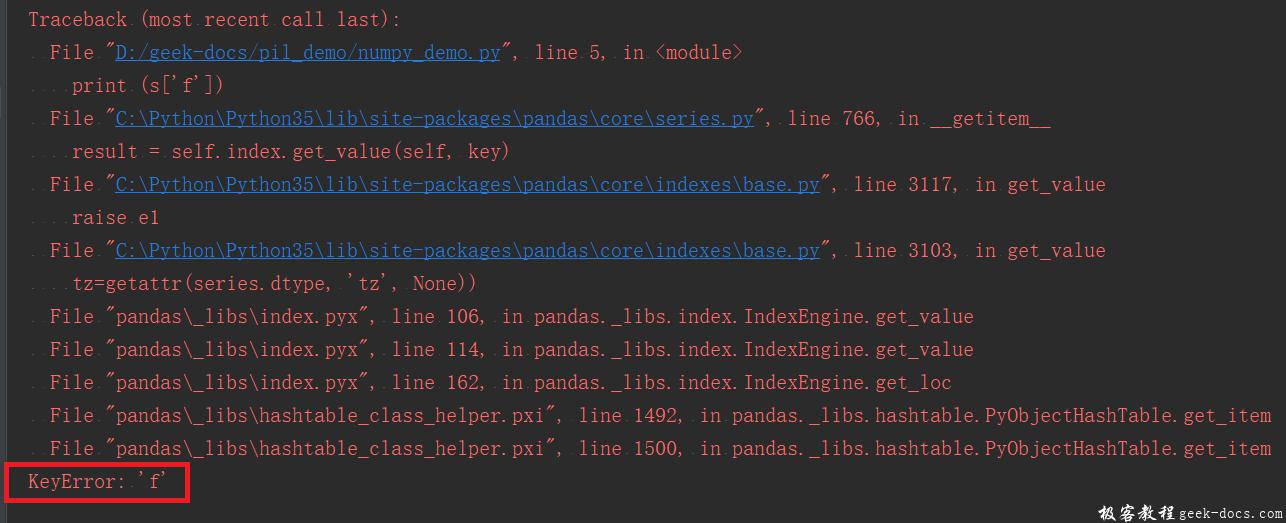
示例3:如果Series中并没有此索引,则会抛出异常。
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5],index = ['a','b','c','d','e'])
#retrieve multiple elements
print (s['f'])
执行上面示例代码,得到以下结果 –
 极客教程
极客教程