Python Pandas DataFrame.transpose
Pandas DataFrame是一个二维的大小可变的、可能是异质的表格数据结构,具有标记的axis(行和列)。算术操作在行和列的标签上对齐。它可以被认为是一个类似于Dict的系列对象的容器。这是Pandas的主要数据结构。
Pandas DataFrame.transpose()函数对数据框架的索引和列进行转置。它通过将行写成列,反之亦然来反映DataFrame在其主对角线上的情况。
语法: DataFrame.transpose(*args, **kwargs)
参数:
copy : 如果为真,基础数据被复制。否则(默认),如果可能的话,不进行复制。
*args, **kwargs :附加的关键字没有任何作用,但为了与numpy兼容,可能会被接受。
返回:换位的数据框架
示例#1:使用DataFrame.transpose()函数来查找给定数据帧的转置。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Weight':[45, 88, 56, 15, 71],
'Name':['Sam', 'Andrea', 'Alex', 'Robin', 'Kia'],
'Age':[14, 25, 55, 8, 21]})
# Create the index
index_ = pd.date_range('2010-10-09 08:45', periods = 5, freq ='H')
# Set the index
df.index = index_
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
输出 :
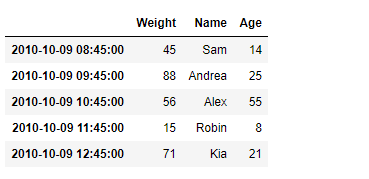
现在我们将使用DataFrame.transpose()函数来寻找给定数据帧的转置。
# 返回值 the transpose
result = df.transpose()
# Print the result
print(result)
输出 :
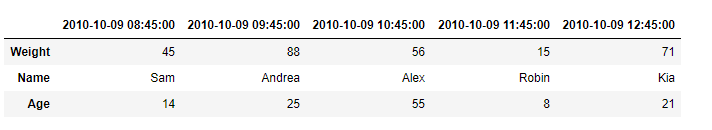
正如我们在输出中看到的,DataFrame.transpose()函数已经成功地返回了给定数据框架的转置。
示例#2:使用DataFrame.transpose()函数来查找给定数据帧的转置。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, None, 1],
"B":[7, 2, 54, 3, None],
"C":[20, 16, 11, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, None, 2, 6]})
# Create the index
index_ = ['Row_1', 'Row_2', 'Row_3', 'Row_4', 'Row_5']
# Set the index
df.index = index_
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
输出 :
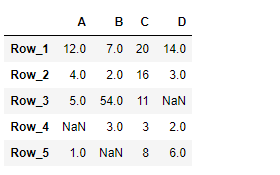
现在我们将使用DataFrame.transpose()函数来寻找给定数据帧的转置。
# 返回值 the transpose
result = df.transpose()
# Print the result
print(result)
输出 :
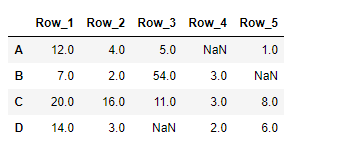
正如我们在输出中看到的,DataFrame.transpose()函数已经成功地返回了给定数据框架的转置。
 极客教程
极客教程