Python Pandas DataFrame.transform
Pandas DataFrame是一个二维的大小可变的、可能是异质的表格数据结构,具有标记的axis(行和列)。算术操作在行和列的标签上对齐。它可以被认为是一个类似于Dict的系列对象的容器。这是Pandas的主要数据结构。
Pandas DataFrame.transform()函数在自己身上调用func,产生一个带有转换值的DataFrame,其axis长与自己相同。
语法: DataFrame.transform(func, axis=0, *args, **kwargs)
参数:
func : 用来转换数据的函数。
axis: {0或’索引’,1或’列’},默认0
*args :传递给func的位置参数。
**kwargs :关键字参数,传递给func。
返回 : DataFrame
示例#1 :使用DataFrame.transform()函数为数据框架中的每个元素添加10。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, None, 1],
"B":[7, 2, 54, 3, None],
"C":[20, 16, 11, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, None, 2, 6]})
# Create the index
index_ = ['Row_1', 'Row_2', 'Row_3', 'Row_4', 'Row_5']
# Set the index
df.index = index_
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
输出 :
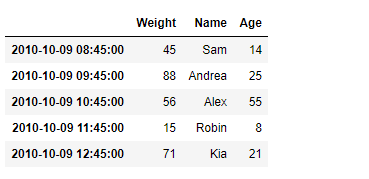
现在我们将使用DataFrame.transform()函数为数据框架的每个元素添加10。
# add 10 to each element of the dataframe
result = df.transform(func = lambda x : x + 10)
# Print the result
print(result)
输出 :
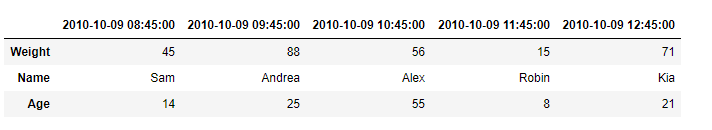
正如我们在输出中看到的,DataFrame.transform()函数已经成功地为给定Dataframe的每个元素添加了10。
示例#2 :使用DataFrame.transform()函数来寻找平方根和欧拉数升至数据帧的每个元素的结果。
# importing pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Creating the DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, None, 1],
"B":[7, 2, 54, 3, None],
"C":[20, 16, 11, 3, 8],
"D":[14, 3, None, 2, 6]})
# Create the index
index_ = ['Row_1', 'Row_2', 'Row_3', 'Row_4', 'Row_5']
# Set the index
df.index = index_
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
输出 :
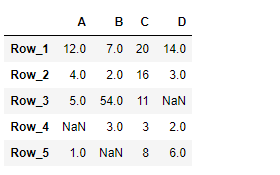
现在我们将使用DataFrame.transform()函数来寻找平方根和欧拉数对数据帧中每个元素的升值结果。
# pass a list of functions
result = df.transform(func = ['sqrt', 'exp'])
# Print the result
print(result)
输出 :
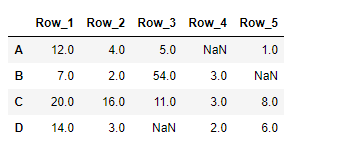
正如我们在输出中看到的,DataFrame.transform()函数已经成功地对给定的数据框架进行了所需的操作。
 极客教程
极客教程